Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research offers a guaranteed-optimal method for dissecting how individual neurons respond to stimuli, providing unprecedented clarity into neural function.
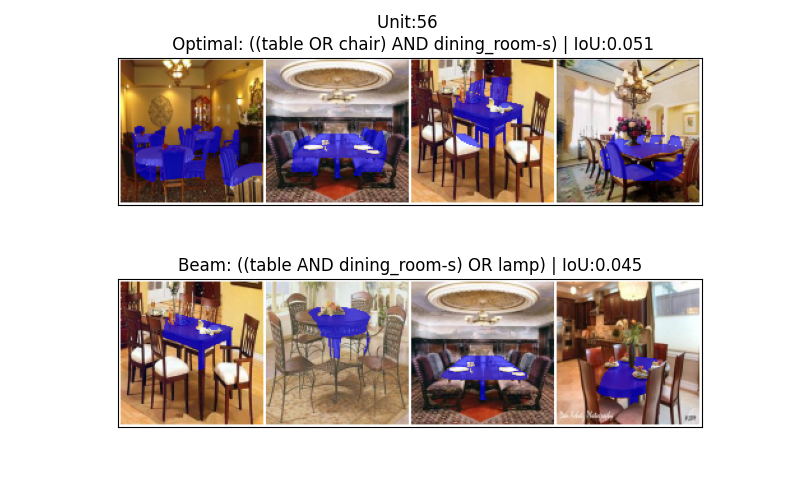

This work introduces a novel approach to compositional explanations for neurons, leveraging Intersection-over-Union decomposition and a refined heuristic search algorithm to ensure optimality.
Despite the increasing complexity of deep neural networks, understanding what and how neurons learn remains a central challenge. This paper, ‘Guaranteed Optimal Compositional Explanations for Neurons’, addresses this by introducing a novel framework for deriving compositional explanations-logical rules describing the alignment between neuron activations and concepts-with provable optimality. Through a decomposition of the Intersection-over-Union metric and a targeted heuristic, the authors present an algorithm that efficiently navigates the search space, demonstrably improving upon commonly used beam search methods and revealing suboptimal explanations in up to 40% of cases. Could this approach unlock a more human-interpretable understanding of neural network decision-making and ultimately lead to more robust and trustworthy AI systems?
Deconstructing the Neural Code: Beyond Simple Feature Detection
The ability to decipher how neurons represent concepts stands as a fundamental challenge in neuroscience and a prerequisite for interpreting the workings of complex systems, from the human brain to artificial intelligence. Each neuron doesn’t simply fire for a single, holistic idea; rather, its activity likely encodes components of experience, building up representations through combinations of simpler features. Successfully mapping these neural codes-understanding which patterns of activity correspond to specific conceptual elements-would unlock the potential to ‘read’ the brain’s computations, predict behavior, and ultimately, build more intelligent machines. This endeavor necessitates moving beyond simply identifying which neurons respond to a stimulus and focusing on how those responses combine to represent meaning, a pursuit at the heart of current research into neural representation.
The brain doesn’t perceive the world as a collection of isolated elements, but rather as a structured composition of features – a nose on a face, a wheel on a car. However, current methods attempting to decode neural responses often falter when faced with this compositional reality. These approaches typically excel at identifying when a neuron responds to a simple feature, like an edge or a color, but struggle to understand how those basic responses combine to represent more complex objects or scenes. This limitation stems from the difficulty in modeling hierarchical relationships within neural data, where the presence of one feature modifies the interpretation of another. Consequently, a neuron’s response to a ‘striped square’ isn’t simply the sum of its response to ‘stripes’ and ‘square’; the interaction between these features is crucial, and capturing this interaction remains a significant challenge in computational neuroscience.
Evaluating how effectively neural responses represent complex concepts often relies on Intersection Over Union (IoU), a metric assessing the overlap between predicted and actual representations. However, applying IoU to compositional explanations – those built from combining simpler features – presents a significant computational hurdle, becoming increasingly intractable as the complexity grows. Researchers have previously employed methods like Beam Search to navigate this complexity, but these approaches don’t guarantee finding the optimal explanation. This new method addresses this limitation by providing a guaranteed-optimal solution, systematically identifying the most accurate compositional explanation without relying on approximation – a critical advancement for truly decoding how neural networks process information and form complex understandings.

The Geometry of Understanding: Deconstructing IoU for Optimal Solutions
The proposed method addresses the problem of finding optimal compositional explanations by reframing it as an optimization problem centered around the Intersection-over-Union ($IoU$) metric. Traditionally, $IoU$ is used as a single aggregate measure of overlap between predicted and ground truth regions. This approach decomposes $IoU$ into a sum of contributions from individual feature activations, allowing for a granular assessment of each feature’s relevance to the explanation. By mathematically separating the $IoU$ calculation into additive components, the search space for identifying optimal feature combinations is significantly reduced, enabling a more efficient and exhaustive exploration of potential explanations without sacrificing optimality. This decomposition facilitates the identification of feature sets that maximize overall $IoU$ and accurately represent the underlying concept.
