Robotic Camera Work: Learning Smooth Motion from Human Demonstrations
![The IRIS system cultivates cinematic robot motion by grounding design in task objectives and nurturing a policy-trained solely on real human demonstrations-that seamlessly transfers from simulation to physical execution through a ROS-based control stack and [latex] goal-conditioned [/latex] imitation learning, anticipating future limitations inherent in any engineered system.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17537v1/x2.png)
Researchers have developed a low-cost, 3D-printed robot arm capable of replicating complex camera movements by learning directly from expert cinematographers.
![The IRIS system cultivates cinematic robot motion by grounding design in task objectives and nurturing a policy-trained solely on real human demonstrations-that seamlessly transfers from simulation to physical execution through a ROS-based control stack and [latex] goal-conditioned [/latex] imitation learning, anticipating future limitations inherent in any engineered system.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17537v1/x2.png)
Researchers have developed a low-cost, 3D-printed robot arm capable of replicating complex camera movements by learning directly from expert cinematographers.
A new analysis reveals that generative AI isn’t just processing information, but actively exploring a high-dimensional space to create knowledge in a fundamentally geometric way.
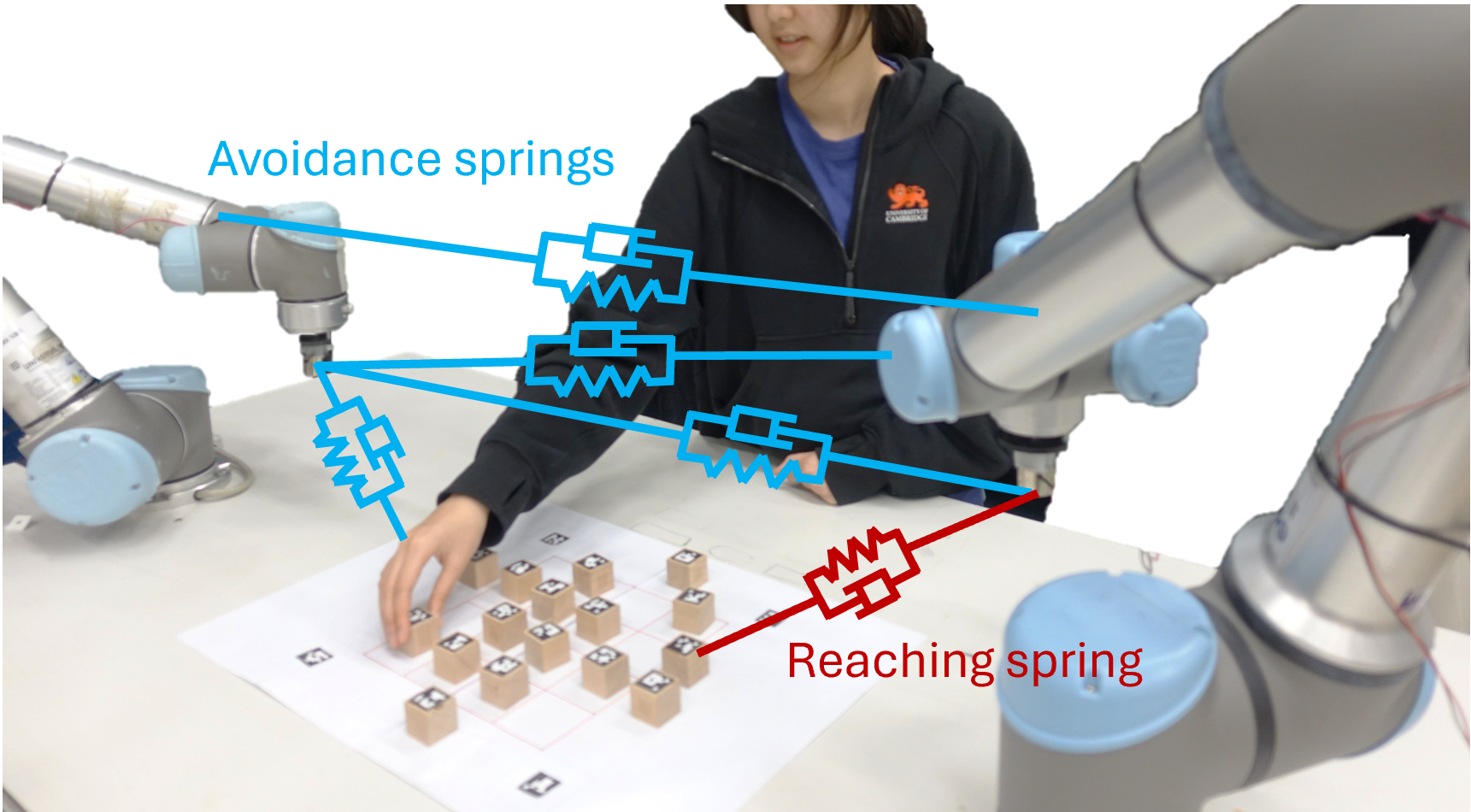
A new framework enables robots and humans to safely and efficiently share workspaces by prioritizing conflict resolution through decentralized control.
