Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new framework leverages the power of collaborative AI agents and next-generation 6G networks to deliver low-latency intelligence for critical applications.
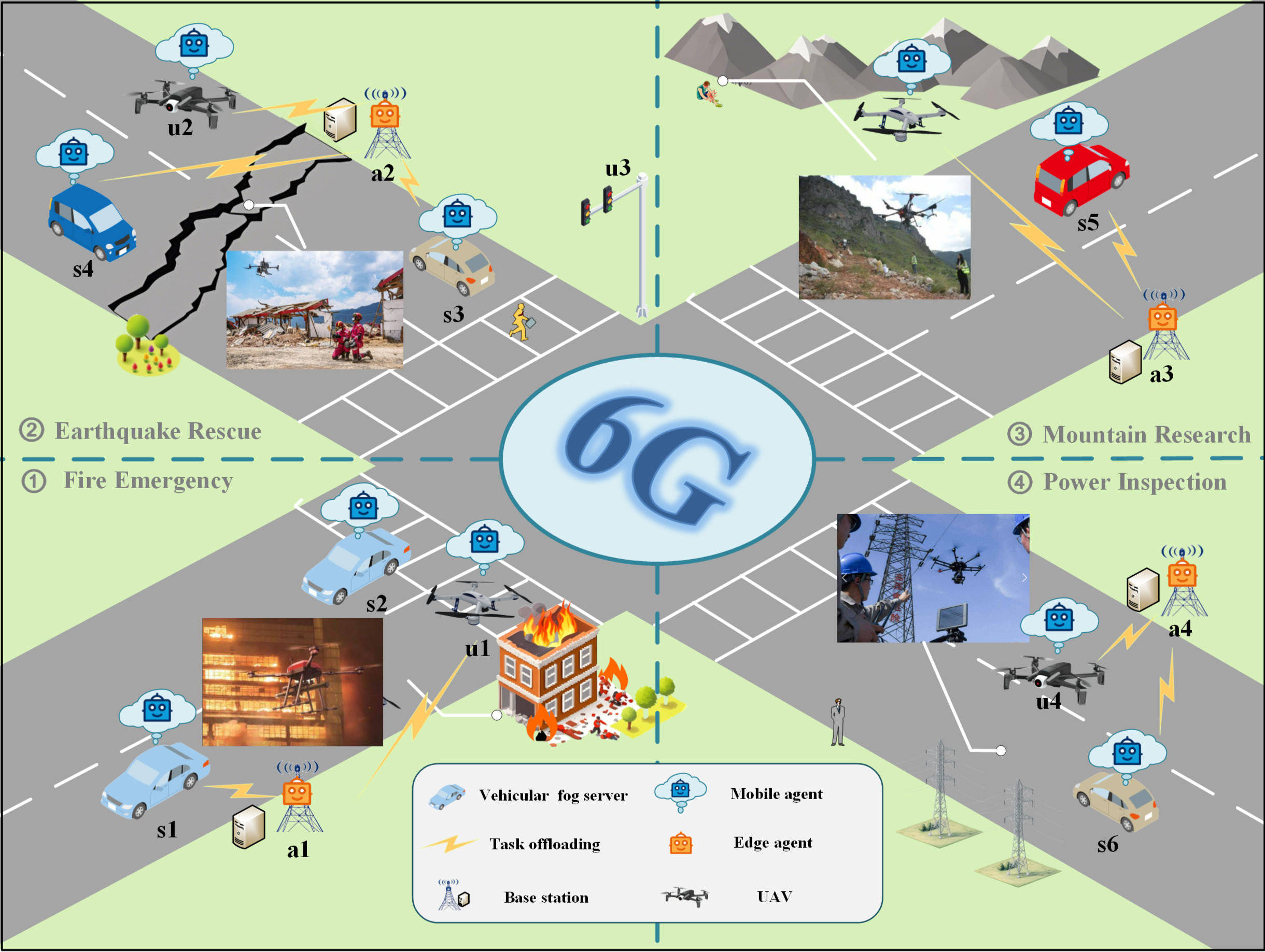
This paper introduces CORE, a system for orchestrating large language model agents across hierarchical edge networks to enhance task completion and reduce communication latency.
