Bridging Logic and Learning: A New Path to Scalable AI

Researchers have developed a novel system architecture that significantly accelerates probabilistic logical reasoning, paving the way for more efficient and adaptable artificial intelligence.

Researchers have developed a novel system architecture that significantly accelerates probabilistic logical reasoning, paving the way for more efficient and adaptable artificial intelligence.
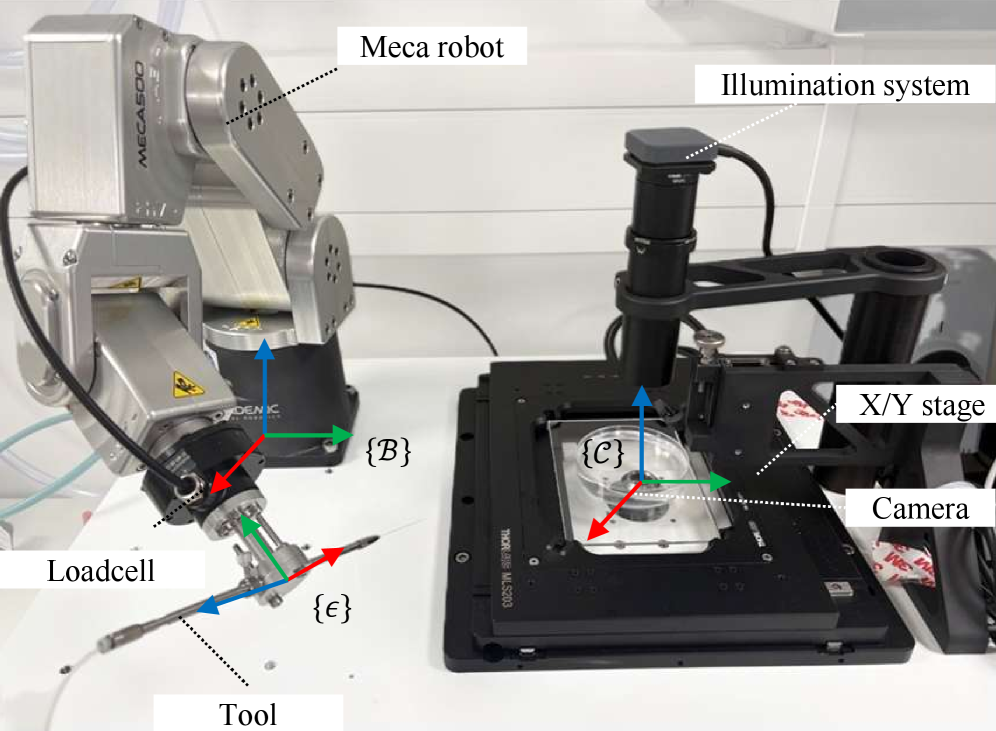
Researchers have developed a new system that uses AI and robotic assistance to reduce the burden on scientists performing delicate tasks under a microscope.
New research suggests that while AI tools can help with coding tasks, over-reliance on them may actually impede the development of core programming skills.

New research reveals that vision-language models are capable of developing task-specific communication systems, diverging from human language in surprising ways.

