Author: Denis Avetisyan
Researchers are exploring ways to imbue large language models with more human-like cognitive patterns to create more realistic and engaging AI characters.
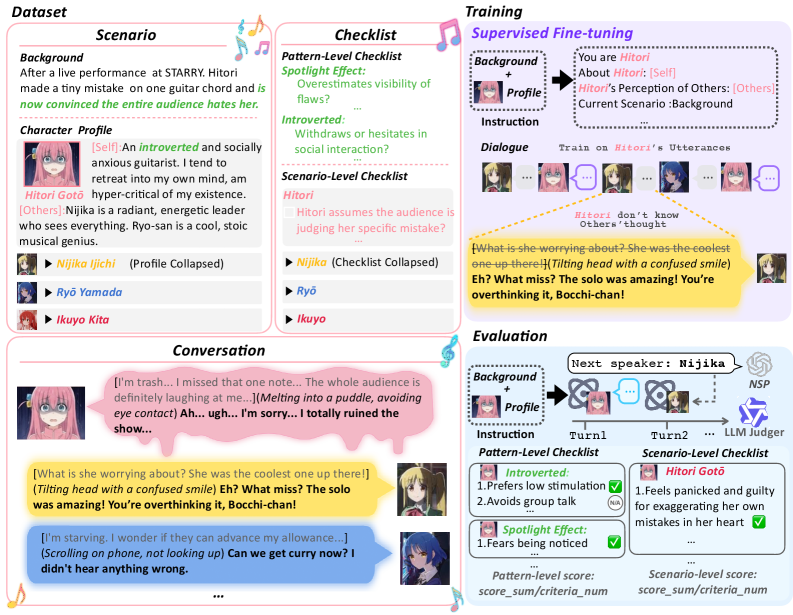
This paper introduces HumanLLM, a framework for benchmarking and reinforcing anthropomorphism in large language models via scenario-based training and the application of human cognitive patterns.
While Large Language Models excel at generating text, truly authentic human-like behavior remains a significant challenge. This is addressed in ‘HUMANLLM: Benchmarking and Reinforcing LLM Anthropomorphism via Human Cognitive Patterns’, which introduces a framework treating psychological patterns as interacting causal forces to enhance LLM realism. By synthesizing over 11,000 scenarios and utilizing a dual-level evaluation checklist, the authors demonstrate that modeling underlying cognitive processes-not just observed actions-improves alignment with human behavior and reveals limitations in holistic evaluation metrics. Could this approach unlock more nuanced and believable characters in artificial intelligence, moving beyond superficial imitation towards genuine psychological simulation?
The Illusion of Agency: Deconstructing LLM Role-Playing
Large language models demonstrate a remarkable ability to simulate human dialogue, constructing grammatically correct and contextually relevant responses with impressive speed. However, this proficiency frequently plateaus at the surface level of interaction, failing to convincingly portray the complex inner lives that drive believable characters. While an LLM can accurately reproduce conversational patterns associated with a specific persona – adopting a particular tone, vocabulary, or even stated preferences – it struggles to consistently manifest the underlying psychological motivations, emotional nuances, and cognitive biases that would inform a character’s choices in nuanced situations. This results in role-playing experiences that, while often coherent, can feel fundamentally hollow, lacking the unpredictable, internally consistent behavior characteristic of genuine human agency and leaving users with the impression of a skillfully crafted imitation rather than a truly dynamic and engaging character.
Current evaluations of large language model role-playing capabilities, such as those utilizing the LifeChoice, CroSS-MR, and CoSER benchmarks, predominantly assess a chatbot’s ability to maintain a consistent persona and logical dialogue flow. However, these metrics often fail to probe the why behind a character’s actions – the underlying motivations, emotional responses, and cognitive biases that drive believable behavior. A chatbot might successfully respond in character, but its choices can feel arbitrary or lack the internal consistency expected of a human agent grappling with complex situations. This emphasis on surface-level coherence allows models to ‘pass’ as convincingly human without actually demonstrating an understanding of psychological principles or the nuanced reasoning that underpins genuine role-playing, revealing a critical gap in current evaluation methodologies.
The shallowness of current large language models in role-playing isn’t simply a matter of imperfect imitation; it reflects a fundamental disconnect from the complex underpinnings of human psychology. These models, trained on vast datasets of text, primarily learn patterns of language rather than the cognitive and emotional processes that drive believable behavior. Consequently, responses often lack internal consistency, failing to account for established principles like cognitive dissonance, emotional regulation, or the influence of past experiences on present actions. Without incorporating frameworks from psychology – such as attachment theory, goal-oriented behavior, or models of moral reasoning – LLMs remain skilled at appearing responsive, but unable to convincingly simulate the nuanced, internally-driven motivations that characterize genuine human interaction. This absence of psychological grounding limits their ability to navigate complex scenarios with the believability necessary for truly immersive role-playing experiences.