Despite the promise of ubiquitous intelligence in future 6G networks, realizing complex reasoning tasks is hindered by fragmented resources across hierarchical edge infrastructure. This paper introduces CORE-Collaborative Orchestration Role at Edge-a novel framework leveraging collaborative orchestration of large language model (LLM) agents distributed across mobile devices and tiered edge servers. CORE optimizes collaboration through real-time perception, dynamic role orchestration, and pipeline-parallel execution, demonstrably enhancing system efficiency and task completion rates in diverse 6G application scenarios. Could this approach unlock a new paradigm for low-latency, AI-driven services at the network edge?
The Evolving Demand for Intelligent Connectivity
The advent of sixth-generation (6G) networks is driven by a need for communication systems capable of supporting increasingly sophisticated and time-sensitive applications. Unlike previous generations focused primarily on increased data rates, 6G prioritizes ultra-reliability and extremely low latency – characteristics essential for enabling technologies like fully autonomous vehicles, remote robotic surgery, and real-time control of critical infrastructure. These applications demand near-instantaneous responsiveness and an exceptionally high degree of connection stability; even brief interruptions or delays could have catastrophic consequences. Consequently, 6G is being designed not simply to transmit data faster, but to guarantee its delivery with unprecedented consistency and speed, fundamentally altering the landscape of wireless communication and ushering in an era of truly connected intelligence.
Current network management strategies, designed for previous generations, are proving inadequate for the demands of 6G technologies. These established methods typically rely on centralized control and static resource allocation, creating bottlenecks and delays that compromise the ultra-reliability and low-latency essential for applications like remote surgery and autonomous vehicles. The inherent rigidity of these systems struggles to adapt to the dynamic and unpredictable needs of 6G-enabled devices, resulting in inefficient bandwidth utilization and increased susceptibility to network congestion. Consequently, the full transformative potential of 6G – including truly immersive extended reality and real-time industrial automation – remains constrained by the limitations of legacy infrastructure and operational paradigms.
The advent of 6G networks demands a fundamental shift in how network resources are managed and data is processed, moving beyond centralized control to a distributed, intelligent edge. This emerging paradigm envisions a network capable of dynamically allocating resources – bandwidth, computing power, and storage – in real-time, responding to the immediate needs of applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. Instead of transmitting all data to a distant cloud, processing will increasingly occur closer to the source – at the network edge – reducing latency and improving reliability. This necessitates advanced technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence to predict demand, optimize performance, and ensure seamless connectivity, ultimately unlocking the full potential of 6G for truly immersive and responsive experiences.
