Author: Denis Avetisyan
This review explores how strategically coordinating artificial intelligence agents can dramatically improve the energy efficiency and security of modern wireless communication systems.
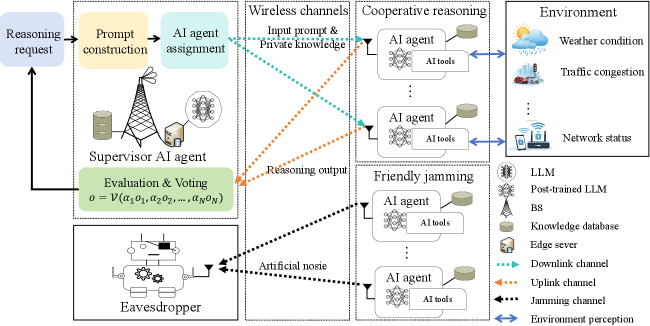
Novel resource allocation schemes are presented for secure wireless agentic AI networks, minimizing energy consumption while maintaining quality of service for cooperative reasoning tasks.
Achieving both robust security and energy efficiency remains a significant challenge in increasingly complex wireless artificial intelligence deployments. This paper introduces a novel framework for ‘Secure and Energy-Efficient Wireless Agentic AI Networks’-a system leveraging dynamic agent selection and cooperative reasoning to minimize energy consumption while upholding quality of service and confidentiality. By jointly optimizing agent allocation, beamforming, and transmission power-and employing both conventional optimization techniques and large language model-based approaches-we demonstrate up to a 59.1% reduction in network energy usage. Could this agentic architecture pave the way for sustainable and scalable AI solutions in resource-constrained environments?
The Evolving Landscape of Wireless Intelligence
Contemporary wireless networks, initially designed for straightforward data transmission, now face substantial challenges supporting the evolving demands of artificial intelligence. Modern AI applications, particularly those involving complex reasoning and environmental interaction, require more than just bandwidth; they necessitate consistent low latency, reliable connectivity, and the capacity to process information at the network edge. Traditional architectures struggle to accommodate these requirements due to their centralized control and static resource allocation, leading to performance bottlenecks and an inability to adapt to the dynamic and unpredictable nature of AI workloads. This mismatch hinders the deployment of sophisticated AI solutions in real-world scenarios, limiting their potential to deliver truly intelligent and responsive services.
Agentic AI represents a significant departure from conventional artificial intelligence, moving beyond simple task completion to systems capable of perceiving their surroundings and independently executing complex goals. This new approach is largely driven by the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), which provide the reasoning and planning abilities necessary for autonomous operation. However, realizing the full potential of agentic systems requires addressing substantial deployment challenges; the computational intensity of LLMs, coupled with the need for real-time responsiveness, necessitates innovative strategies for resource allocation and efficient execution. Successfully overcoming these hurdles will be crucial to unlock a future where AI agents can seamlessly integrate into and operate within dynamic, real-world environments, offering truly intelligent automation and proactive problem-solving.
WirelessAgenticAI represents a significant evolution in intelligent networking by distributing agentic systems-powered by Large Language Models-directly into wireless environments. This innovative approach moves beyond centralized cloud processing, instead leveraging the computational resources available at the network edge – think base stations, routers, and even user devices. By processing data closer to its source, WirelessAgenticAI dramatically reduces latency and improves responsiveness, crucial for time-sensitive applications like autonomous vehicles or real-time robotics. Furthermore, this distributed architecture enhances scalability; as demand increases, the system can readily expand by incorporating additional edge resources, avoiding the bottlenecks associated with centralized infrastructure and creating a more robust and adaptable wireless intelligence solution.
