AI’s New Classroom: Transforming Science Education
Artificial intelligence is poised to reshape how we teach and learn science, but realizing its potential requires careful consideration of ethics and equity.
Artificial intelligence is poised to reshape how we teach and learn science, but realizing its potential requires careful consideration of ethics and equity.

A new approach to human-robot interaction prioritizes long-term relationships and adaptability over short-term tasks.
Artificial intelligence is poised to fundamentally change how we teach and learn science, demanding a thoughtful redesign of core learning materials.

A new system offers a privacy-focused look at real-world conversations with large language models, revealing how users interact with and are affected by these powerful tools.
![A novel machine learning approach constructs an approximation [latex]\sigma_n[/latex] directly within the space [latex]V_n[/latex] from data, enabling a quantifiable reconstruction error relative to the target function and circumventing traditional modeling constraints.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17985v1/Figures/newparadigm.jpg)
A new approach explores how algorithms can learn effectively by leveraging the underlying geometry of data, reducing the need for extensive labeled datasets.
![A robotic system achieves coordinated movement through a distributed planning strategy, wherein a designated leader [latex]r_3[/latex] calculates a global path towards a desired formation, while subordinate robots navigate to assigned partial goals [latex]p_2, ..., p_N[/latex], maintaining formation integrity via virtual spring and damper connections.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.18260v1/x1.png)
Researchers have developed a new framework for coordinating groups of legged robots, allowing them to navigate complex environments with improved robustness and flexibility.
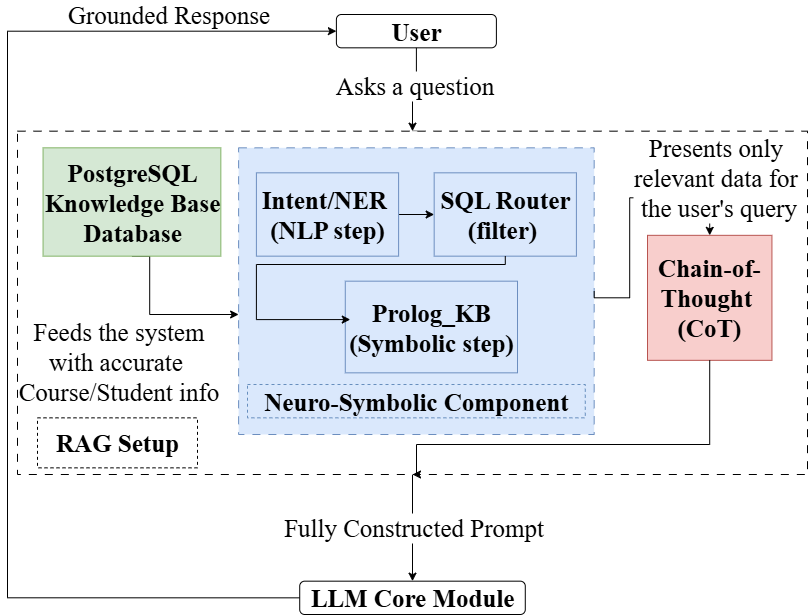
A new system combines the power of language models with structured reasoning to deliver more accurate and transparent academic advising.
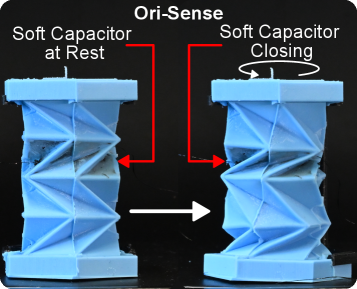
A new capacitive sensing approach leverages the mechanics of folded paper to provide robust proprioception for delicate soft robotic systems.
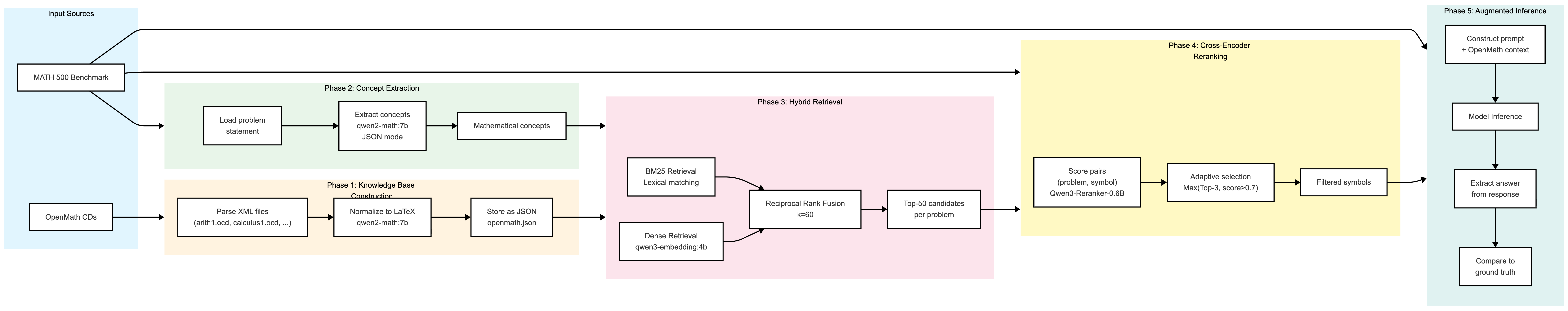
New research explores how combining the power of language models with formal mathematical definitions can dramatically improve the reliability of complex reasoning tasks.
![A nested training regime fosters adaptive interaction by first establishing a set of human policies against fixed robotic behaviors, then training a second-level robot against these adaptive policies-a process that utilizes latent embeddings to approximate beliefs over multiple partner strategies within a nested partially observable Markov decision process [latex]I-POMDP[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17737v1/images/arch.png)
A new reinforcement learning framework enables artificial intelligence to dynamically adjust to human teammates, fostering more effective and intuitive collaboration.