A Collaborative Intelligence Architecture: CORE
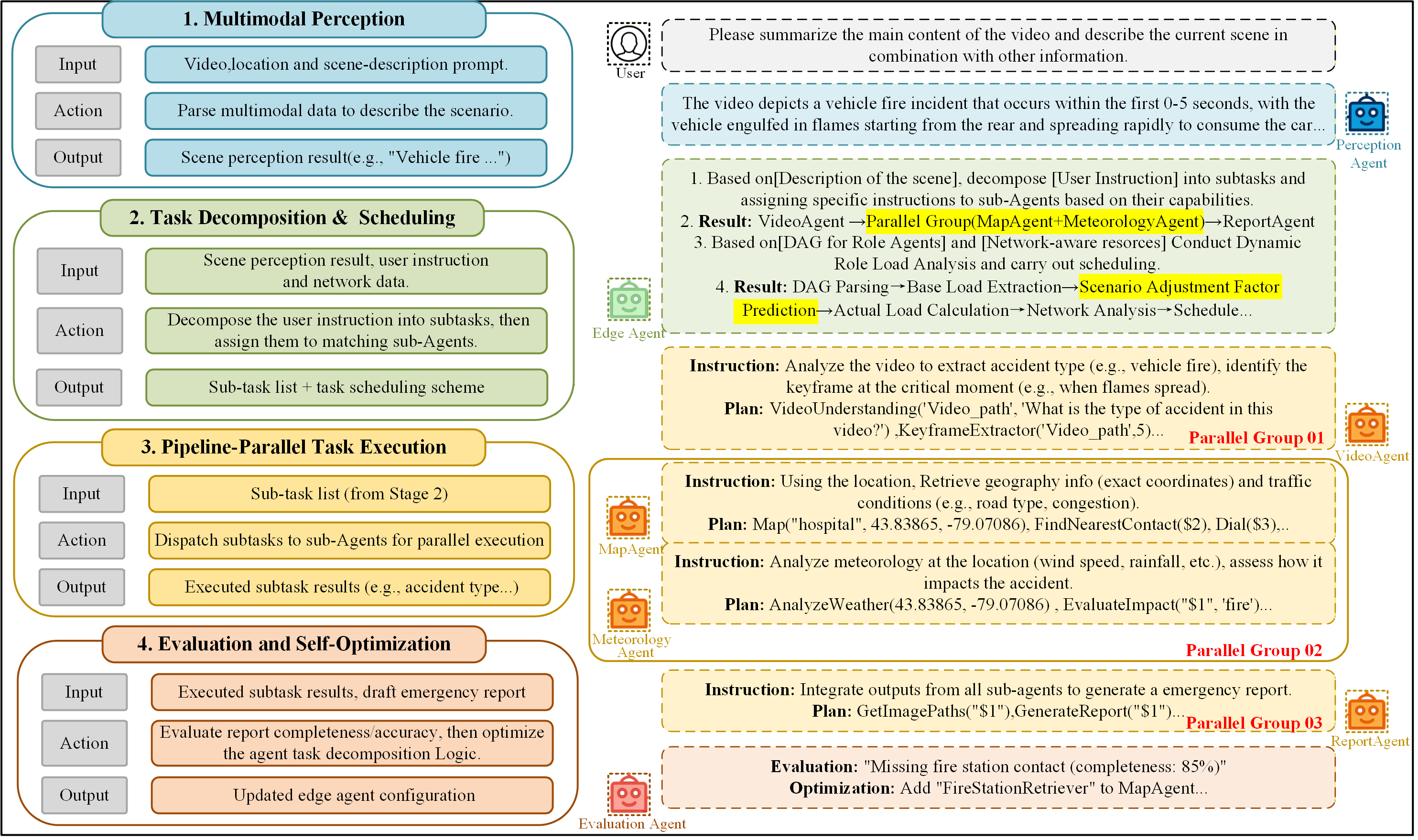
The CORE framework addresses limitations of traditional, monolithic systems in 6G networks by facilitating the collaborative execution of user-agent interactive tasks. These monolithic architectures often create bottlenecks and lack the flexibility required for the dynamic demands of future applications. CORE, conversely, distributes processing and intelligence, allowing multiple agents to contribute to task completion. This distributed approach improves scalability, reduces latency, and enhances the overall responsiveness of the network to user interactions. By moving away from centralized processing, CORE enables a more efficient and robust architecture capable of supporting complex, interactive services within the 6G environment.
The CORE framework utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) not as singular entities, but as distributed components within a Collaborative Learning System. This system fragments LLM functionality, assigning specialized roles – such as planning, knowledge retrieval, or execution – to individual LLM agents. This role-based distribution allows for parallel processing and optimized resource allocation, enhancing overall efficiency. Agents can be dynamically assigned and reconfigured based on task requirements and available network resources, moving beyond the limitations of single, monolithic LLM deployments. The Collaborative Learning System also facilitates knowledge sharing and continuous learning amongst the distributed agents, improving performance over time.
Dynamic Role Orchestration within the CORE framework utilizes real-time network conditions and device capabilities to assign tasks to Large Language Model (LLM) agents. The Role Affinity Scheduling Algorithm evaluates factors such as available bandwidth, computational resources of edge devices, and LLM agent specialization to optimize task allocation. This ensures tasks are directed to the most suitable agent, minimizing latency and maximizing throughput. Specifically, the algorithm considers device proximity to the data source, processing power, and the specific expertise of each LLM agent – for example, assigning a language translation task to an LLM specializing in natural language processing. The system continuously monitors performance metrics and dynamically adjusts task assignments to maintain optimal efficiency and responsiveness, even under fluctuating network conditions.
Pipeline-parallel execution within the CORE framework improves performance by dividing a user-agent task into multiple independent subtasks. These subtasks are then distributed across available LLM agents and processed concurrently, rather than sequentially. This approach reduces overall task completion time by leveraging the parallel processing capabilities of the distributed system. The efficiency of this method is predicated on minimizing inter-subtask dependencies and optimizing data transfer between agents to avoid bottlenecks, thereby maximizing throughput and reducing latency for interactive applications within the 6G network.