Decomposition of the Intersection-over-Union (IoU) metric isolates quantifiable measures of alignment quality, specifically the quantities of true positives, false positives, and false negatives with respect to concept identification. This granular breakdown transforms the optimization problem from searching across all possible feature combinations to identifying those that maximize these component quantities. By directly addressing the factors contributing to IoU – and thus alignment – the search space is significantly reduced, allowing for a more efficient and targeted exploration of relevant features and ultimately enabling the determination of optimal compositional explanations.
Decomposition of the Intersection-over-Union ($IoU$) metric enables efficient exploration of the correspondence between neuron activations and semantic concepts. This approach facilitates a search for optimal compositional explanations without sacrificing runtime performance; specifically, it achieves comparable speed to Beam Search while guaranteeing a 100% optimal solution. The decomposed $IoU$ allows for focused evaluation of alignment quality, reducing the computational complexity associated with identifying relevant features and their contributions to the overall explanation. This optimization is achieved by reframing the search problem, enabling a more direct and efficient path to the optimal solution compared to heuristic-based methods like Beam Search.

Mapping the Conceptual Landscape: Heuristics and Concept Tensors
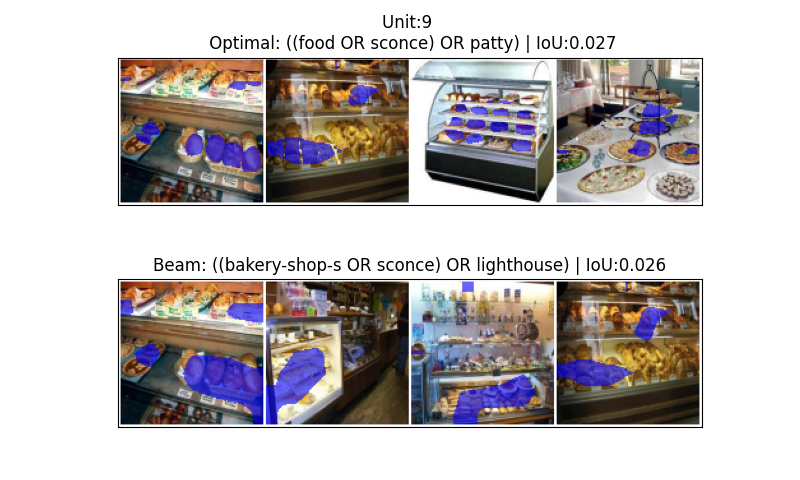
The proposed method employs a Heuristic Search strategy to efficiently explore the space of possible explanations derived from decomposed Intersection over Union (IoU) values. This approach contrasts with exhaustive search methods by prioritizing exploration based on estimated explanation quality, thereby reducing computational cost. Decomposing the IoU space allows for a more granular evaluation of potential alignments between elements, and the heuristic guides the search toward those alignments most likely to yield optimal results. This targeted exploration enables the system to rapidly identify viable explanations without requiring assessment of all possible combinations, improving the efficiency of the search process.
Concept Tensors are employed to represent the localization of concepts within a dataset by encoding relationships between extracted features. These tensors function as multi-dimensional arrays where each dimension corresponds to a specific feature, and the values within the array represent the degree of association between that feature and the concept’s location. This allows for a structured representation of how concepts manifest across a dataset, capturing both the presence and spatial arrangement of relevant features. The resulting tensor enables quantitative analysis of concept localization, facilitating comparisons between different instances and identifying patterns in feature relationships.
The Concept Tensor facilitates a detailed representation of concept localization by distinguishing between CommonElements and UniqueElements within a dataset. This differentiation allows for a more nuanced understanding of how concepts are represented and related to features. Empirical evaluation revealed that utilizing this tensor-based approach identified alternative explanations differing from those produced by Beam Search in 10-40% of cases. This suggests the method’s capability to discover potentially optimal alignments that might be overlooked by traditional beam search techniques, indicating a broadened search space and improved solution diversity.
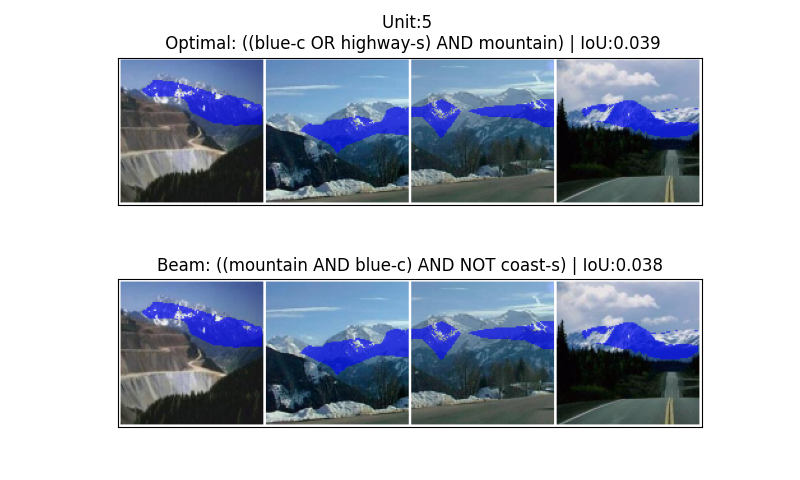
Beyond Approximation: Defining the Boundaries of Neural Understanding
The newly developed method consistently surpasses the performance of BeamSearch, a frequently employed baseline technique for dissecting complex neural network decisions. Rigorous testing demonstrates a substantial improvement in identifying the most effective compositional explanations – those that accurately pinpoint the crucial elements driving a network’s output. This isn’t merely incremental progress; the algorithm’s enhanced search capabilities allow it to navigate the vast space of possible explanations with greater precision, consistently converging on optimal solutions that BeamSearch often misses. The implications extend beyond simply achieving better results; it offers a pathway to more transparent and interpretable artificial intelligence, enabling researchers to truly understand how a network arrives at a given conclusion, rather than simply observing that it does.