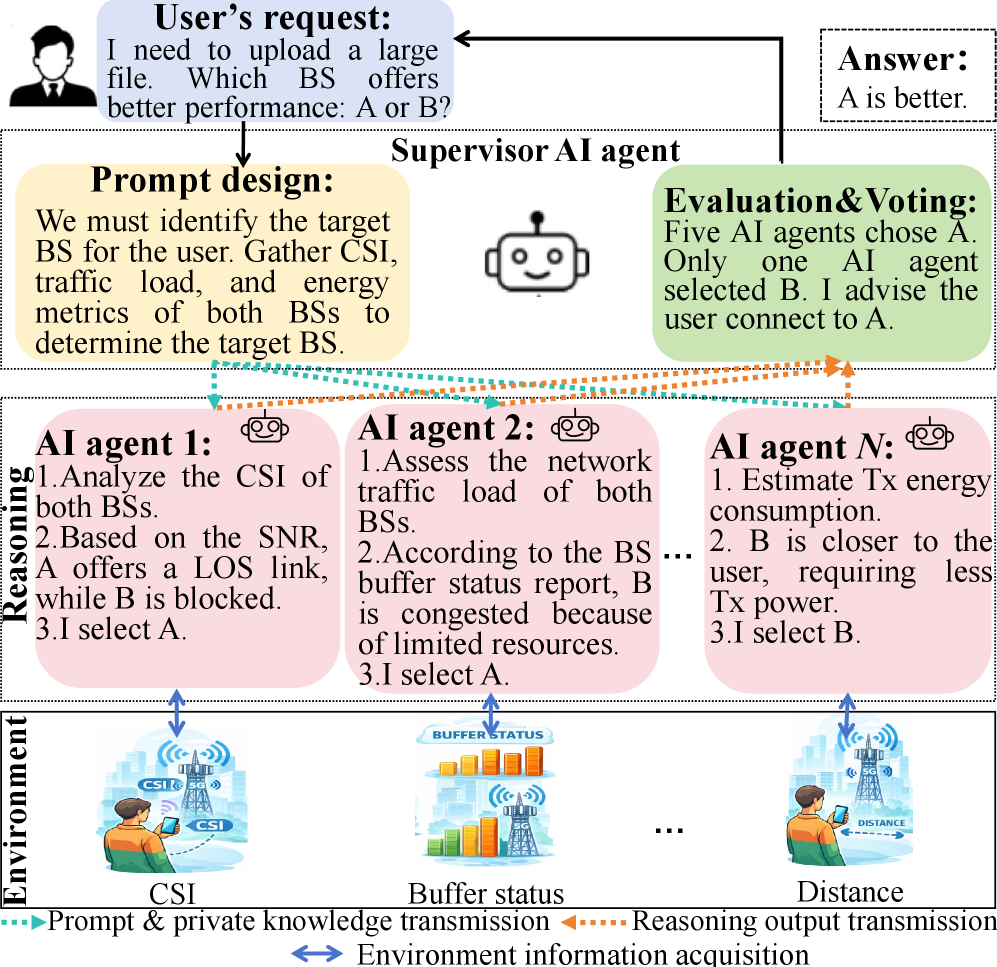
Optimized Efficiency: Minimizing Energy Expenditure
Minimizing energy consumption in wireless networks is a critical design objective due to the limited battery life of mobile devices and the increasing density of wireless deployments. Maintaining acceptable Quality of Service (QoS) – encompassing metrics such as data rate, latency, and packet loss – is equally important and cannot be compromised in the pursuit of energy savings. These competing demands necessitate careful resource allocation strategies that balance performance with power efficiency. Wireless network operators and device manufacturers prioritize designs that extend operational lifespan and reduce the environmental impact of wireless communications, driving research and development into energy-efficient protocols and hardware.
The WirelessAgenticAI framework incorporates an EnergyMinimization function focused on dynamic resource allocation to reduce overall power consumption. This optimization process targets transmission energy specifically, achieving a measured consumption of 1.19 x 104 J. The system achieves this level of efficiency by intelligently managing network resources based on real-time demands and constraints, prioritizing energy conservation without compromising network performance metrics. This measured energy consumption represents a key performance indicator for evaluating the system’s efficacy in power management.