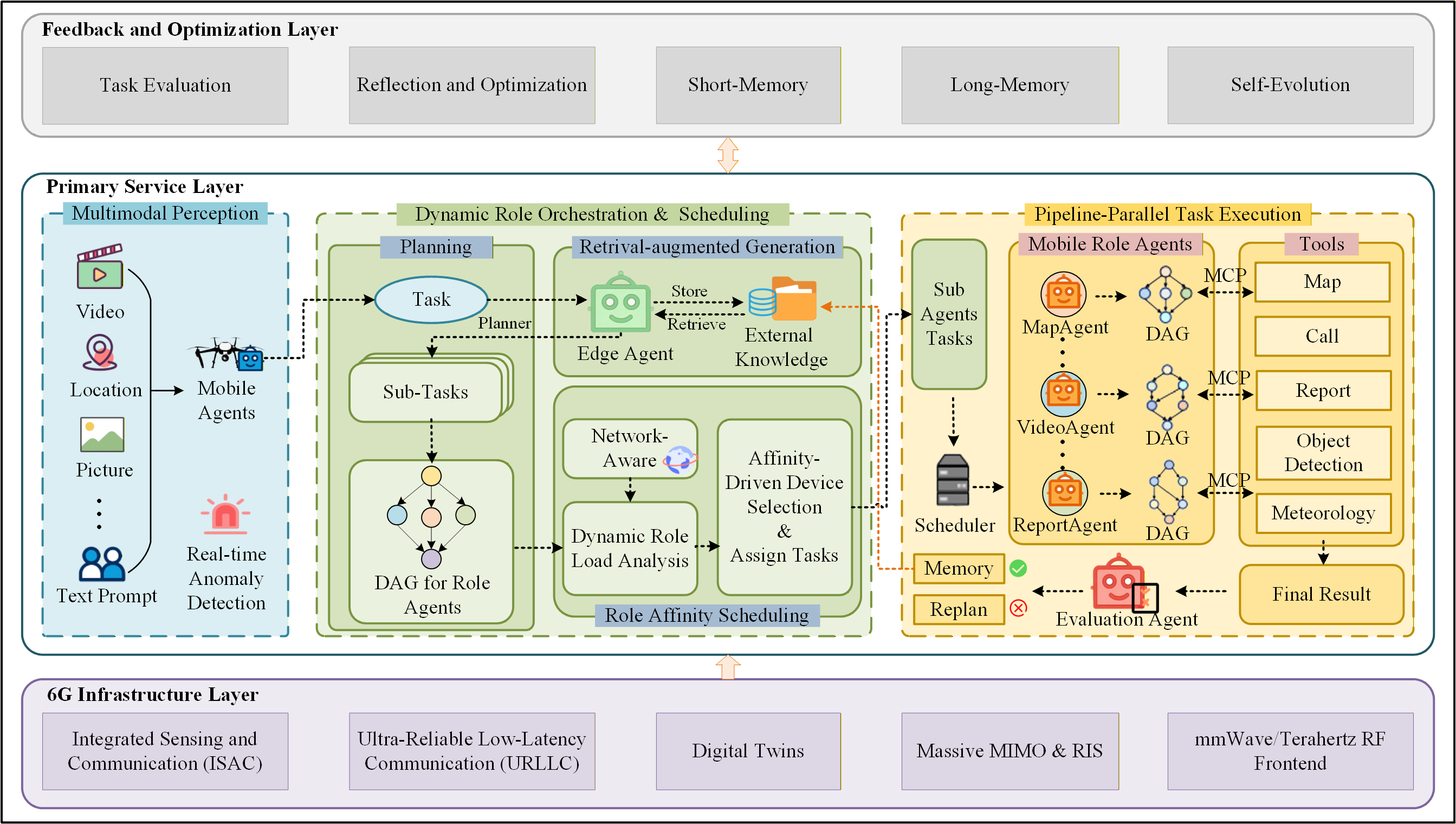
Context, Sensing, and Virtualization: Enabling CORE
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) facilitates communication between Large Language Model (LLM) agents by standardizing the format and content of exchanged information. This protocol defines a structured data schema for representing contextual elements, including relevant history, current state, and specific task parameters. By explicitly defining these elements, the MCP minimizes ambiguity and reduces the need for agents to infer meaning, thereby decreasing computational load. The protocol supports compression and selective transmission of context, prioritizing information critical for the current task and reducing bandwidth requirements. Furthermore, the MCP enables efficient context switching between tasks, allowing agents to rapidly adapt to new objectives without reprocessing large volumes of irrelevant data, ultimately improving overall system coherence and responsiveness.