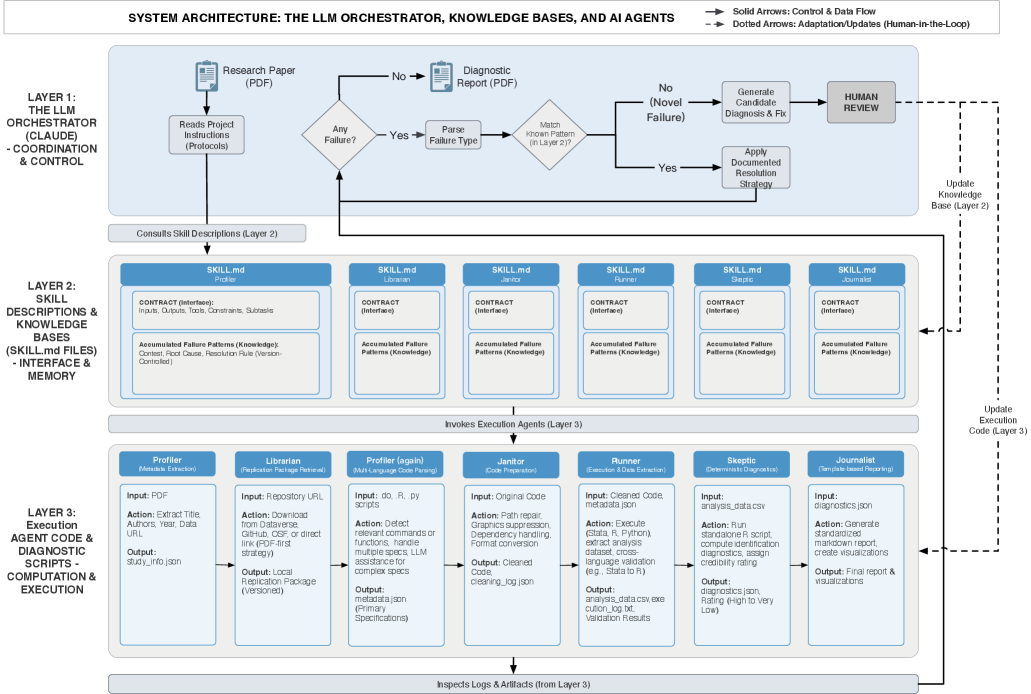
A new workflow leverages artificial intelligence to automate the complex process of reanalyzing empirical social science research, addressing critical challenges in verification and scaling.
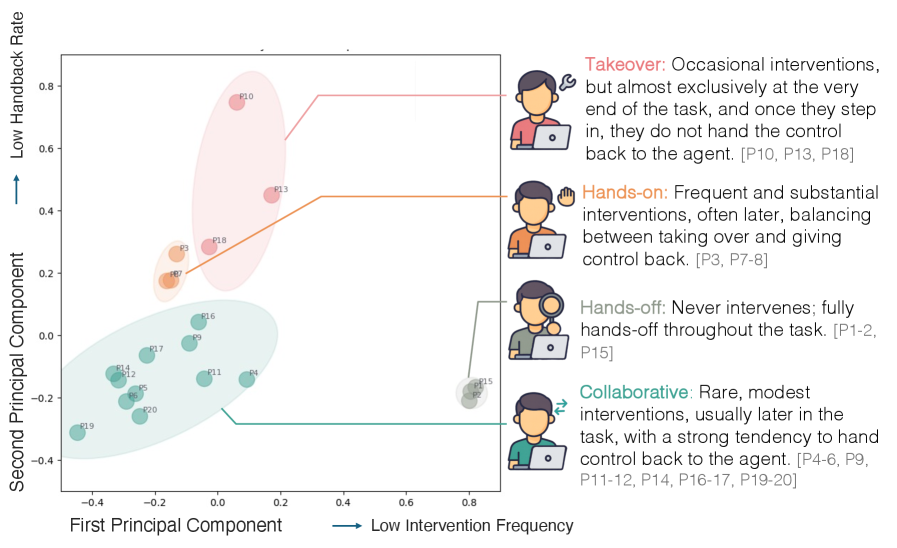
New research introduces a comprehensive dataset of human-computer web interactions designed to improve AI’s ability to predict when human assistance is required.
