The AI Scientist: Automating Discovery in Operations Research
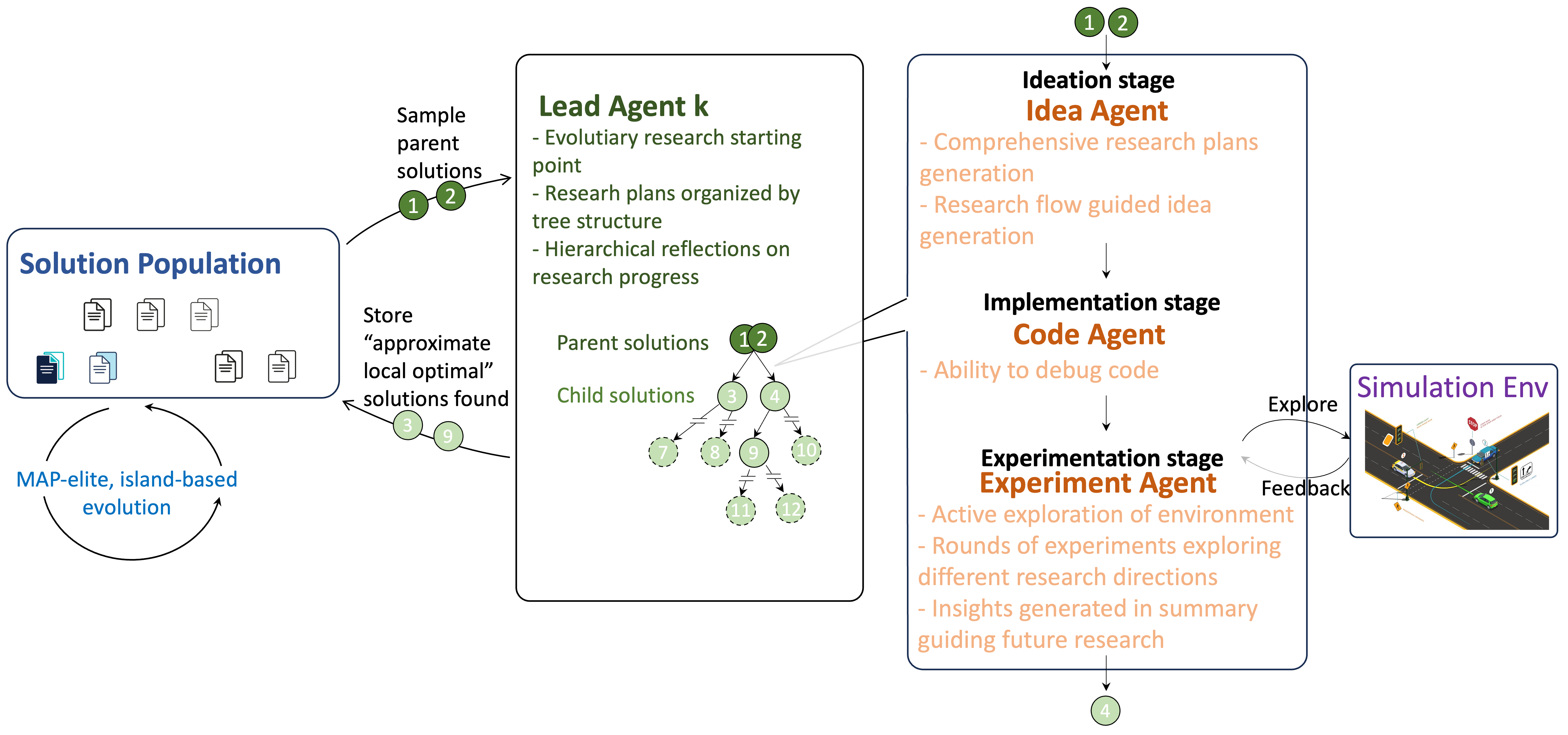
A new multi-agent system combines the power of large language models and systematic search to autonomously explore and validate algorithms for complex problems.

A new multi-agent system combines the power of large language models and systematic search to autonomously explore and validate algorithms for complex problems.