New research shows how continuous-time neural networks can enhance our ability to model and understand complex systems from limited data.
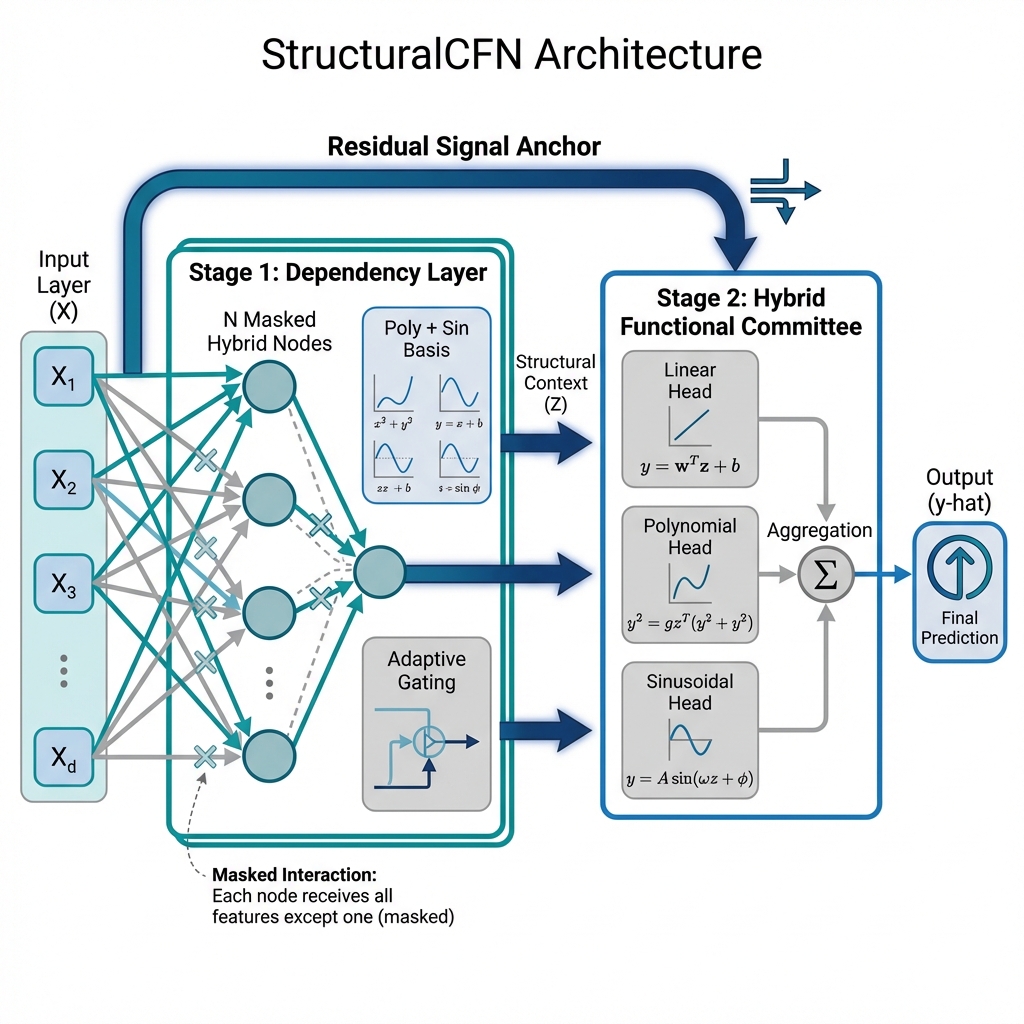
A new neural network architecture prioritizes interpretability and efficiency by explicitly modeling the mathematical connections between features in structured data.
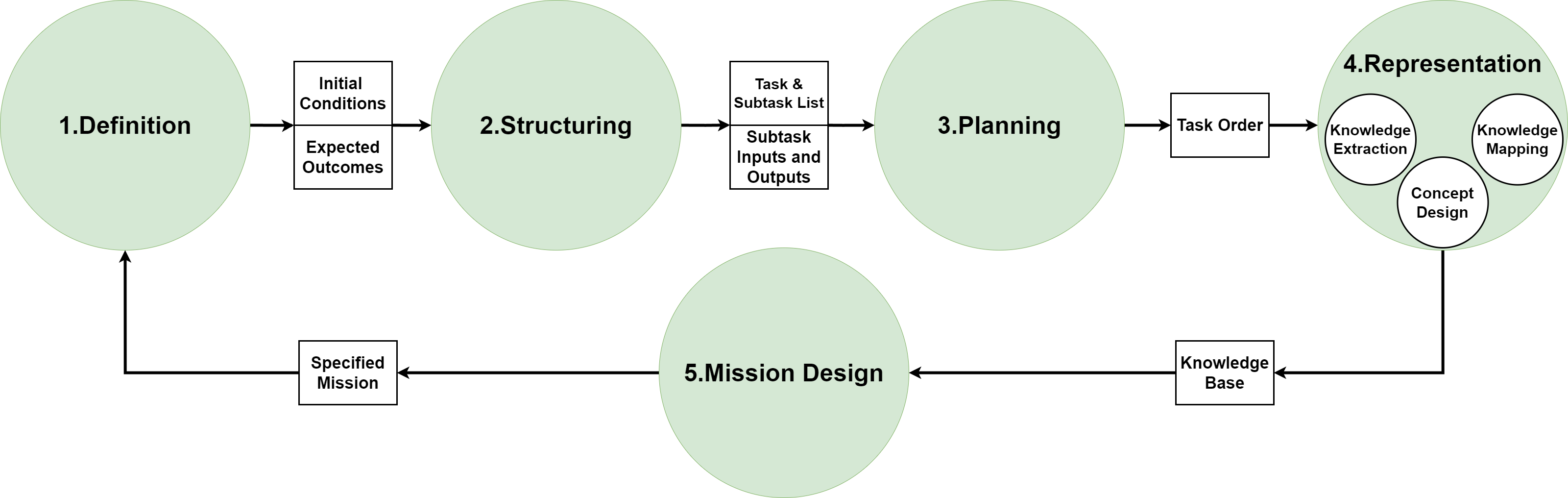
New research details a robust methodology for equipping robots with knowledge graphs, enabling more intelligent and adaptable mission execution.