The system achieves reduced energy consumption by employing advanced optimization algorithms to address the inherent complexity of wireless resource allocation. Specifically, Successive Convex Approximation (SCA) and Semidefinite Relaxation (SDR) are utilized to convert the non-convex problem into a series of convex subproblems that can be solved efficiently. SCA iteratively refines the solution through local convex approximations, while SDR relaxes the problem by representing variables as positive semidefinite matrices, enabling the application of convex optimization techniques. Comparative analysis demonstrates that this algorithmic approach consistently yields lower energy consumption than conventional resource allocation schemes, providing a quantifiable improvement in network efficiency.
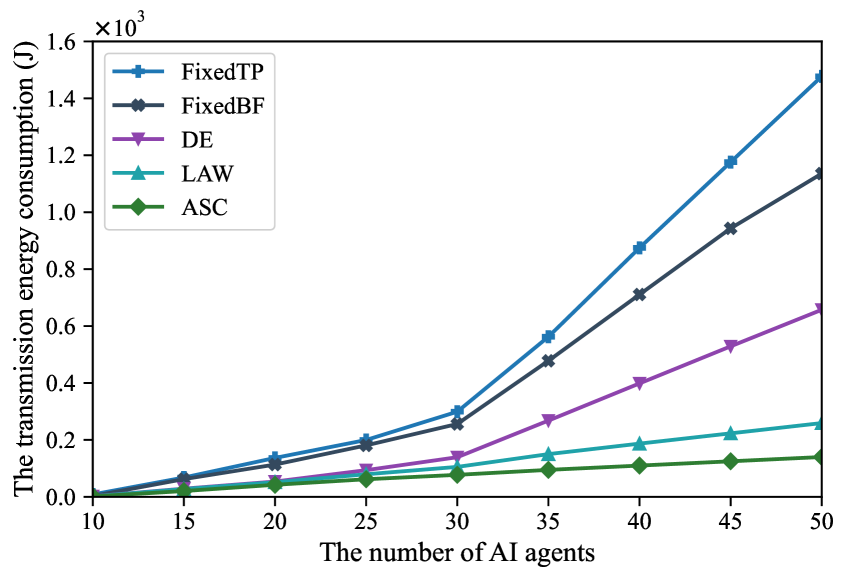
Scalable Coordination: An Algorithm for Agent Harmony
The Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) serves as a foundational element within the Algorithm for Scalable Coordination (ASC) due to its capacity to decompose a centralized optimization problem into smaller, more manageable subproblems. This decomposition facilitates parallel processing and allows for distributed computation across multiple agents, improving scalability. Specifically, ADMM iteratively solves these subproblems and coordinates solutions via dual variable updates, effectively handling the constraints inherent in resource allocation. The method is particularly well-suited to scenarios involving a large number of agents and complex interdependencies, providing a computationally efficient approach to achieving a globally optimal or near-optimal solution.
The Algorithm for Scalable Coordination (ASC) addresses non-convex optimization problems in multi-agent systems by integrating the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM), Successive Convex Approximation (SCA), and a specialized resource allocation strategy. This combined approach facilitates efficient distribution of resources among agents, resulting in a measured execution energy consumption of 1.19 x 104 Joules when operating with a network size of N=30 agents. The efficacy of this method stems from ADMM’s ability to decompose the global problem into smaller, manageable subproblems, while SCA iteratively refines the solution by approximating the non-convex objective function with a series of convex relaxations.
AgentSelection is a critical component of the agentic system’s performance, directly influencing reasoning accuracy. The process involves identifying and deploying AI agents specifically suited to individual reasoning tasks, rather than relying on a single, generalized agent. This targeted approach has demonstrated reasoning accuracies of 85% when evaluated on the ARC-E (Everyday Common Sense Reasoning) and ARC-C (Commonsense Reasoning) benchmarks. Incorrect agent assignment, or the lack of specialized agents, will negatively impact the system’s ability to solve complex problems and achieve optimal results.