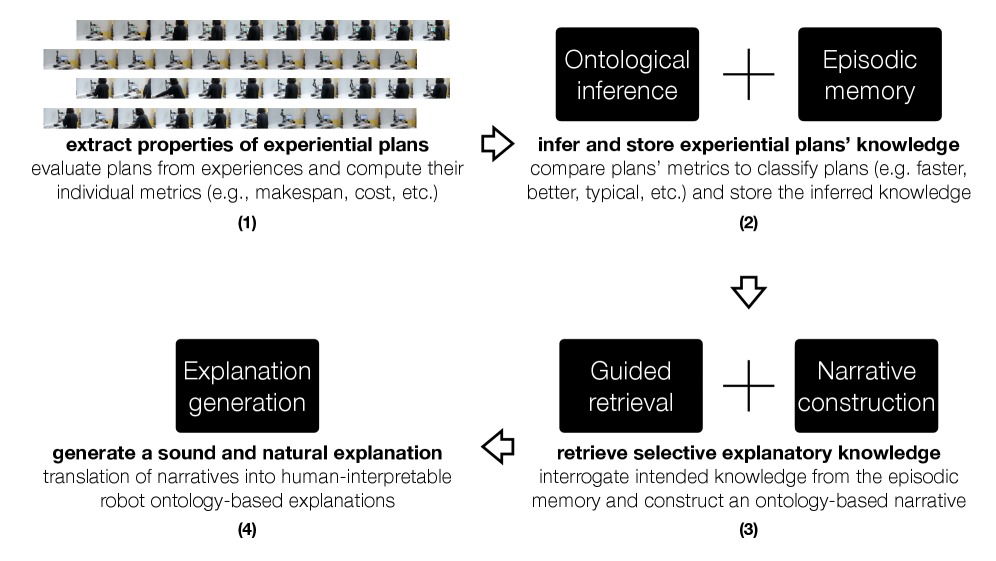
A new framework leverages the power of large language models and structured knowledge to help robots articulate their reasoning, fostering clearer communication and trust in human-robot teams.
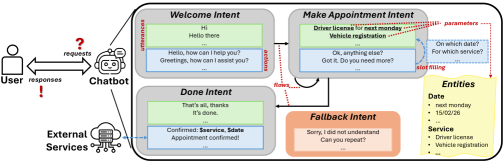
A new review examines the current state of automated testing methods for task-based chatbots and highlights the challenges in ensuring their reliability.
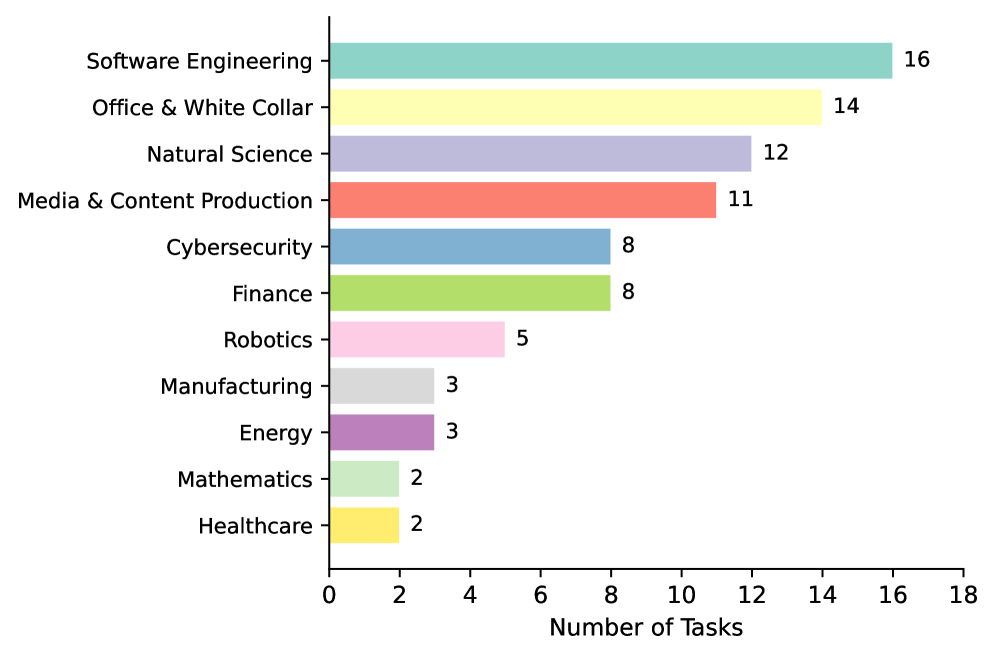
New research demonstrates that equipping AI agents with curated skills dramatically boosts performance across diverse tasks, offering a significant leap beyond simple prompt engineering.