Multi-Modal Perception within the CORE framework utilizes the concurrent processing of data from multiple sensor types – including, but not limited to, visual, auditory, thermal, and radio frequency signals – to construct a comprehensive understanding of the operational environment. This integration surpasses the limitations of single-sensor systems by providing redundancy and corroboration of information, increasing accuracy and reliability in complex scenarios. The resulting enriched environmental model supports dynamic task allocation by enabling the system to assess the capabilities required for a given situation and assign tasks to the most appropriate LLM agent, optimizing resource utilization and improving overall system performance. Furthermore, the system can adapt to changing conditions by continuously refining its perception based on incoming data streams.
Digital twins within the CORE framework function as dynamic virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems. These representations are created through the continuous synchronization of data from various sources, including sensors, historical records, and real-time operational data. This allows for the execution of “what-if” simulations to predict performance under varying conditions, optimize operational parameters, and proactively identify potential failures. The integration of digital twins enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and the validation of control strategies without disrupting the physical system, ultimately reducing costs and improving efficiency. Data fidelity and low-latency communication are critical requirements for effective digital twin implementation within the CORE architecture.
Network slicing, a key 6G feature, enables the creation of multiple virtual networks on a common physical infrastructure, each tailored to specific performance requirements of CORE applications. Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) further enhances this infrastructure by allowing 6G base stations to simultaneously perform communication and sensing functions, providing real-time environmental data crucial for contextual awareness. This combination allows CORE to dynamically allocate resources and prioritize bandwidth to agents based on their specific needs and the sensed environment, optimizing performance and reducing latency. Specifically, ISAC provides data for locationing, object detection, and environmental mapping, while network slicing guarantees the quality of service required for reliable data transfer and agent interaction within the CORE framework.
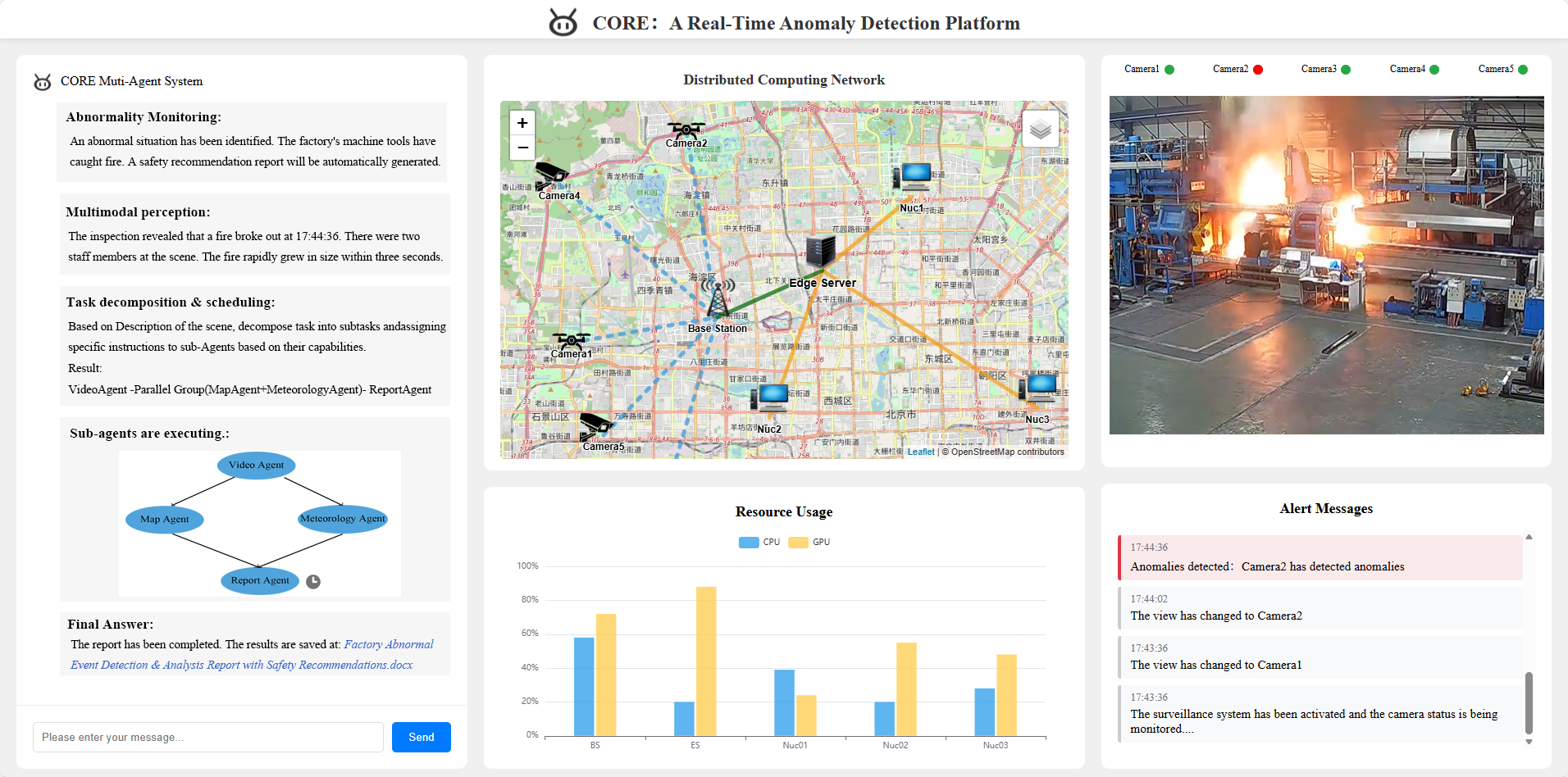
A Performance Leap: CORE vs. Traditional Approaches
The CORE framework distinguishes itself from single-agent approaches – such as ReAct and LLMCompiler – through a fundamentally collaborative architecture. While those methods rely on a single large language model to handle all aspects of a task, CORE distributes workload across multiple specialized agents. This division not only enhances the system’s ability to tackle complex problems, but also introduces inherent resilience; should one agent encounter difficulties, others can compensate, preventing complete failure. Crucially, this collaborative design enables superior scalability, allowing the system to effectively manage increasing task demands and data volumes without significant performance degradation – a limitation often observed in single-agent systems striving to handle ever-larger workloads.
