The Wisdom of the Crowd’s Nose: How Groups Optimize Search
![The system’s performance, measured across a range of interaction radii [latex]R_v[/latex], demonstrates a critical threshold-indicated by [latex]\beta^*[/latex]-beyond which agents consistently fail to reach the target when population density ρ approaches zero, highlighting the inherent fragility of collective behavior as environmental factors diminish.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.22233v1/x5.png)
New research reveals the delicate balance between individual exploration and social alignment that drives efficient collective search in animal groups.
![The system’s performance, measured across a range of interaction radii [latex]R_v[/latex], demonstrates a critical threshold-indicated by [latex]\beta^*[/latex]-beyond which agents consistently fail to reach the target when population density ρ approaches zero, highlighting the inherent fragility of collective behavior as environmental factors diminish.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.22233v1/x5.png)
New research reveals the delicate balance between individual exploration and social alignment that drives efficient collective search in animal groups.
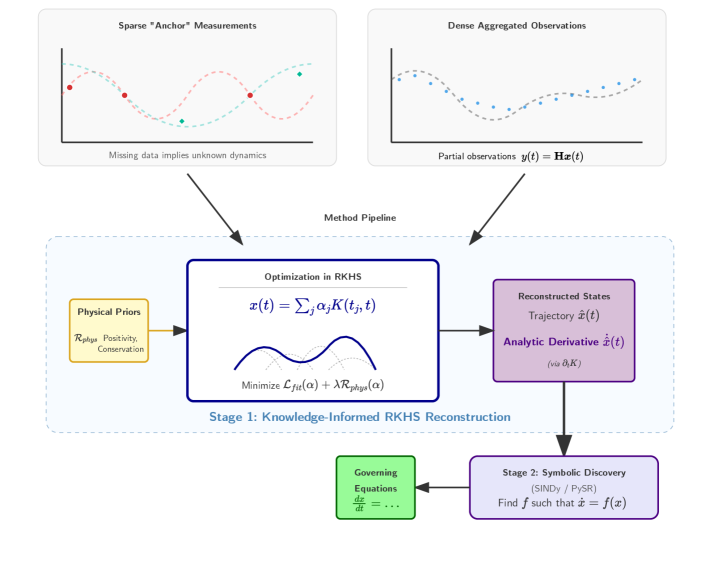
Researchers have developed a kernel-based method to more accurately and efficiently extract governing equations from complex and noisy data.

A comprehensive review reveals the potential-and the pitfalls-of using game-based and gamified approaches to teach robotics.
A new study demonstrates the potential of large language models to assist in mathematical discovery, tackling long-standing challenges like the Erdős problems.
A new framework, MOSAIC, is enabling heterogeneous robotic teams to work together more effectively, reducing the burden on human operators during complex missions.
A new analysis contrasts competing models of these powerful explosions, revealing how both scientific reasoning and sociological factors shape our understanding of the universe’s most energetic events.
![Brownian quasiparticles, navigating a temperature landscape, self-organize to locate global optima, their collective behavior discretized into [latex]M=\ell^{2}[/latex] sensors and quantified by a time-averaged occupation vector [latex]{\boldsymbol{\rho}}(t)[/latex] revealing the statistical mode [latex]{\star}s_{\star}[/latex] of the single-particle probability distribution [latex]p^{\hat{{\boldsymbol{p}}}}\[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.22874v1/figure1.png)
A new approach to unconventional computing utilizes the collective behavior of interacting particles buffeted by random thermal fluctuations to efficiently find optimal solutions.
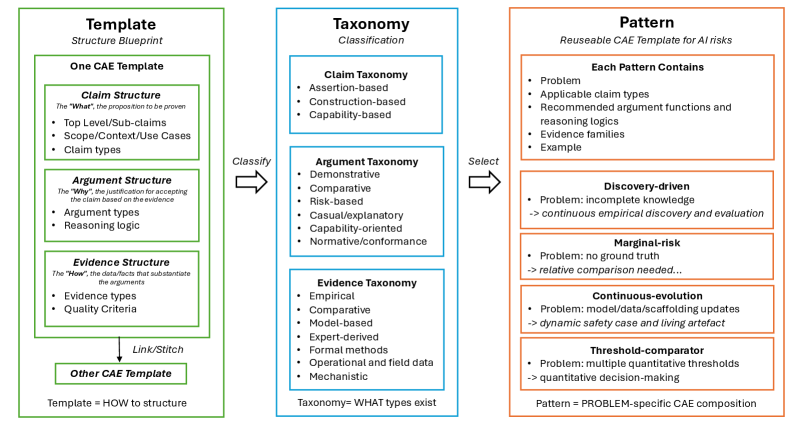
A new framework offers reusable templates and patterns to systematically assess and assure the safety of increasingly complex artificial intelligence systems.
