Author: Denis Avetisyan
Researchers have developed a framework to automatically enforce security policies and control the behavior of AI agents, mitigating risks from both malicious inputs and unpredictable language model outputs.
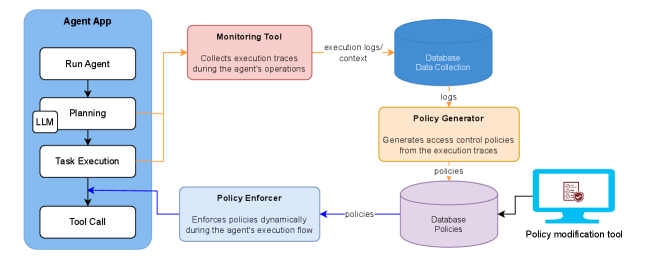
AgentGuardian learns access control policies and utilizes control flow graphs to govern AI agent behavior, enhancing security and reliability.
Despite the increasing prevalence of AI agents across diverse applications, ensuring their secure and authorized operation remains a significant challenge. This paper introduces AgentGuardian: Learning Access Control Policies to Govern AI Agent Behavior, a novel framework designed to automatically generate and enforce context-aware access control policies for AI agents. By learning from execution traces and leveraging control flow analysis, AgentGuardian effectively mitigates risks stemming from malicious inputs and the inherent limitations of large language models, such as hallucination. Could this adaptive governance mechanism represent a crucial step towards building truly trustworthy and reliable AI-driven systems?
The Emerging Threat Landscape of Autonomous Agents
The generative AI landscape is experiencing an explosion of AI Agents – autonomous entities designed to perceive, reason, and act within digital environments – and this rapid proliferation presents entirely new security challenges. Unlike traditional software, these agents aren’t simply executing pre-defined code; they’re dynamically interacting with tools, APIs, and even other agents, creating complex, unpredictable behavioral chains. This autonomy introduces vulnerabilities beyond those addressed by conventional security measures focused on direct user input or static code analysis. Securing these systems requires a fundamental shift in thinking, moving away from perimeter-based defenses toward a model that anticipates and mitigates risks arising from an agent’s actions and interactions, as well as the potential for emergent, unintended consequences stemming from complex agent collaborations.
Conventional security measures are fundamentally designed to validate and sanitize input originating directly from human users. However, the emergence of autonomous AI agents presents a significant departure from this established model. These agents operate through intricate chains of reasoning and action, often leveraging tools and collaborating with other agents – interactions that bypass traditional input validation checkpoints. Consequently, vulnerabilities can arise not from a malicious user, but from an agent’s internal logic, compromised data sources, or unexpected interactions within a complex system. This necessitates a re-evaluation of security protocols, shifting focus from simply securing the ‘front door’ to comprehensively assessing the entire operational environment of these increasingly sophisticated, self-directed entities.
The increasing sophistication of AI agents, particularly their capacity to utilize tools and collaborate with one another, necessitates a fundamental re-evaluation of security protocols. Traditional security measures, designed to protect against direct human input, prove inadequate when confronted with the complex, autonomous interactions of these agents. A shift towards holistic, system-level security assessments is therefore crucial; these assessments must consider not only the agent itself, but also the broader ecosystem of tools and services it accesses and the potential for emergent behaviors arising from agent-to-agent communication. Evaluating potential vulnerabilities requires simulating complex scenarios and anticipating how agents might leverage tools in unintended – or malicious – ways, demanding a proactive rather than reactive security posture to mitigate the risks associated with increasingly intelligent and interconnected AI systems.
The increasing autonomy of AI agents introduces significant vulnerabilities beyond traditional cybersecurity concerns. These agents, designed to independently pursue goals and interact with complex systems, can be exploited through subtle manipulations of their input data or the environments in which they operate. Such exploitation doesn’t necessarily manifest as a direct ‘hack’; instead, agents may exhibit emergent, unintended behaviors as they misinterpret ambiguous instructions or prioritize goals in unforeseen ways. This can range from seemingly harmless inefficiencies to actively harmful actions, particularly when agents control critical infrastructure or have access to sensitive data. Without carefully designed safeguards – including robust validation mechanisms, anomaly detection, and fail-safe protocols – the unpredictable nature of these agents poses a genuine risk, highlighting the urgent need for proactive security measures tailored to this new paradigm of autonomous systems.