Researchers have developed a new interface that lets users communicate animation ideas to artificial intelligence through intuitive, hand-drawn sketches and iterative refinement.
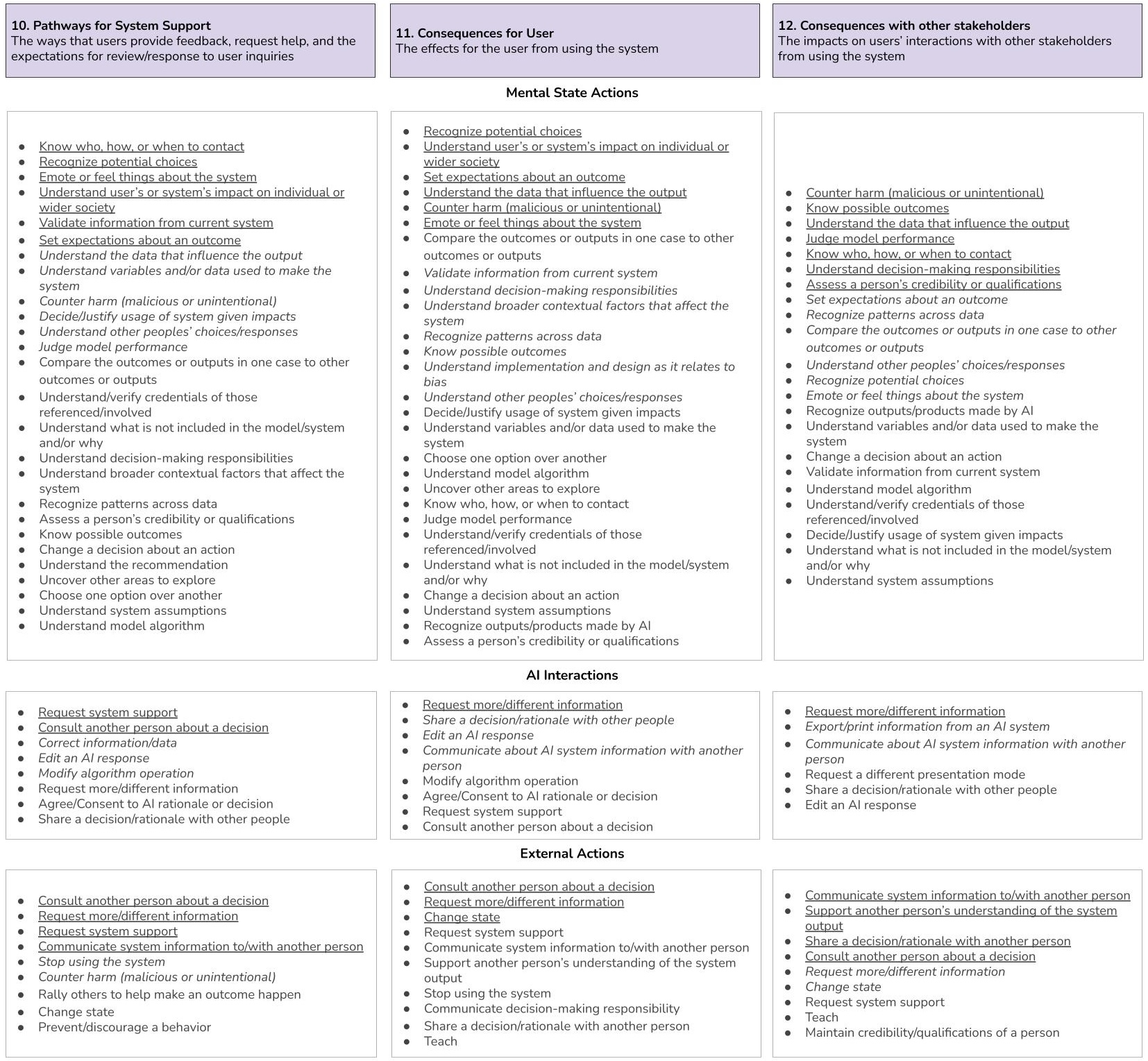
A new framework assesses how well AI explanations empower users to take meaningful action, shifting the focus from interpretability to practical impact.
![The system operates through a layered planning process, initially guided by a large language model →, then extended through specialized modules [latex] \Rightarrow [/latex] to refine and expand upon the initial strategic framework.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.20577v1/x1.png)
A new framework enables teams of robots to learn from past tasks, dramatically improving efficiency and reducing the need for constant re-planning.