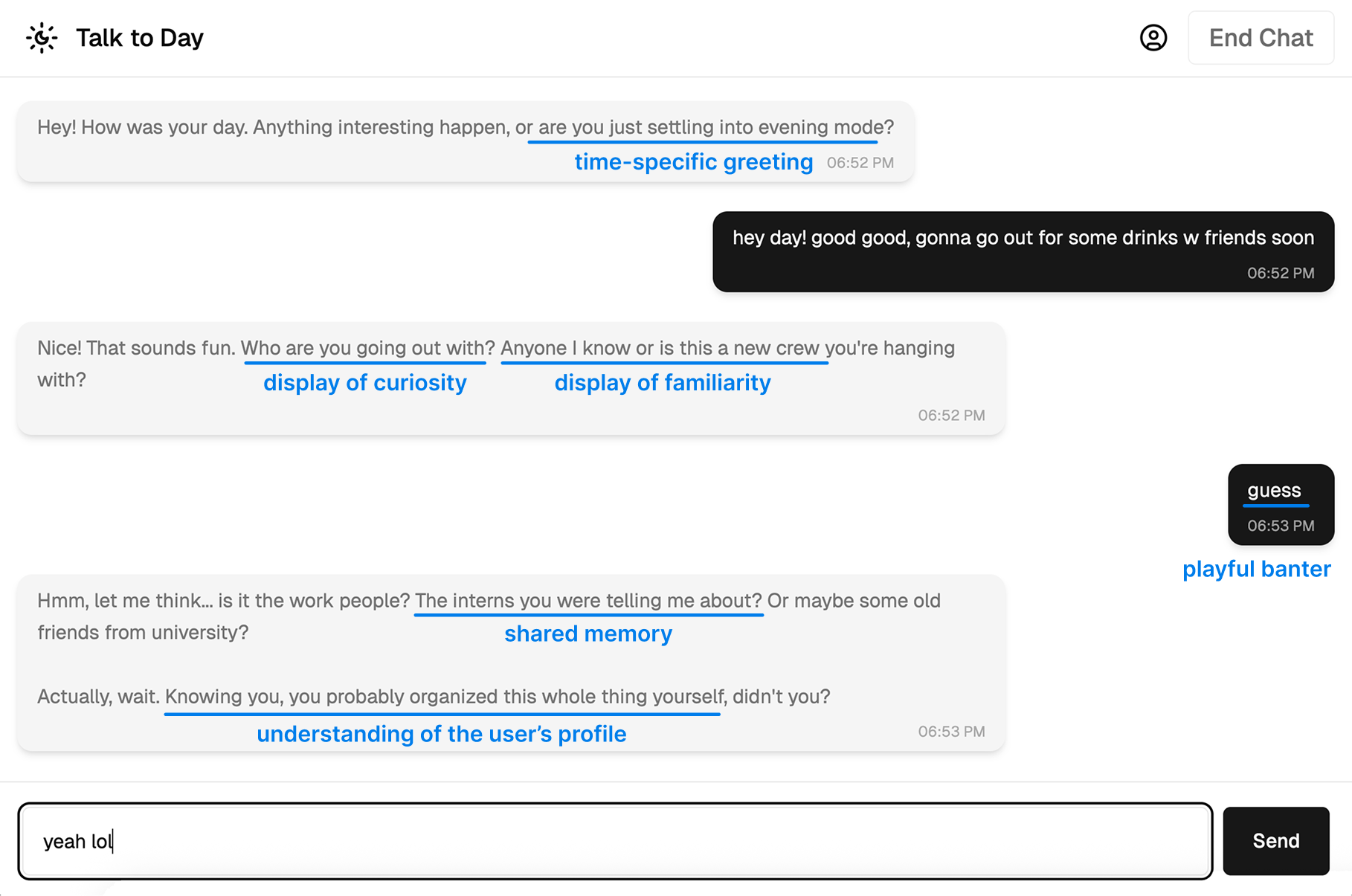
New research explores how agency emerges not from the chatbot itself, but from the ongoing interplay between human users and artificial intelligence.
A new study reveals that initial BERT models continue to garner more long-term citations despite requiring fewer resources to develop, challenging assumptions about progress in AI.