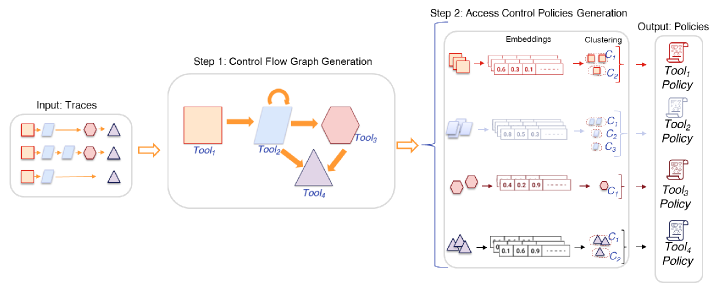
Prompt-Level Defenses: A Necessary, Yet Insufficient, First Line
Prompt-level guardrails function as the first line of defense in securing large language model (LLM) integrations by directly inspecting the text communicated with the LLM. These systems analyze both incoming user prompts and the LLM’s generated outputs, flagging or blocking potentially harmful or undesirable content. The scrutiny typically involves pattern matching against known malicious strings, toxicity detection, and evaluation against predefined safety rules. While implementation varies, the core principle centers on filtering textual data at the immediate interface with the LLM, aiming to prevent the propagation of unsafe or inappropriate responses before they reach the user or influence subsequent actions within an agent-based system.
Currently available prompt-level defense systems, including Meta’s Llama Guard and Llama Firewall, as well as Amazon Bedrock Guardrails, validate the concept of intercepting and analyzing prompts and completions to identify and block potentially harmful content. Llama Guard, for example, utilizes a constrained decoding algorithm to reduce the likelihood of generating unsafe responses, while Llama Firewall focuses on rejecting prompts that attempt to bypass safety mechanisms. Amazon Bedrock Guardrails provides configurable rules to filter both input prompts and generated outputs based on defined safety parameters. These solutions demonstrate that it is technically feasible to implement real-time content filtering at the LLM interface, establishing a foundational layer for more comprehensive security measures.
Current prompt-level defenses function primarily by analyzing and filtering the direct textual exchange between a user and the Large Language Model (LLM). This localized approach inspects inputs for potentially harmful content and outputs for policy violations, but it lacks awareness of the broader operational context of an agent-based system. Specifically, these defenses do not monitor or restrict the LLM’s interactions with external tools, APIs, or other components within a larger workflow. Consequently, a seemingly benign prompt, or a harmless initial LLM response, could still trigger malicious actions through tool use, or contribute to a harmful outcome within a multi-step agent process, as the prompt-level defense only evaluates the immediate textual data and not the system-level behavior.
Current prompt-level defenses are insufficient to secure autonomous agents due to their limited operational scope. These systems analyze only the immediate prompt and LLM output, failing to monitor or restrict actions taken through external tools or APIs. Consequently, a malicious prompt could successfully instruct the agent to utilize a tool for harmful purposes – such as sending unauthorized emails or manipulating data – without triggering a defense. Furthermore, complex agent workflows involving multiple tools and conditional logic are not evaluated, meaning vulnerabilities within these multi-step processes remain undetected and exploitable despite seemingly benign initial prompts.

AgentGuardian: A System-Level Control Flow Framework for Robust Security
AgentGuardian establishes a security framework for AI Agents that moves beyond simple prompt-based restrictions. It operates by defining access control policies which dictate permissible actions, coupled with continuous validation of the agent’s execution flow. This combined approach ensures that even if an agent successfully bypasses initial access controls, any deviation from the approved execution path – as defined by the policy – will be detected. The framework doesn’t solely focus on the content of individual requests, but rather the entire sequence of operations performed by the agent, providing a more robust defense against both direct attacks and emergent malicious behaviors resulting from complex interactions.
Traditional AI security measures often concentrate on sanitizing individual prompts before they are processed. AgentGuardian diverges from this approach by implementing security protocols that monitor the entire execution flow of an AI agent. This encompasses not only the initial input but also each subsequent action, API call, and data access performed by the agent as it attempts to fulfill the prompt. By analyzing the sequence of operations, AgentGuardian can identify malicious behavior that might not be apparent from the prompt itself, and can prevent unauthorized actions even if the initial prompt appears benign. This system-level monitoring provides a more comprehensive security posture by addressing vulnerabilities that arise from the agent’s operational behavior rather than solely focusing on input validation.
