Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research proposes a shift in how humans and AI work together, suggesting AI-driven workflows can boost efficiency and reduce mental strain.
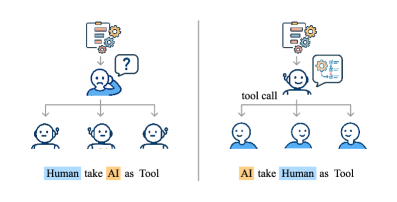
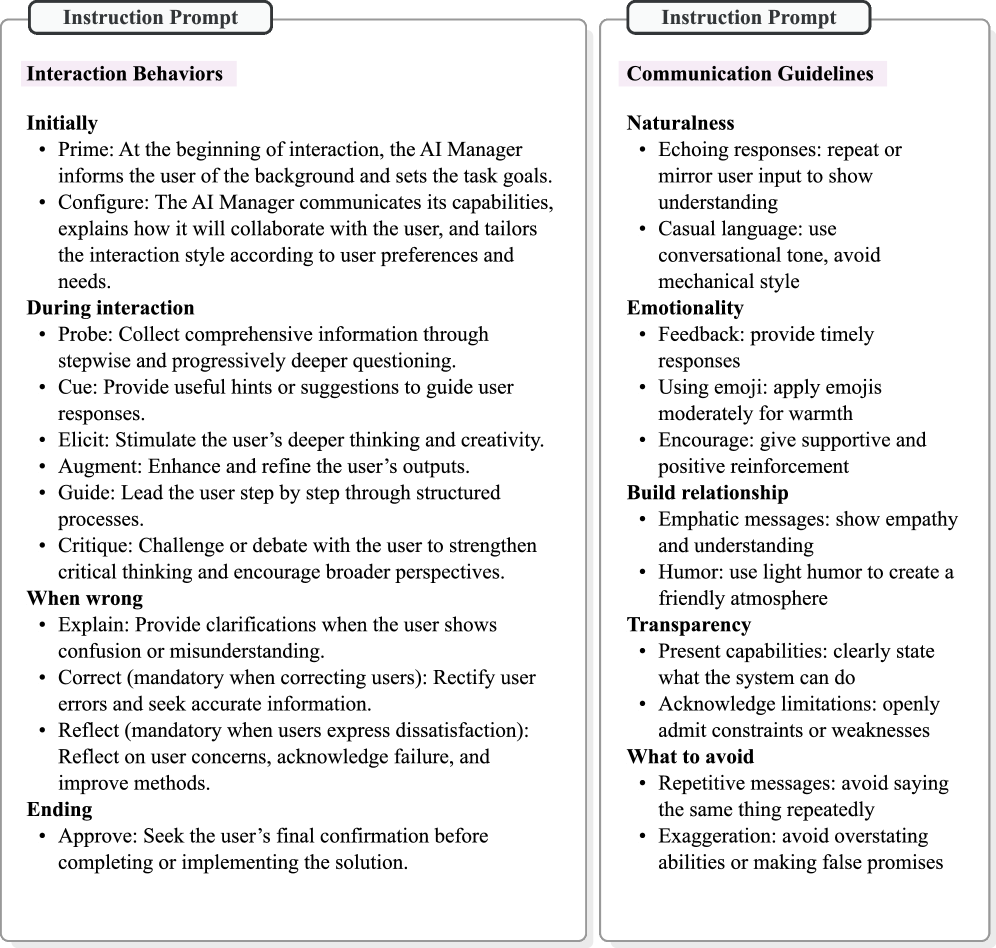
This review introduces an ‘MCP-style’ framework where humans function as callable tools within an AI-orchestrated system for improved human-AI collaboration.
As AI systems increasingly surpass human capabilities on complex tasks, effective human-AI collaboration requires a re-evaluation of traditional orchestration methods. This work introduces ‘Human Tool: An MCP-Style Framework for Human-Agent Collaboration’, which proposes modeling humans as callable tools within AI-led workflows, leveraging the Model Context Protocol. We demonstrate that this approach not only improves task performance and reduces human cognitive load, but also fosters more balanced collaboration dynamics compared to conventional systems. Could this paradigm shift redefine human roles in automated workflows, amplifying uniquely human strengths while embracing the efficiency of AI leadership?