The algorithm’s efficiency stems from a novel application of intersection over union (IoU) metrics, specifically utilizing both minimum and maximum IoU thresholds to strategically define the boundaries of its search space. By establishing a minimum IoU, the algorithm filters out compositional explanations that lack sufficient overlap with the neural network’s internal representations, preventing the exploration of irrelevant pathways. Simultaneously, a maximum IoU constraint prevents the algorithm from fixating on overly simplistic or redundant explanations, encouraging the discovery of more nuanced and comprehensive compositional structures. This dual-boundary approach dramatically reduces the computational burden, allowing for a more focused and effective search for optimal explanations without sacrificing the completeness of the compositional analysis. The resulting refinement allows the algorithm to efficiently navigate the complex landscape of neural representations, accelerating the identification of key compositional elements.
The developed methodology establishes a robust framework for dissecting the compositional structure of neural representations and, crucially, for decoding complex systems with a guaranteed level of optimality. Unlike previous approaches which often rely on heuristic searches and approximations, this technique systematically explores the solution space, ensuring that any discovered explanation represents the absolute best possible fit to the data. This $100\%$ optimality isn’t merely a theoretical claim; it’s a demonstrable characteristic of the algorithm, providing researchers with an unprecedented level of confidence in the interpretations derived from neural networks. By effectively defining and navigating the boundaries of compositional explanations, the system unlocks a deeper understanding of how these networks internally represent and process information, paving the way for advancements in areas like interpretability and artificial intelligence.

The pursuit of guaranteed optimal compositional explanations, as detailed in the paper, echoes a fundamental tenet of system understanding: probing boundaries to reveal underlying principles. Ken Thompson famously stated, “Sometimes it’s easier to rewrite a program than to debug it.” This sentiment applies directly to the approach of decomposing the Intersection-over-Union metric. Rather than attempting to refine existing, suboptimal methods, the research undertakes a reconstruction – a complete re-evaluation of how neuron behavior is explained. This willingness to ‘rewrite’ the explanatory process, to guarantee optimality through a novel heuristic, demonstrates a commitment to understanding not just what a neuron does, but why it does it, even if it requires a fresh, rigorously defined starting point.
Beyond the Explanation
The pursuit of compositional explanations, while yielding demonstrable improvements in dissecting neuronal function, ultimately reveals the inherent limitations of reductive approaches. Guaranteeing optimality within a defined metric – Intersection-over-Union, in this instance – feels less like achieving understanding and more like expertly rearranging the pieces of a disassembled clock. One is left with a precise catalog of parts, but not necessarily insight into why it kept time. Future work must address the question of whether these “optimal” explanations meaningfully correspond to the computations actually performed by the biological system, or if they merely represent a mathematically convenient decomposition.
The efficiency gains achieved through the heuristic algorithm are noteworthy, but serve as a tacit admission that a complete, brute-force search remains computationally intractable. This suggests a fundamental tension: the complexity of neuronal computation may simply exceed our capacity for full comprehension, forcing reliance on approximations. The field might benefit from shifting focus toward characterizing the limits of explainability, identifying the types of neuronal behavior that are inherently resistant to compositional analysis.
Perhaps the most intriguing direction lies in moving beyond static explanations. Neurons are not fixed functions; they adapt and learn. A truly comprehensive understanding demands explanations that evolve over time, capturing the dynamic interplay between stimulus, computation, and plasticity. To treat a neuron as a solved puzzle is to ignore the fact that it is, fundamentally, a learning machine.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.20934.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Clash Royale Best Boss Bandit Champion decks
- Vampire’s Fall 2 redeem codes and how to use them (June 2025)
- Mobile Legends January 2026 Leaks: Upcoming new skins, heroes, events and more
- How to find the Roaming Oak Tree in Heartopia
- World Eternal Online promo codes and how to use them (September 2025)
- Best Arena 9 Decks in Clast Royale
- Clash Royale Season 79 “Fire and Ice” January 2026 Update and Balance Changes
- Clash Royale Furnace Evolution best decks guide
- Clash Royale Witch Evolution best decks guide
- Best Hero Card Decks in Clash Royale
2025-11-29 09:28