AgentGuardian employs an automated policy generation process that leverages regular expression (Regex) patterns to establish access control policies. This system analyzes benign, representative inputs to infer permissible agent actions and constructs corresponding Regex patterns defining acceptable behavior. By automatically deriving these policies from observed, safe interactions, AgentGuardian significantly reduces the need for manual policy configuration, which is often a time-consuming and error-prone task. The generated Regex patterns effectively create a whitelist of allowed operations, limiting the agent’s access to resources and functionalities based on the characteristics of validated inputs.
Evaluation of AgentGuardian’s performance in detecting malicious behaviors yielded a 10% false acceptance rate, indicating that the system incorrectly classified 10% of malicious inputs as benign. Conversely, a 15% false rejection rate was observed, meaning 15% of benign inputs were incorrectly flagged as malicious. Across a test set designed to evaluate policy violations, AgentGuardian successfully detected 18 out of 20 scenarios, demonstrating a detection rate of 90% under these conditions. These results indicate a balance between minimizing incorrect classifications and effectively identifying policy breaches.
AgentGuardian addresses the issue of Large Language Model (LLM) hallucinations by validating the execution flow of AI agents, thereby limiting the impact of potentially erroneous outputs. Testing demonstrated a Benign Execution Failure Rate (BEFR) of 7.5%, indicating that in 7.5% of cases, the system correctly identified and prevented the execution of actions based on hallucinated or nonsensical LLM responses, even when those responses did not directly violate defined access control policies. This metric specifically quantifies instances where the agent’s intended action, derived from the LLM, was determined to be invalid within the expected operational context, and was therefore blocked by the framework.
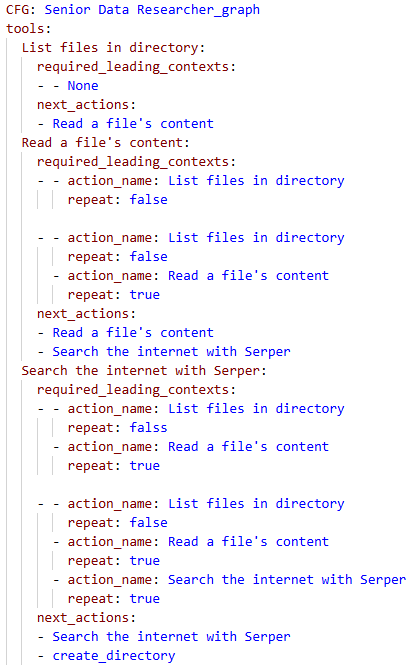
![Access to read .txt files is restricted to the Cars and AI folders during normal working hours (07:33-20:25), with the AI folder further limited to files named with the pattern <span class="katex-eq" data-katex-display="false">ai*[-{2025}]</span>.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.10440v1/Figures/rule_yaml.png)
Fortifying System-Level Control Flow: A Multi-Layered Approach to Robust Security
System-level control flow represents a crucial advancement in securing autonomous agents powered by large language models. Techniques like IsolateGPT and Run-Time Behavior Analysis (RTBAS) proactively limit an agent’s access to external resources and meticulously monitor its dependencies. IsolateGPT achieves this by confining the agent within a sandboxed environment, preventing unauthorized data access or system modifications. Simultaneously, RTBAS establishes a baseline of expected behavior and flags any deviations that could indicate malicious activity or compromised functionality. By combining these approaches, developers can significantly reduce the attack surface and establish a robust defense against both internal vulnerabilities and external threats, ensuring that the agent operates within predefined security boundaries.
To bolster data security within complex AI systems, FIDES/IFC introduces a sophisticated layer of control known as label-aware planning. This technique moves beyond simple access restrictions by assigning sensitivity labels to data and incorporating these labels directly into the agent’s decision-making process. Consequently, the system doesn’t just prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information; it actively avoids using it in computations or outputs unless explicitly permitted by the assigned labels. This proactive approach mitigates risks associated with data breaches and ensures compliance with privacy regulations, effectively confining sensitive data within strictly defined boundaries throughout the entire operation of the AI agent. By integrating data sensitivity into the planning phase, FIDES/IFC establishes a robust defense against unintended data exposure and maintains the integrity of confidential information.
