Smarter LaTeX: An AI Editor for Researchers
A new AI-powered editor aims to dramatically simplify the academic writing process, from initial draft to polished manuscript.
A new AI-powered editor aims to dramatically simplify the academic writing process, from initial draft to polished manuscript.
New research reveals that effective collaboration with artificial intelligence in building management hinges less on specialized knowledge and more on the ability to communicate effectively with the system.
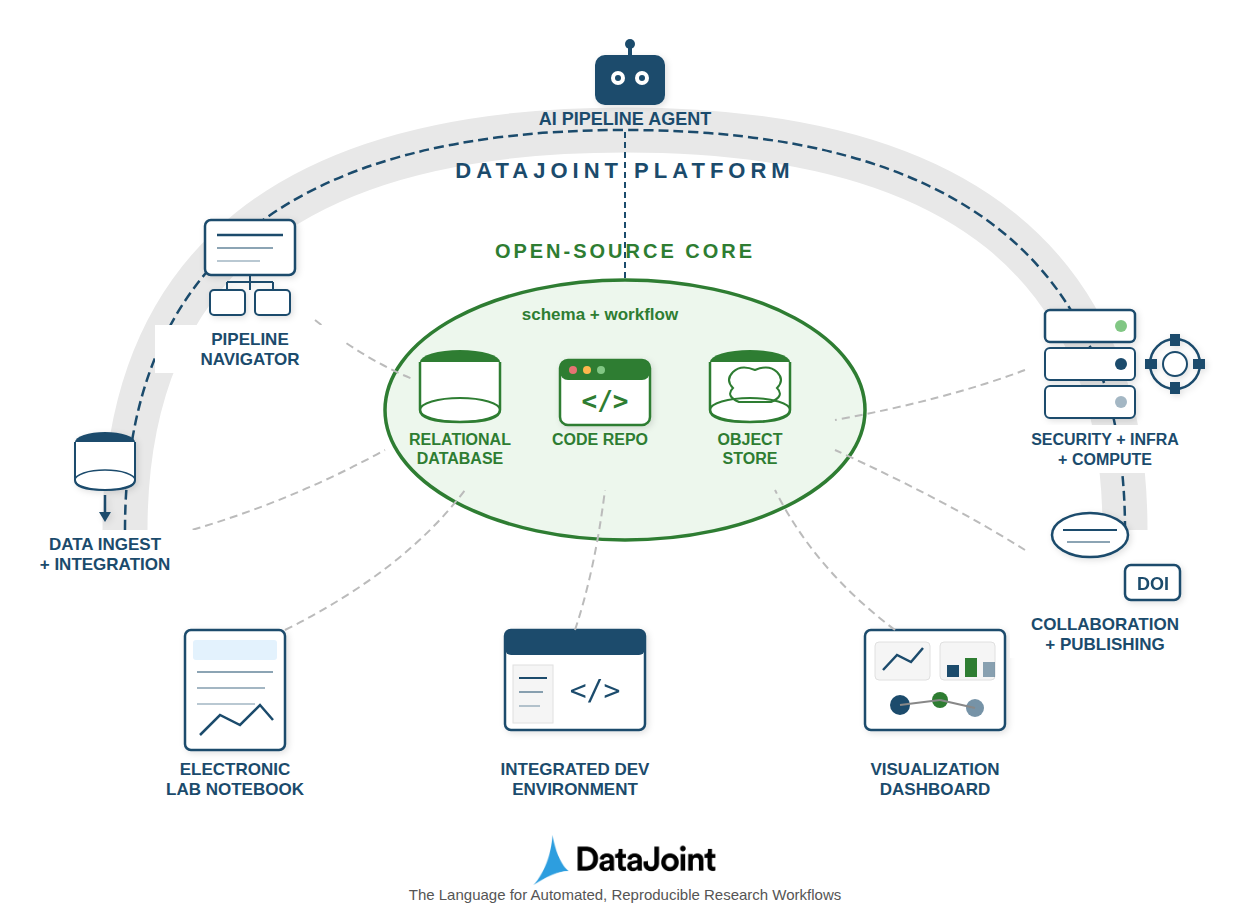
A new framework unifies data and computation, empowering researchers to create reliable and scalable scientific workflows.