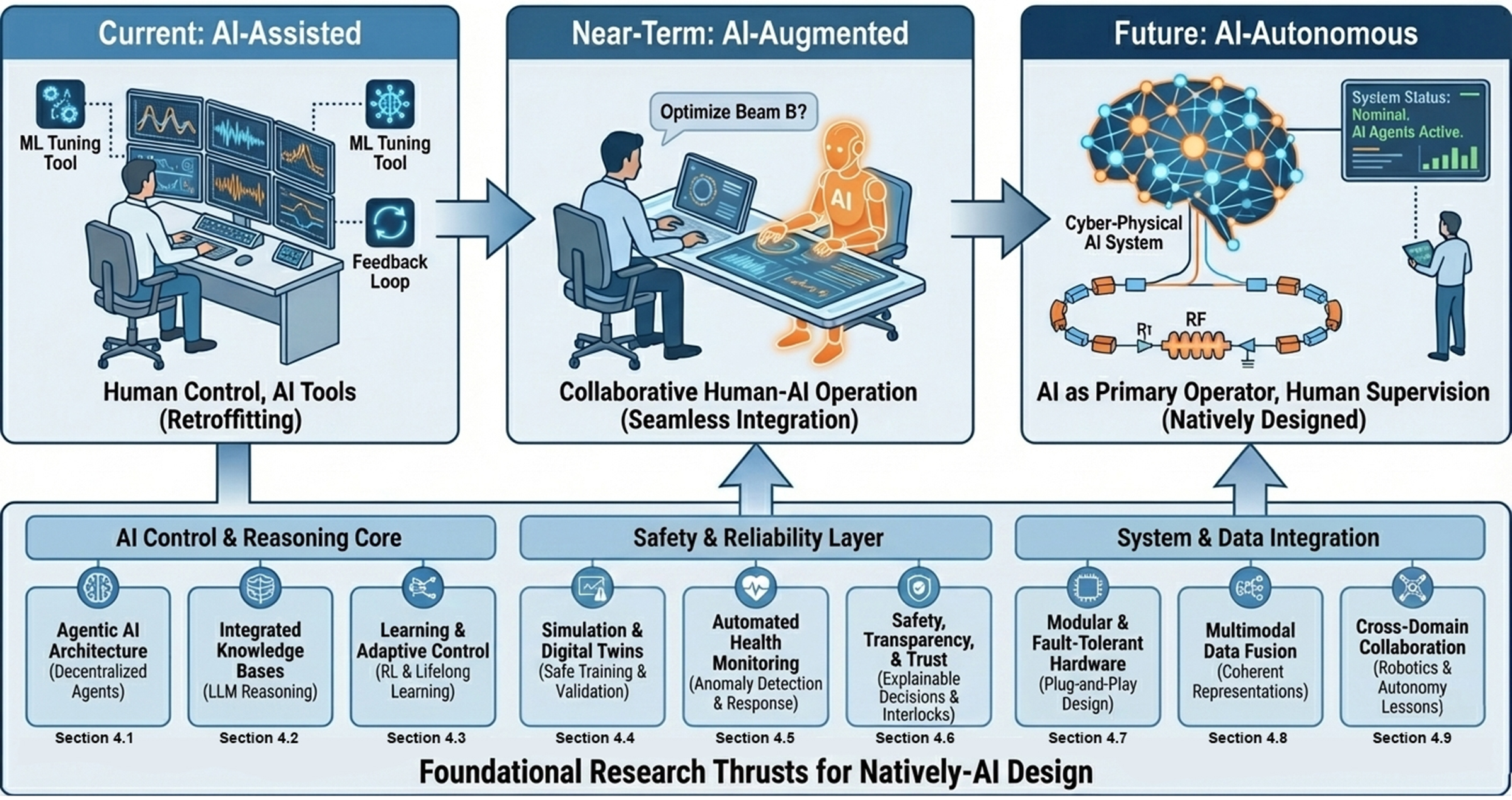
A new vision for particle physics facilities proposes shifting control from human operators to intelligent AI systems, promising greater efficiency and adaptability.