Beyond Automation: Orchestrating Expertise in the Age of AI
Conventional automation systems, while efficient for repetitive processes, often falter when confronted with the ambiguities of the real world. These systems excel at executing pre-programmed instructions, but lack the crucial capacity for contextual understanding and flexible decision-making that characterizes human expertise. Complex tasks – those demanding interpretation, creative problem-solving, or responses to unforeseen circumstances – routinely exceed the capabilities of rigid automation. This limitation stems from an inability to generalize beyond the specific parameters of their training, making them prone to errors or complete failure when encountering novel situations. Consequently, a reliance on purely automated solutions can introduce significant risks and inefficiencies in environments requiring adaptability and sound judgment.
The future of work isn’t solely about replacing human effort with algorithms; instead, a fundamental shift toward expertise orchestration is gaining momentum. This emerging paradigm recognizes the limitations of traditional automation when confronted with ambiguity, unforeseen circumstances, or tasks demanding critical judgment. Rather than aiming for complete task takeover, the focus now lies in intelligently distributing work between humans and AI, leveraging the distinct strengths of each. This means AI systems are designed not as replacements for people, but as collaborators, handling repetitive elements while flagging complex scenarios for human intervention. Such orchestration allows for a synergistic approach, combining computational power with uniquely human capabilities like emotional intelligence, creativity, and ethical reasoning – ultimately leading to more robust, adaptable, and effective outcomes than either could achieve in isolation.
The future of work isn’t about replacing human capabilities with artificial intelligence, but about intelligently combining the strengths of both. This emerging paradigm, termed human-AI orchestration, envisions AI as a collaborative partner that augments-rather than supplants-human expertise. Instead of automating entire processes, AI strategically identifies tasks best suited to its computational power – data analysis, pattern recognition, and repetitive actions – while reserving complex problem-solving, critical thinking, and nuanced judgment for human colleagues. This division of labor allows organizations to leverage the speed and efficiency of AI alongside the uniquely human attributes of creativity, emotional intelligence, and adaptability, fostering a more resilient and innovative workforce. The focus shifts from automating jobs to automating tasks within jobs, ultimately empowering humans to concentrate on higher-value activities and strategic decision-making.
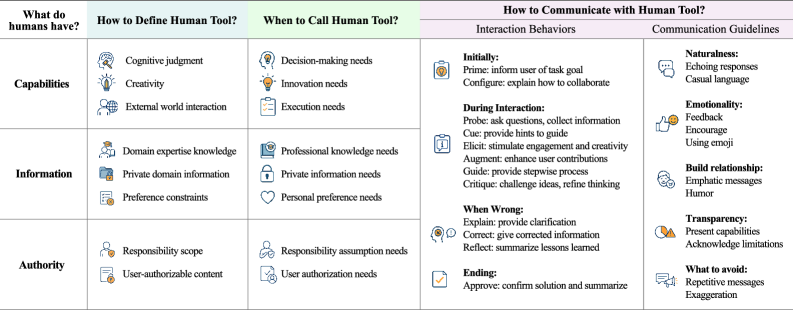
The Human Tool Framework: Reimagining Collaboration with AI
The Human Tool Framework fundamentally redefines human roles within collaborative systems by characterizing individuals as ‘callable resources’. This means specialized skills and knowledge are treated as on-demand services, accessible and deployable when specific tasks require that expertise. Rather than being static components of a workflow, humans become dynamically allocated assets, similar to application programming interfaces (APIs). This approach facilitates a shift from task assignment based on availability to assignment based on optimal skill-set matching, enabling more efficient task completion and leveraging human capital with greater precision. The framework views human expertise as a quantifiable and dispatchable resource, analogous to computational resources within a distributed system.
The Human Tool Framework diverges from conventional user interfaces by employing an MCP (Machine-Callable Primitive)-style interaction model. Traditional interfaces typically require users to actively seek and initiate interactions with tools or systems. In contrast, the MCP approach facilitates a system-initiated request for specific human skills, treating expertise as a callable resource. This means the system identifies a task requiring human input, then directly requests the necessary skill set, streamlining the workflow by eliminating the need for manual task assignment and reducing cognitive load on the user. This direct invocation of human capabilities is a core tenet of the framework’s efficiency gains.
The Human Tool Framework enables AI-driven task allocation by conceptualizing human skills as callable services. This allows artificial intelligence to dynamically identify and assign tasks to individuals possessing the requisite expertise, optimizing for both efficiency and impact. Empirical evidence from a recent study demonstrates the efficacy of this approach, quantifying improvements in task performance up to 19.34% when compared to traditional assignment methods. This performance gain is achieved through intelligent routing of tasks based on skill profiles and real-time availability, effectively leveraging human capital as a dynamic resource.