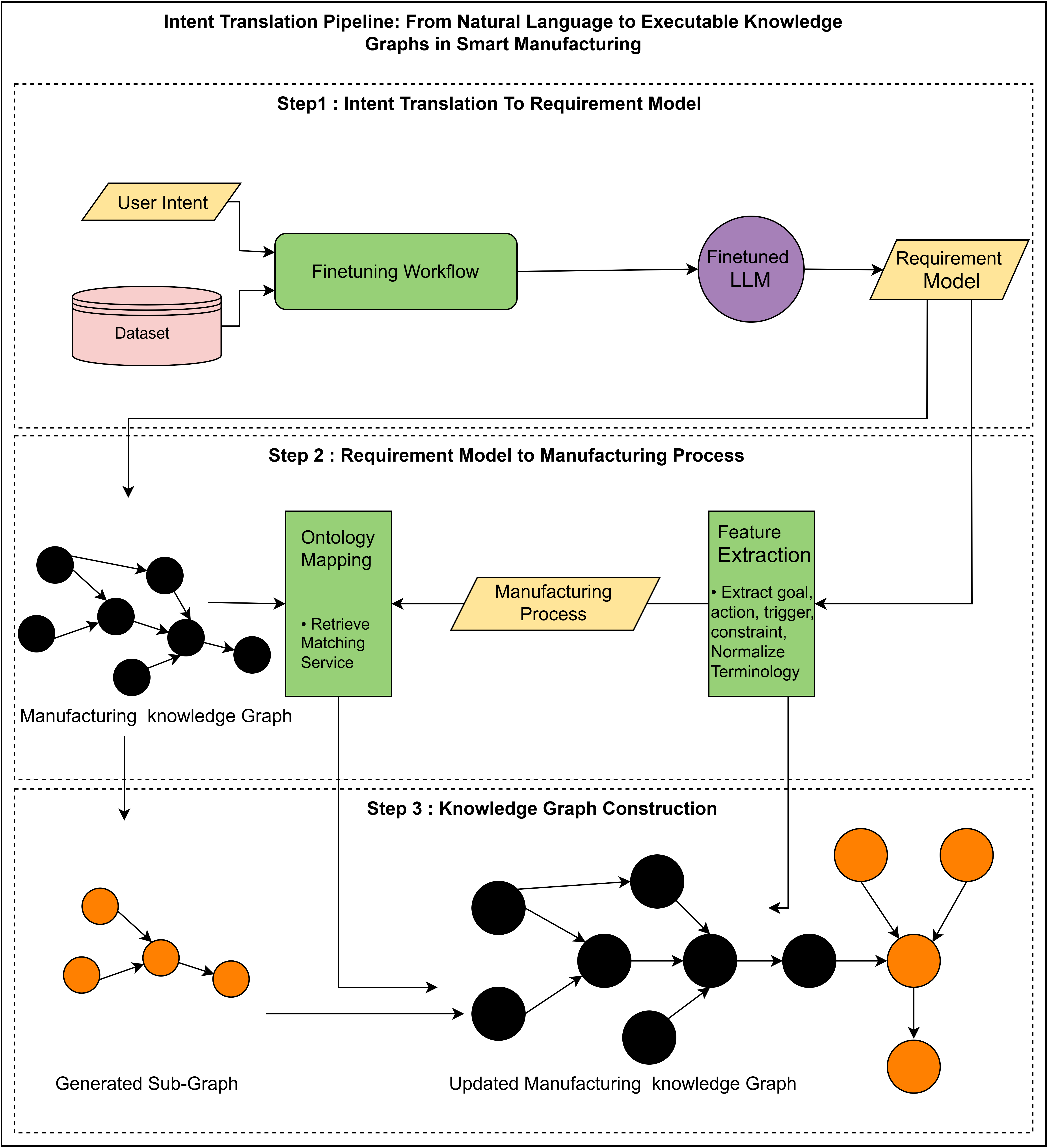
A new framework translates natural language instructions into executable manufacturing plans, promising more adaptable and intelligent production systems.