HumanLLM: A Foundation for Psychologically Consistent AI
HumanLLM employs Kurt Lewin’s Field Theory, which posits behavior as a function of the person and their environment (B = f(P, E)), to establish a contextual basis for character actions. This is integrated with the DIAMONDS model – comprising Disposition, Information, Arousal, Motivation, Output, and Dynamics – to simulate the cognitive processes influencing decision-making. By representing character traits as dispositions, current situation as information, emotional state as arousal, and underlying needs as motivation, the framework generates outputs-actions-shaped by the interplay of these factors and their dynamic shifts over time. This approach moves beyond simple stimulus-response mechanisms by modeling the psychological forces acting on a character within a given environment, resulting in more plausible and consistent motivations.
Current large language models (LLMs) often produce responses lacking consistent internal motivation. HumanLLM addresses this by integrating established psychological frameworks, specifically the Big Five personality traits – Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism – to define character profiles. Beyond static traits, the framework also incorporates Social-Cognitive Patterns, such as the Ultimate Attribution Error, which describes the tendency to attribute others’ negative behaviors to their disposition while attributing one’s own to situational factors. This allows for the simulation of biased reasoning and more realistic, context-dependent responses, moving beyond purely generative output towards behavior grounded in modeled psychological principles.
HumanLLM employs Psychological Cognitive Patterns as the primary mechanism for establishing character consistency. These patterns, derived from established psychological research, define how a character perceives, interprets, and reacts to stimuli within various contexts. Rather than relying on explicitly programmed responses, the framework uses these patterns to dynamically generate behavior, ensuring actions are congruent with the character’s established cognitive biases and tendencies, even when presented with novel situations. This approach facilitates nuanced behavior by modeling predictable irrationalities and variations in judgment, leading to more believable and engaging character interactions across diverse scenarios.

Quantifying Believability: Supervised Fine-Tuning and Evaluation Metrics
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) was implemented to enhance the Large Language Model’s (LLM) performance in both following instructions and adhering to established psychological principles. This process utilized the OpenThoughts dataset, a resource specifically designed to provide examples of human-like reasoning and behavior. By training the LLM on this dataset, the model learns to better interpret and respond to complex prompts while simultaneously increasing its alignment with expected psychological realism. The SFT methodology directly addresses limitations in base LLM performance related to nuanced instruction-following and the generation of psychologically plausible responses, improving the overall quality and believability of the model’s outputs.
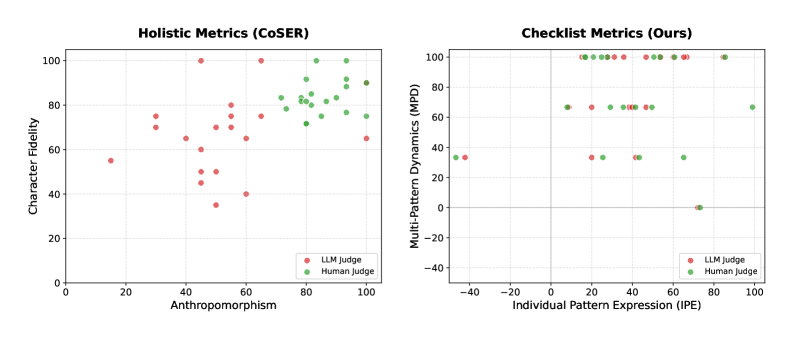
The HumanLLM-32B model was evaluated using metrics designed to quantify psychological realism, resulting in an Individual Pattern Expression (IPE) score of 32.6% and a Multi-Pattern Dynamics (MPD) score of 73.8%. IPE measures the model’s capacity to consistently express identifiable behavioral patterns within generated responses, while MPD assesses the diversity and adaptability of these patterns across different scenarios. These scores indicate a statistically significant correlation between the model’s generated behavior and established principles of human psychological expression, suggesting a robust ability to simulate nuanced and dynamic human-like responses.
The evaluation of model-generated behavior utilized a Dual-Level Checklists framework, employing GPT-5-mini to assess responses at both the individual pattern expression level and within the broader scenario context. This evaluation revealed a substantial divergence in anthropomorphism assessment between the LLM judge and human experts; the GPT-5-mini judge assigned a score of 5 out of 100, while human experts averaged 93.3 out of 100. This constitutes a difference of -32.2, highlighting a significant discrepancy in how the automated evaluation and human assessors perceived the human-like qualities of the model’s responses.