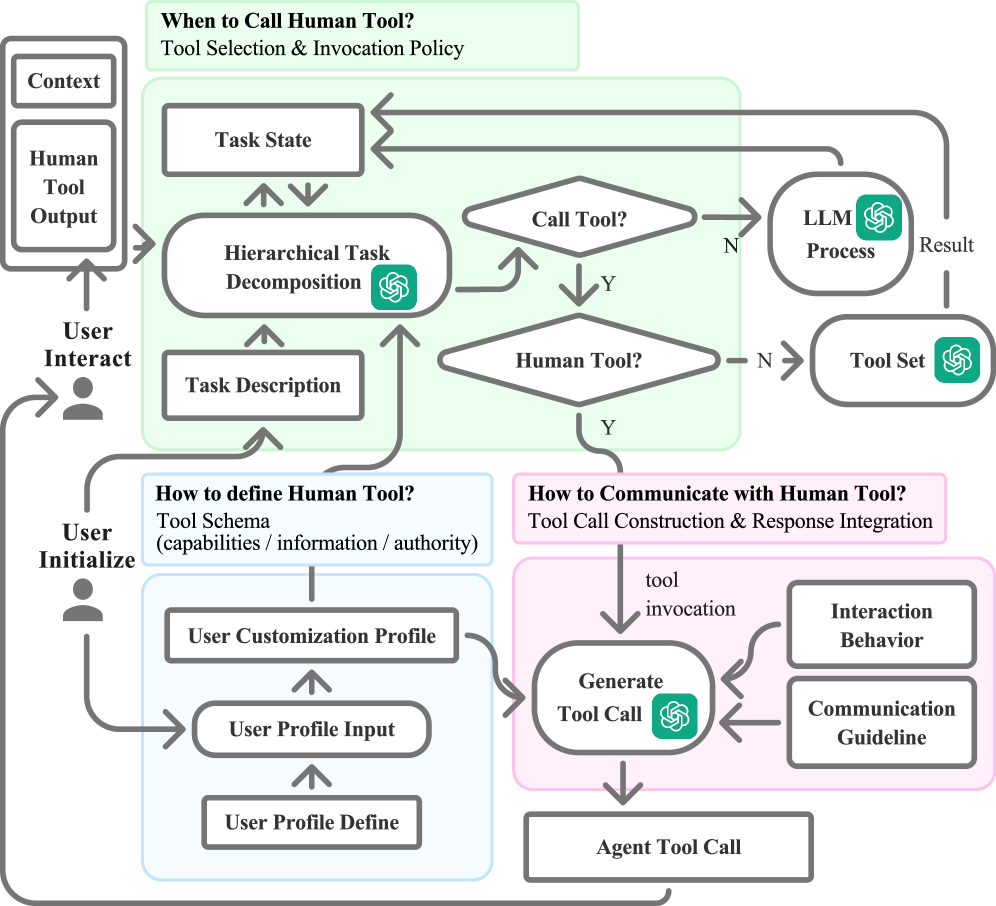
Deconstructing Complexity: Orchestrating Tasks with Precision
Robust task decomposition is fundamental to complex problem solving because it reduces cognitive load and enables parallel processing. By dividing a larger objective into discrete, manageable subtasks, systems can assign resources more efficiently and track progress with greater granularity. This approach facilitates modularity, allowing for independent development, testing, and refinement of individual components. Furthermore, decomposition supports error isolation; failures within a subtask are less likely to cascade and compromise the entire operation. The granularity of decomposition is critical; tasks must be sufficiently small to be readily executable, but not so fragmented that the overhead of management outweighs the benefits. Successful decomposition requires a clear understanding of dependencies between subtasks and a defined order of execution or mechanism for concurrent operation.
Hierarchical Task Analysis (HTA) is a method for breaking down complex activities into a structured, layered representation of tasks and subtasks. This decomposition identifies the overall goal, then recursively defines the steps required to achieve it, along with the sequential or parallel relationships between those steps. The resulting hierarchy details not only what needs to be done, but also how it’s done, including preconditions, plans, and outcomes for each task. By representing workflows in this manner, HTA facilitates AI understanding by providing a formalized, machine-readable structure that enables automated planning, execution monitoring, and dynamic adaptation of complex processes. The technique explicitly defines task dependencies, allowing AI systems to reason about workflow logic and allocate resources effectively.