The CORE framework demonstrates a substantial advancement over conventional multi-agent systems such as Crew_Ai and Static_Dual_Loop through its refined orchestration and intelligent scheduling capabilities. Rigorous testing reveals that CORE achieves a 25% higher success rate on medium-complexity tasks and a notable 20% improvement on challenging, hard-complexity tasks when benchmarked against the Static_Dual_Loop system. This performance leap isn’t merely incremental; it indicates a fundamental shift in how complex tasks are broken down, allocated, and ultimately resolved, suggesting CORE’s dynamic approach allows for more effective resource utilization and adaptation to unforeseen challenges during execution.
Within the CORE framework, efficient resource allocation is achieved through DynaRole-HEFT, a dynamic task assignment strategy. This approach moves beyond static assignments by intelligently evaluating the computational demands of each sub-task and matching them to the most suitable agent based on real-time availability and processing capacity. By considering both task complexity and agent capabilities, DynaRole-HEFT minimizes idle time and maximizes overall throughput. This optimization isn’t simply about dividing work; it’s a continuous recalibration, ensuring that resources are consistently deployed where they yield the greatest impact, leading to substantial gains in performance and reduced latency, particularly crucial for the demanding requirements of next-generation 6G networks.
Significant performance gains achieved through the CORE framework directly address the critical need for low latency in next-generation communication systems. Studies demonstrate a substantial 52% reduction in high-load latency, enabling faster response times and improved user experiences. This is facilitated by an orchestrator inference time of just 180-320 milliseconds, which, while representing 25-40% of the total end-to-end delay under heavy load, remains a pivotal factor in optimizing overall system speed. Such responsiveness is particularly crucial for the demanding requirements of 6G applications, where real-time data processing and minimal delays are paramount for services like augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
The Future of Intelligent Networks with CORE
The CORE framework distinguishes itself not as a solution tailored solely to the demands of current 6G implementations, but rather as a deliberately flexible and extensible architectural foundation for the networks of tomorrow. Its modular design and emphasis on abstraction allow it to transcend specific technological iterations, positioning it to accommodate unforeseen advancements and emerging paradigms in network infrastructure. This foresight is crucial, as future networks will likely incorporate technologies beyond the scope of present-day 6G, such as terahertz communication, quantum networking, and potentially entirely new forms of data transmission and processing. By prioritizing adaptability over immediate optimization, CORE aims to remain relevant and effective across multiple generations of network technology, fostering a long-term, sustainable path toward truly intelligent and interconnected systems.