Beyond Mimicry: The Implications of Psychologically Grounded AI
HumanLLM signals a fundamental departure in large language model (LLM) architecture, transitioning from systems that primarily mimic human communication to those built upon computational models of human psychology. Previous LLMs excelled at statistically predicting the next word, effectively becoming sophisticated pattern-matching engines; HumanLLM, however, integrates established psychological principles – such as cognitive biases, emotional responses, and motivational drives – directly into its core design. This isn’t merely about generating text as if a human wrote it, but rather about simulating the processes underlying human thought and behavior. The result is an AI capable of more nuanced, consistent, and believable interactions, potentially unlocking a new era of artificial intelligence characterized by genuine psychological plausibility rather than superficial imitation.
The increased believability offered by models like HumanLLM promises a revolution in interactive entertainment, particularly in the creation of non-player characters (NPCs). Traditionally, NPCs have followed pre-programmed scripts or relied on rudimentary AI, resulting in predictable and often jarring interactions. However, by grounding AI behavior in psychological principles, these digital characters can now exhibit nuanced emotional responses, consistent personalities, and adaptive behaviors that mirror human complexity. This moves beyond simple responsiveness to genuine reactivity, allowing NPCs to convincingly simulate thought processes and motivations. Consequently, players are no longer interacting with programmed automatons, but with entities that feel authentically alive within the game world, significantly increasing immersion and fostering deeper emotional engagement – potentially transforming gaming from a series of challenges into truly compelling narrative experiences.
Artificial intelligence systems traditionally prioritize task completion, often resulting in interactions that, while functional, lack the nuance of human communication. However, a growing body of research demonstrates that anchoring AI behavior in established psychological principles – such as reciprocity, emotional consistency, and theory of mind – significantly enhances believability and trustworthiness. When an AI responds in ways aligned with human expectations for social interaction, users are more likely to perceive it as competent, friendly, and even relatable. This foundation of psychological realism isn’t simply about creating more convincing chatbots; it paves the way for genuinely meaningful human-AI collaboration, fostering deeper engagement in applications ranging from therapeutic support and educational tutoring to immersive gaming and personalized assistance, ultimately moving beyond mere utility toward authentic connection.
The pursuit of realistic LLM behavior, as demonstrated by HumanLLM, echoes a fundamental principle of mathematical elegance: the search for invariants. The framework’s focus on cognitive patterns and scenario-based training attempts to establish consistent, predictable responses-traits that remain constant even as the complexity of input ‘N’ approaches infinity. As Bertrand Russell observed, “The whole problem of philosophy is to find out what things really are.” HumanLLM, in its way, attempts a similar endeavor, seeking to define ‘what a realistic agent really is’ through the rigorous application of psychological principles and a dual-level checklist, ultimately striving for provable consistency rather than merely functional performance.
The Horizon of Mimicry
The pursuit of anthropomorphism in large language models, as exemplified by HumanLLM, reveals a curious predicament. Success is not measured by achieving sentience-a metaphysical distraction-but by the fidelity with which these systems simulate cognitive patterns. The framework represents a step towards a more nuanced performance, yet fundamentally remains a mirroring exercise. The true challenge lies not in replicating observable behavior, but in establishing a provable connection between the simulated patterns and the underlying principles governing human cognition-a task bordering on the intractable.
Future work must address the inherent limitations of scenario-based training. The dataset, however comprehensive, will always be a finite representation of an infinite reality. A more elegant solution might involve formalizing the rules governing human response-a system of axioms from which behavior can be derived, rather than inferred. This necessitates moving beyond empirical observation and embracing a more mathematical definition of ‘human-like’ interaction.
Ultimately, the value of such research rests not in creating convincing illusions, but in illuminating the very nature of intelligence-both artificial and organic. The framework provides a valuable testing ground for hypotheses regarding the human mind, but the ultimate metric of success will be the emergence of principles that are both computationally efficient and psychologically sound-a harmony of symmetry and necessity.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.10198.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Clash Royale Best Boss Bandit Champion decks
- Vampire’s Fall 2 redeem codes and how to use them (June 2025)
- World Eternal Online promo codes and how to use them (September 2025)
- Best Arena 9 Decks in Clast Royale
- How to find the Roaming Oak Tree in Heartopia
- Country star who vanished from the spotlight 25 years ago resurfaces with viral Jessie James Decker duet
- Mobile Legends January 2026 Leaks: Upcoming new skins, heroes, events and more
- M7 Pass Event Guide: All you need to know
- Solo Leveling Season 3 release date and details: “It may continue or it may not. Personally, I really hope that it does.”
- ATHENA: Blood Twins Hero Tier List
2026-01-17 11:58