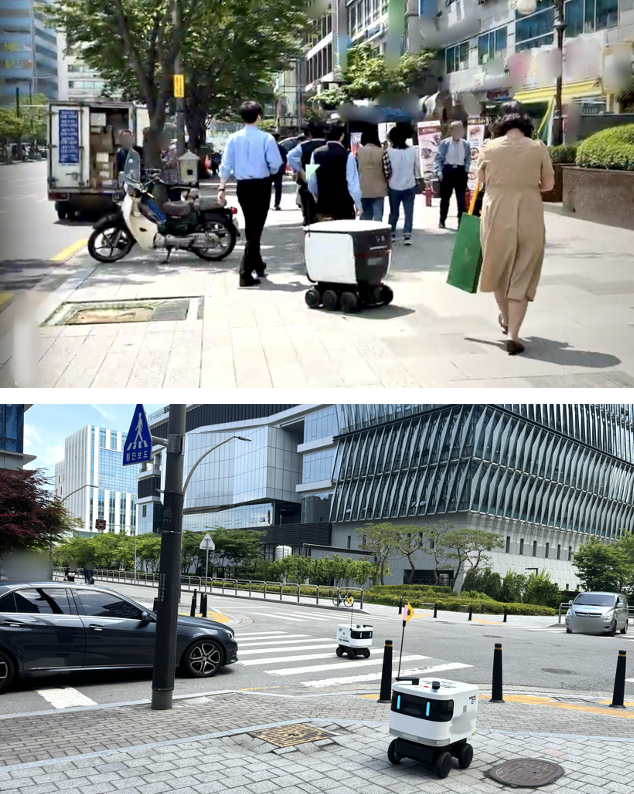

As autonomous delivery robots become increasingly common in cities, understanding how they navigate complex public spaces and interact with people is crucial.
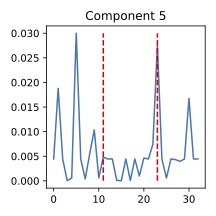
A new pipeline leverages the power of artificial intelligence to automate and accelerate the analysis of animal behavior, offering a deeper understanding of complex neural processes.
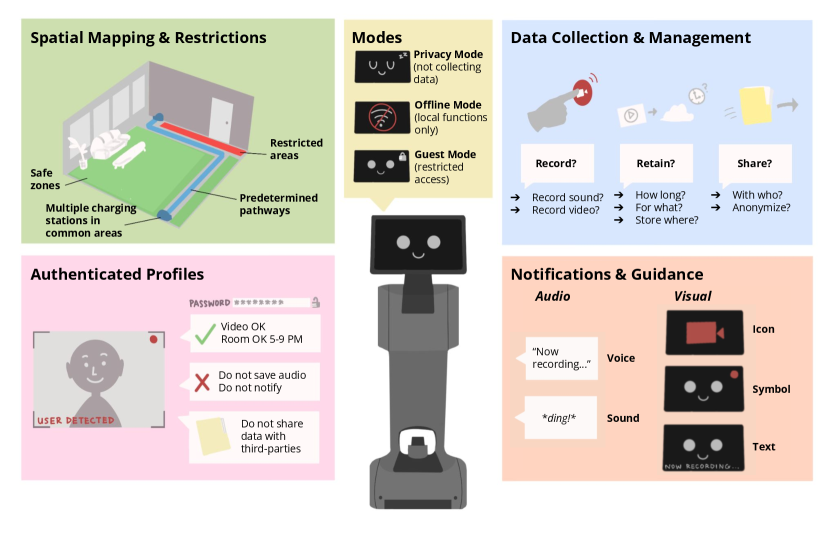
As household robots become more commonplace, understanding how families balance convenience with data privacy is crucial for responsible design and adoption.
A new study explores how AI agents can move beyond simple task completion to actively collaborate with researchers in the humanities and social sciences.