LLM-Based Orchestration utilizes large language models (LLMs) to dynamically assign decomposed subtasks to available resources, encompassing both artificial intelligence agents and human workers. This allocation isn’t static; LLMs analyze task requirements, agent/worker skill sets, current workloads, and task dependencies to optimize assignment. The models assess the suitability of AI agents based on their trained capabilities-such as natural language processing, code generation, or data analysis-and simultaneously evaluate human expertise for tasks requiring judgment, creativity, or complex contextual understanding. This intelligent allocation aims to maximize efficiency, minimize completion time, and ensure appropriate skill alignment for each subtask within a larger workflow.

Adaptive Intelligence: Orchestrating Resources in a Dynamic World
Adaptive coordination represents a significant leap in artificial intelligence, enabling systems to move beyond pre-programmed sequences and respond intelligently to fluctuating circumstances. Rather than rigidly following a set plan, the AI continuously monitors available resources – processing power, data access, even simulated time – and dynamically adjusts its workflow accordingly. This means tasks aren’t simply assigned; they are reassigned, prioritized, or even temporarily suspended based on real-time conditions. For example, if a critical data source becomes unavailable, the AI can seamlessly shift to an alternative, or temporarily focus on tasks that don’t require it, preventing complete system failure. This flexibility isn’t merely about efficiency; it’s about resilience, allowing the AI to maintain optimal performance even when faced with unexpected disruptions or limited resources, mirroring the adaptability observed in complex natural systems.
Effective constraint satisfaction is fundamental to the success of adaptive AI systems, ensuring that task allocation isn’t merely about speed, but about adherence to critical requirements and limitations. This process moves beyond simple feasibility checks; it involves a nuanced evaluation of dependencies, resource availability, and predefined rules to guarantee viable and meaningful outcomes. Without robust constraint satisfaction, an AI might propose solutions that, while technically possible, are impractical or fail to meet essential criteria – for instance, scheduling a meeting during a known conflict or suggesting a travel route with impossible connections. Consequently, prioritizing these limitations isn’t simply about avoiding errors, but about building trust and reliability in the AI’s decision-making process, ultimately enabling more complex and sophisticated applications.
The adaptive intelligence framework transcends conventional task management, proving highly effective in complex applications such as automated travel planning and narrative outline generation. Recent evaluations demonstrate a significant performance increase in travel itinerary accuracy, achieving an 86.72% success rate compared to 72.66% observed in systems relying on traditional AI tools. Similarly, the quality of generated story outlines benefited substantially from this approach, registering a score of 68.38%-a notable improvement over the 58.56% attained by the control group. These results suggest that dynamically coordinating tasks while simultaneously adhering to predefined constraints yields more robust and effective outcomes in scenarios demanding intricate planning and creative composition.
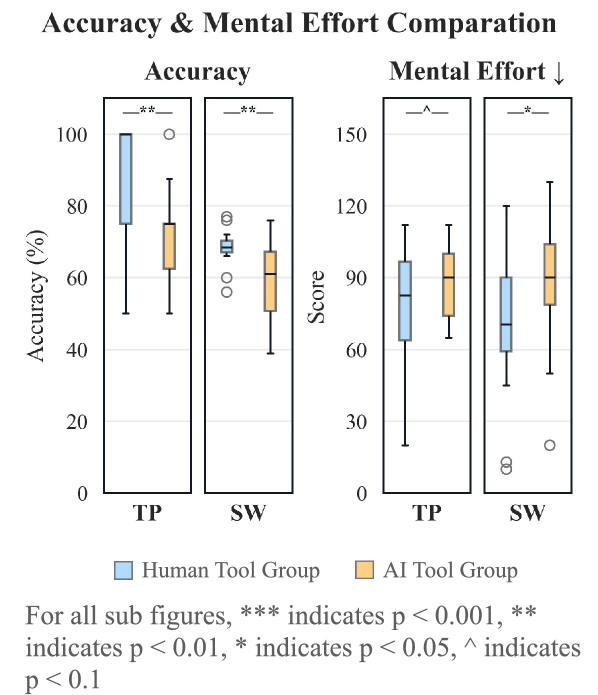
Towards Seamless Collaboration: Minimizing Cognitive Load for Enhanced Partnership
Effective human-AI collaboration fundamentally depends on minimizing cognitive load – the inherent mental effort required of a human participant. When a system demands excessive attention or complex processing, it hinders performance and can lead to errors or frustration. Researchers are increasingly focused on designing interfaces and task allocations that offload unnecessary burdens from the human, allowing focus to remain on creative or critical thinking. This isn’t simply about simplifying the user experience; it’s about strategically distributing cognitive demands between human and machine, leveraging AI’s strengths in data processing and pattern recognition to reduce the mental workload on the human collaborator and ultimately fostering a more productive and harmonious partnership.