The true potential of the CORE framework extends far beyond its initial 6G applications, promising transformative advancements when coupled with sophisticated sensor networks and edge computing capabilities. This synergy allows for real-time data processing and localized decision-making, critical for the complex demands of autonomous robotics, enabling swift reactions to dynamic environments. Similarly, smart cities can benefit from CORE’s enhanced data analytics, optimizing traffic flow, resource allocation, and public safety measures with unprecedented efficiency. Beyond practical applications, the framework also paves the way for truly immersive experiences – virtual and augmented reality applications demanding ultra-low latency and high bandwidth will flourish as CORE distributes processing power closer to the user, creating seamless and responsive digital interactions.
The inherent adaptability of the CORE framework will be significantly bolstered by ongoing investigations into dynamic role adaptation and collaborative learning algorithms. These advanced algorithms will enable network nodes to fluidly adjust their functions based on real-time demands and environmental conditions, moving beyond static configurations. This dynamic capability isn’t merely about responding to failures-it’s about proactively optimizing network performance and resource allocation. Furthermore, collaborative learning, where nodes share insights and refine their operational strategies as a collective, promises to enhance CORE’s resilience against unforeseen disruptions and dramatically improve its scalability to accommodate exponentially increasing device density and data volumes. The resulting network will not only be more robust but also capable of self-optimization and continuous improvement, paving the way for truly intelligent and responsive connectivity.
The promise of next-generation networks extends beyond simply faster data transfer; it envisions a fundamentally interconnected world capable of proactive responsiveness. Achieving this requires a shift towards collaborative intelligence, where network elements operate not as isolated components, but as a unified, learning system. This approach facilitates dynamic resource allocation, predictive maintenance, and optimized performance, enabling applications ranging from real-time traffic management in smart cities to seamless coordination of autonomous robotic systems. By fostering a network that anticipates and adapts to evolving needs, a truly connected and responsive world becomes increasingly attainable, unlocking unprecedented levels of efficiency, innovation, and societal benefit.
The pursuit of ubiquitous 6G intelligence, as outlined in this work, benefits from a rigorous adherence to simplicity. CORE’s framework, focusing on collaborative orchestration of LLM agents at the edge, exemplifies this principle. It prioritizes efficient task completion and low latency-essential for real-time applications. As Brian Kernighan observed, “Debugging is twice as hard as writing the code in the first place. Therefore, if you write the code as cleverly as possible, you are, by definition, not smart enough to debug it.” This sentiment mirrors the design philosophy behind CORE; complexity is actively minimized, favoring a streamlined architecture that enhances maintainability and reduces the potential for errors in a distributed, intelligent network.
What Remains?
The pursuit of ubiquitous intelligence, as exemplified by the CORE framework, inevitably reveals the limits of current orchestration. The ease with which large language models are deployed should not obscure the enduring problem of true collaboration – not merely parallel execution, but genuine synergistic problem-solving. Latency, while addressed, remains a symptom, not the disease. The real challenge lies in minimizing cognitive overhead – the wasted cycles of re-explanation, misinterpretation, and redundant analysis within the multi-agent system.
Future work must prioritize a more austere design. The temptation to add agents, to broaden scope, should be resisted. Instead, attention should be focused on refining the existing architecture – streamlining communication protocols, developing more robust error-correction mechanisms, and, crucially, establishing clear hierarchies of expertise. A smaller, more focused system, capable of rapid, decisive action, will ultimately prove more valuable than a sprawling, unwieldy one.
The promise of 6G lies not in simply accelerating data transfer, but in fundamentally altering the nature of computation. CORE offers a glimpse of that future, but only by embracing simplicity – by relentlessly pruning away the superfluous – can the true potential of collaborative intelligence be realized. The next step is not to build more, but to unbuild – to reveal the elegant core beneath the layers of complexity.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.21822.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- CookieRun: Kingdom 5th Anniversary Finale update brings Episode 15, Sugar Swan Cookie, mini-game, Legendary costumes, and more
- Robots That React: Teaching Machines to Hear and Act
- Call the Midwife season 16 is confirmed – but what happens next, after that end-of-an-era finale?
- Taimanin Squad coupon codes and how to use them (March 2026)
- Heeseung is leaving Enhypen to go solo. K-pop group will continue with six members
- How to get the new MLBB hero Marcel for free in Mobile Legends
- Alan Ritchson’s ‘War Machine’ Netflix Thriller Breaks Military Action Norms
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Brent Oil Forecast
- 10 New Books You Should Read in March
2026-02-01 08:47