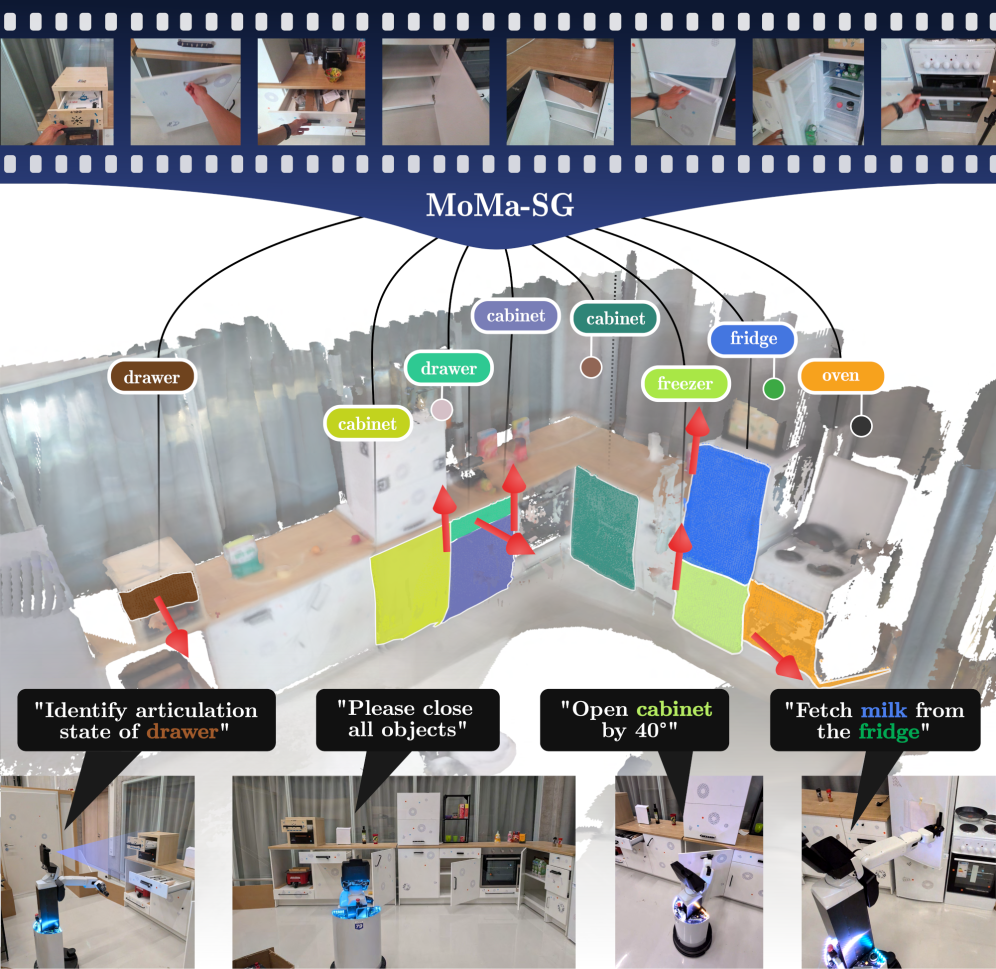
Researchers have developed a new framework allowing mobile robots to create detailed 3D representations of environments, focusing on how objects move and connect.
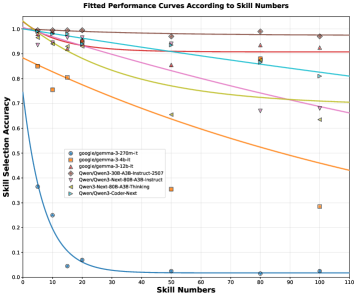
This review explores how carefully crafted ‘skill frameworks’ unlock the potential of smaller language models for complex tasks in real-world industrial settings.

Researchers have successfully trained reinforcement learning agents to manipulate and unfold cloth in real-time, bridging the gap between simulation and real-world robotics.
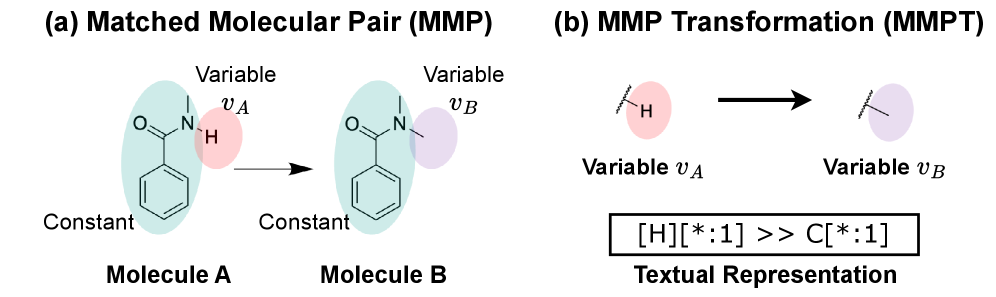
A new approach uses artificial intelligence to predict how changing a molecule’s structure will affect its properties, accelerating the search for better drug candidates.