New research reveals that the effectiveness of AI companions in alleviating loneliness is heavily influenced by individual attachment styles and age groups.

A new framework improves how multiple AI agents learn and collaborate by enabling them to build and share a unified understanding of their environment.
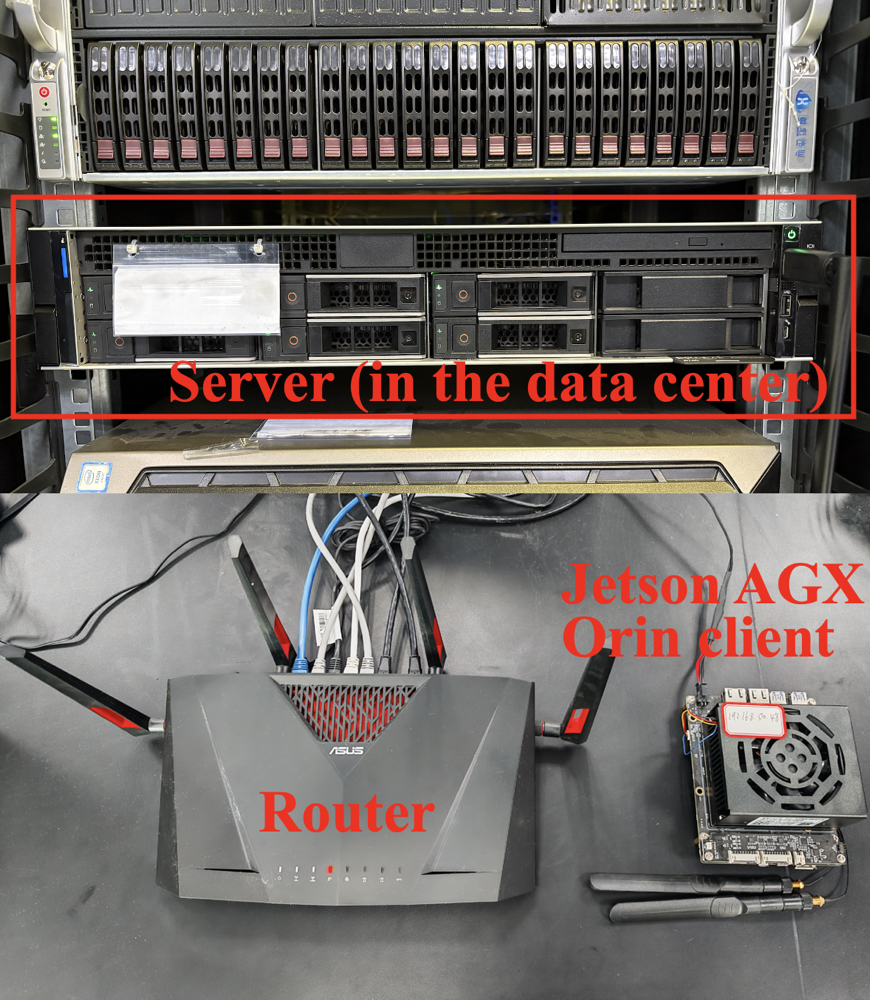
A new framework balances performance and efficiency for deploying large AI models in real-world embodied systems.
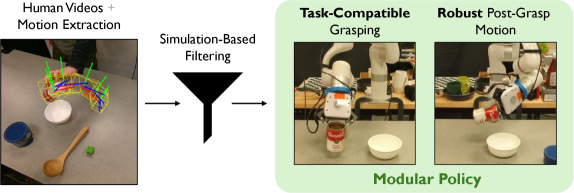
A new framework allows robots to acquire complex manipulation skills simply by observing human demonstrations in video, bypassing the need for time-consuming and expensive robot-specific training.

Researchers present X-SYS, a comprehensive architecture designed to bridge the gap between explainable AI research and real-world application.