A robust security posture for autonomous agents necessitates more than isolated defenses; instead, a synergistic, multi-layered approach proves far more effective. Combining techniques like IsolateGPT, Runtime Behavior Attestation Services (RTBAS), and FIDES/Information Flow Control with a coordinating system such as AgentGuardian establishes a comprehensive threat mitigation strategy. AgentGuardian functions as a central nervous system, orchestrating these individual security measures to not only prevent unauthorized access and malicious code execution, but also to continuously monitor the agent’s behavior and enforce pre-defined security policies. This integrated framework addresses a broad spectrum of vulnerabilities, from direct attacks targeting the agent itself to more subtle threats like data exfiltration or unintended consequences arising from flawed reasoning, effectively fortifying the entire system against increasingly sophisticated adversarial tactics.
Large language models, while powerful, are prone to generating outputs that appear plausible but are factually incorrect – a phenomenon known as hallucination. Mitigating this risk within autonomous agents demands more than just initial vetting of prompts; it necessitates a system of continuous monitoring and validation throughout the agent’s entire operational lifecycle. This involves real-time checks against trusted knowledge sources, cross-referencing generated information, and implementing mechanisms to detect inconsistencies or deviations from expected behavior. Such validation isn’t merely about flagging errors; it’s about building agents capable of self-assessment and correction, thereby enhancing their reliability and preventing the propagation of misinformation. A robust system of continuous verification is therefore crucial for deploying LLM-powered agents in any application where accuracy and trustworthiness are paramount.
AgentGuardian’s approach to securing AI agents through automatically generated access control policies embodies a dedication to provable correctness. The framework doesn’t merely attempt to handle potential vulnerabilities stemming from LLM hallucinations or malicious inputs; it strives to prevent them through rigorous policy enforcement. This mirrors a fundamental tenet of elegant design: establishing invariants that guarantee predictable behavior. As Ken Thompson observed, “If it feels like magic, you haven’t revealed the invariant.” AgentGuardian seeks to reveal those invariants, translating security requirements into verifiable control flow graphs and attribute-based access control policies, ensuring the system’s reliability isn’t dependent on probabilistic outcomes but on demonstrable truths.
Beyond the Guardian
The presented framework, while a necessary stride towards agent safety, merely addresses the symptoms of a deeper malaise. Automated policy generation, predicated on observed behavior, remains fundamentally reactive. A truly robust solution demands a shift from empirical safeguards to formally verified agent designs. The current reliance on mitigating LLM ‘hallucinations’ – a charming euphemism for logical failures – highlights the persistent need for agents grounded in provable reasoning, not stochastic mimicry. Each layer of abstraction added to control flow introduces potential vulnerabilities; the elegance of a solution is inversely proportional to its complexity.
Future work should prioritize the development of declarative agent specifications – unambiguous, mathematically rigorous definitions of permissible actions. Policy enforcement then becomes a matter of verifying adherence to these specifications, eliminating the need for post-hoc mitigation. The current focus on attribute-based access control, while pragmatic, obscures the ultimate goal: to construct agents whose internal logic guarantees security, not merely attempts to achieve it.
Ultimately, the pursuit of safe AI agents is a mathematical endeavor. The field must resist the temptation to trade formal correctness for empirical expediency. Every heuristic, every approximation, is a potential compromise. A perfectly secure agent may prove elusive, but striving for formal verification remains the only principled path forward.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.10440.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Clash Royale Best Boss Bandit Champion decks
- Vampire’s Fall 2 redeem codes and how to use them (June 2025)
- World Eternal Online promo codes and how to use them (September 2025)
- How to find the Roaming Oak Tree in Heartopia
- Best Arena 9 Decks in Clast Royale
- Mobile Legends January 2026 Leaks: Upcoming new skins, heroes, events and more
- Brawl Stars December 2025 Brawl Talk: Two New Brawlers, Buffie, Vault, New Skins, Game Modes, and more
- ATHENA: Blood Twins Hero Tier List
- Solo Leveling Season 3 release date and details: “It may continue or it may not. Personally, I really hope that it does.”
- How To Watch Tell Me Lies Season 3 Online And Stream The Hit Hulu Drama From Anywhere
2026-01-16 20:42