Fortified Networks: Securing Communication Through Interference
FriendlyJamming represents a paradigm shift in securing the WirelessAgenticAI network against unauthorized access. Rather than relying solely on encryption or complex authentication protocols, this system proactively disrupts potential eavesdropping attempts through calculated interference. The core innovation lies in repurposing unselected agents – those not currently engaged in primary tasks – to generate targeted radio frequency noise. This noise, while seemingly disruptive, is carefully calibrated to obscure sensitive communications from unintended recipients without significantly impacting the reliability of legitimate data transfer. By essentially creating a ‘digital smokescreen’ around critical exchanges, FriendlyJamming offers a dynamic and adaptable layer of security, continuously evolving alongside the network’s operational needs and presenting a substantial challenge to passive listening attempts.
The system proactively safeguards sensitive communications through a technique called FriendlyJamming, which leverages the network’s unselected agents as a dynamic interference source. Rather than relying solely on encryption or access control, this approach introduces carefully calibrated noise to disrupt potential eavesdropping attempts. Unselected agents, those not currently engaged in primary tasks, are strategically activated to transmit signals that mask legitimate communications, making it significantly more difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept and decode data. This method is particularly effective against passive attacks, where adversaries attempt to monitor network traffic without actively disrupting it, and offers a layer of security that complements existing encryption protocols, enhancing the overall resilience of the WirelessAgenticAI network against malicious interference.
The integration of FriendlyJamming isn’t simply an add-on, but rather a foundational element bolstering the entire WirelessAgenticAI system’s architecture. By proactively addressing potential eavesdropping, this security measure directly supports the platform’s ongoing optimization processes – ensuring that gains in efficiency and responsiveness aren’t undermined by vulnerabilities. This synergistic approach creates a demonstrably robust and secure environment, vital for the reliable deployment of complex agentic AI applications that demand both high performance and unwavering confidentiality. The resulting platform is poised to facilitate more sophisticated interactions and data exchanges, confidently navigating the inherent risks of a connected network.
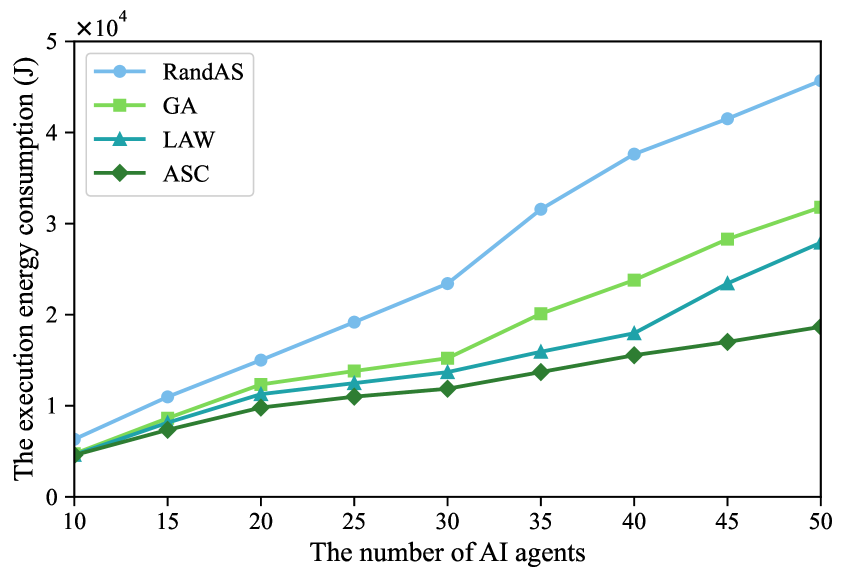
Validated Performance and Pathways to Future Advancement
Rigorous evaluation of the system’s reasoning abilities was conducted utilizing established benchmark datasets, notably ARC – which challenges understanding of scientific concepts – and BoolQ, focused on question answering requiring yes/no responses. Performance on these datasets serves as quantifiable evidence of the Qwen LLMs’ capacity for complex thought processes and effective knowledge retrieval. Results demonstrate not only the system’s ability to accurately answer questions, but also its potential to generalize these reasoning skills to novel, unseen scenarios, solidifying its position as a promising foundation for advanced artificial intelligence applications.