Researchers have developed a new system enabling robots to actively adjust onboard illumination, dramatically improving their ability to map and navigate complex environments.
A new study investigates whether artificial intelligence can effectively assist novices performing complex biological experiments.
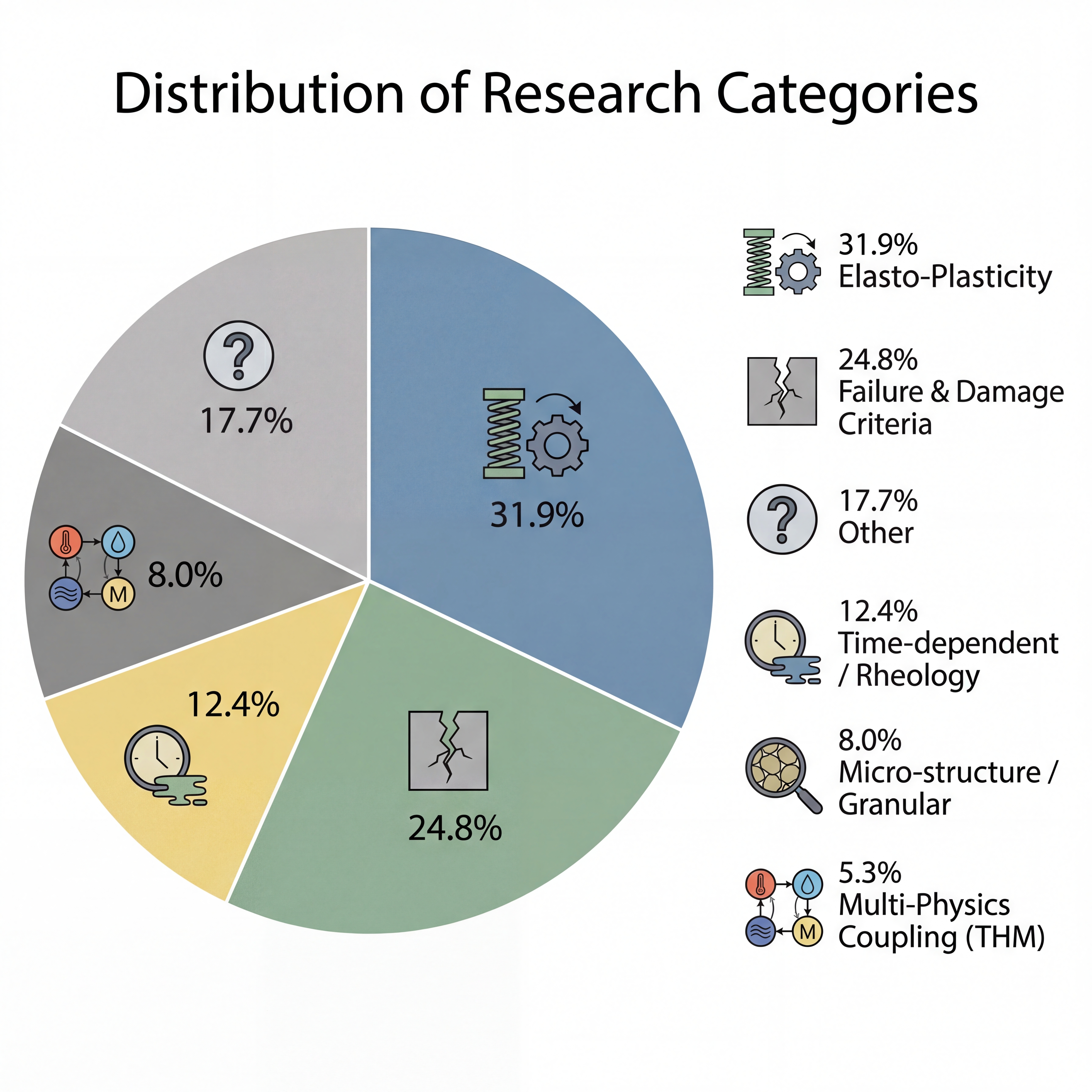
A new workflow automatically extracts material properties from scientific literature, offering a powerful tool for more accurate and efficient cultural heritage conservation.