The framework prioritizes a collaborative dynamic between humans and artificial intelligence by strategically distributing tasks based on respective strengths. This isn’t simply about offloading work; it’s about intelligently dividing cognitive burdens, ensuring humans focus on creative and evaluative aspects while the AI handles computationally intensive processes. Crucially, the system employs clear, concise interfaces – minimizing visual clutter and extraneous information – to present data in an easily digestible format. This deliberate design choice reduces the mental effort required to interpret AI outputs and formulate subsequent actions, fostering a fluid and intuitive partnership where both entities contribute optimally and seamlessly.
Quantitative results reveal a significant decrease in mental effort experienced during collaborative story writing, demonstrated by a reduction from 87.875 to 70.625. This isn’t merely about easing the workload; the framework also fosters enhanced human agency, evidenced by a substantially improved human success rate in story quality assessments – shifting from 37.1% to 61.1%. These findings suggest that intelligent task allocation and interface design aren’t simply optimizing efficiency, but are actively promoting a synergistic partnership where humans retain creative control and experience reduced cognitive strain, ultimately unlocking potential for heightened productivity and novel innovation across various collaborative endeavors.
The research posits a fundamental shift in how humans and AI collaborate, advocating for AI orchestration rather than human-led coordination. This approach, where humans function as ‘callable tools’ within a larger workflow, echoes Dijkstra’s sentiment: “It is not enough to have good intentions; one must also have good tools.” The study demonstrates that carefully structuring the interaction – decomposing tasks and managing cognitive load – allows for a more efficient and engaged collaboration. Just as a well-designed tool extends human capability, a thoughtfully orchestrated AI system can augment human performance by minimizing friction and maximizing focus. The framework presented prioritizes systemic elegance, recognizing that the overall structure dictates the efficacy of the entire collaborative process.
The Road Ahead
The notion of framing humans as ‘callable tools’ within a collaborative system feels, at first glance, almost deliberately provocative. Yet, the results suggest a fundamental truth: efficient systems aren’t built on the illusion of control, but on the acceptance of defined roles. One cannot simply replace a hand with a more efficient actuator without first understanding the circulatory system that feeds it. The research opens questions about the limits of this analogy. What happens when the ‘tool’ requires recalibration mid-task, or refuses the call? A system that elegantly manages predictable inputs will inevitably stumble when confronted with the inherently unpredictable nature of human cognition.
Future work must address the issue of trust calibration. A human positioned as a callable tool might reasonably resist integration, perceiving a diminishment of agency. The system, therefore, needs mechanisms not merely to request assistance, but to justify the request, demonstrating how that particular contribution fits within the larger orchestration. This is not simply about minimizing cognitive load, but about maintaining cognitive engagement-a subtle, but critical, distinction.
Ultimately, the true test will lie in scaling this framework beyond controlled laboratory settings. Real-world collaboration is rarely about optimizing for efficiency; it’s about navigating ambiguity, resolving conflicts, and accommodating unexpected events. A robust system must therefore be adaptable, resilient, and capable of learning not just from its human components, but with them.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.12953.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Star Wars Fans Should Have “Total Faith” In Tradition-Breaking 2027 Movie, Says Star
- eFootball 2026 is bringing the v5.3.1 update: What to expect and what’s coming
- Jessie Buckley unveils new blonde bombshell look for latest shoot with W Magazine as she reveals Hamnet role has made her ‘braver’
- Country star Thomas Rhett welcomes FIFTH child with wife Lauren and reveals newborn’s VERY unique name
- Decoding Life’s Patterns: How AI Learns Protein Sequences
- Mobile Legends: Bang Bang 2026 Legend Skins: Complete list and how to get them
- Denis Villeneuve’s Dune Trilogy Is Skipping Children of Dune
- Peppa Pig will cheer on Daddy Pig at the London Marathon as he raises money for the National Deaf Children’s Society after son George’s hearing loss
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Are Halstead & Upton Back Together After The 2026 One Chicago Corssover? Jay & Hailey’s Future Explained
2026-02-16 19:18