The performance of large language models isn’t simply a matter of algorithmic ingenuity; it’s fundamentally linked to the scale of both the model itself and the dataset used for training. This relationship is formalized by ScalingLaws, empirical principles revealing a predictable power-law correlation between model size, dataset size, and resulting performance on various tasks. Specifically, these laws demonstrate that increasing either parameter count or training data yields consistent improvements in language understanding and generation capabilities – with larger models generally exhibiting more robust reasoning and generalization abilities. Consequently, informed system design relies heavily on leveraging these principles to strategically allocate computational resources, optimize training procedures, and predict the performance gains achievable through scaling, ultimately leading to more efficient and capable LLMs.
The current framework is envisioned as a stepping stone towards increasingly sophisticated applications of agentic AI, with future investigations concentrating on deployment within more complex, real-world scenarios. Researchers aim to move beyond benchmark datasets and explore the potential of these large language models to autonomously manage and optimize wireless networks-a domain characterized by dynamic conditions and intricate interdependencies. This includes tackling challenges such as resource allocation, interference mitigation, and proactive network adaptation, potentially leading to self-optimizing wireless systems capable of delivering enhanced performance and reliability. Further exploration will also focus on extending the agent’s reasoning capabilities to handle multi-faceted objectives and integrate seamlessly with existing network infrastructure, paving the way for truly intelligent wireless environments.
The pursuit of optimized resource allocation within agentic AI networks, as detailed in the study, echoes a fundamental principle of elegant design. Hilbert posited, “We must be able to answer every question that can be formulated in the system.” This aligns directly with the paper’s focus on maximizing the efficiency of communication and reasoning – ensuring each agent receives necessary resources without waste. The study’s methodology, striving to minimize energy consumption while upholding quality of service, demonstrates an understanding that true intelligence isn’t about complexity, but about achieving the desired outcome with the least possible overhead. Every parameter, every allocation, must serve a demonstrable purpose, contributing to the network’s overall ability to respond to any given query.
Where Do We Go From Here?
The pursuit of efficient agentic networks, while seemingly pragmatic, reveals a deeper unease. This work attempts to sculpt order from inherent complexity, to dictate resource allocation as if predictability were a natural state. It succeeds, to a degree, but exposes the fundamental limitation: optimization is always of something, and that ‘something’ is invariably a simplification of reality. The true cost of minimized energy consumption is not merely measured in watts, but in the potential for unforeseen consequences arising from a constrained solution space.
Future effort should not focus on further refinement of allocation algorithms – the law of diminishing returns applies with brutal efficiency. Instead, attention must shift toward understanding the limits of agentic coordination. What classes of problems are fundamentally unsuitable for distributed reasoning? What metrics, beyond simple efficiency, truly capture the value of a cooperative AI? A relentless pursuit of optimization, without acknowledging these boundaries, risks building exquisitely efficient systems capable only of exquisitely efficient failures.
Ultimately, the question is not whether these networks can be made more efficient, but whether that efficiency serves a purpose beyond its own existence. The elegance of a solution is meaningless if the problem itself was poorly defined. Perhaps the most fruitful avenue for research lies not in improving the tools, but in questioning the necessity of building them in the first place.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.15212.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- MLBB x KOF Encore 2026: List of bingo patterns
- Overwatch Domina counters
- eFootball 2026 Jürgen Klopp Manager Guide: Best formations, instructions, and tactics
- 1xBet declared bankrupt in Dutch court
- Brawl Stars Brawlentines Community Event: Brawler Dates, Community goals, Voting, Rewards, and more
- eFootball 2026 Starter Set Gabriel Batistuta pack review
- Honkai: Star Rail Version 4.0 Phase One Character Banners: Who should you pull
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Lana Del Rey and swamp-guide husband Jeremy Dufrene are mobbed by fans as they leave their New York hotel after Fashion Week appearance
- Clash of Clans March 2026 update is bringing a new Hero, Village Helper, major changes to Gold Pass, and more
2026-02-19 01:03