Author: Denis Avetisyan
This review offers a comprehensive, engineering-focused approach to designing, deploying, and maintaining robust agentic AI systems in real-world applications.
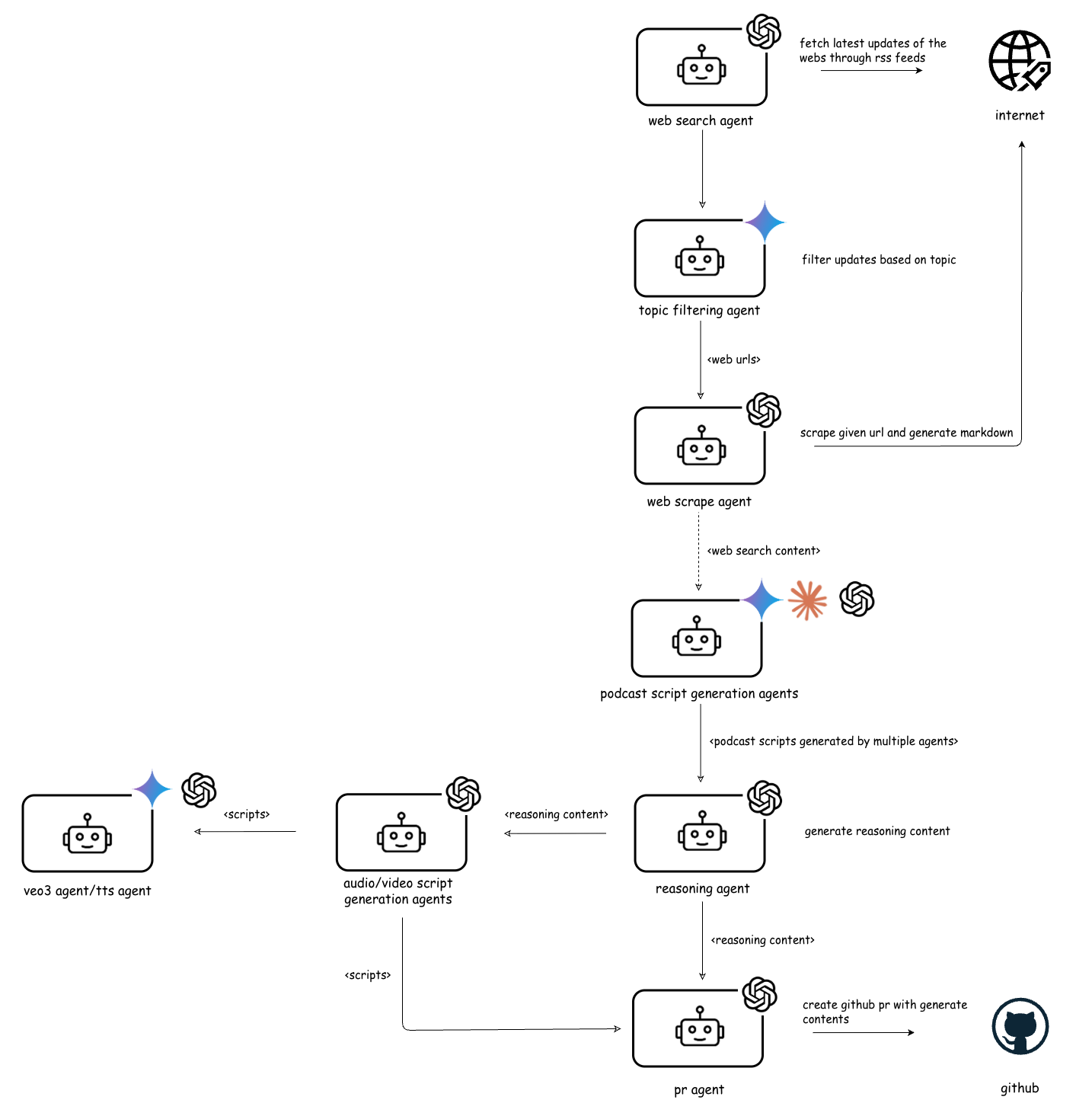
We present a framework emphasizing modularity, deterministic execution, and responsible AI practices through a multimodal news-to-podcast generation case study leveraging the Model Context Protocol.
While the promise of autonomous systems powered by large language models is substantial, translating agentic AI from research prototypes to robust, production-ready workflows remains a significant challenge. This paper, ‘A Practical Guide for Designing, Developing, and Deploying Production-Grade Agentic AI Workflows’, addresses this gap by presenting a structured engineering lifecycle and associated best practices for building reliable, observable, and responsibly-aligned agentic systems. We demonstrate that modular design, deterministic execution, and a ‘tool-first’ approach are crucial for scalable and maintainable workflows, illustrated through a multimodal news-analysis and media-generation case study. As agentic AI adoption accelerates, how can organizations best standardize these engineering principles to unlock its full potential and mitigate emerging risks?
Beyond Mere Prediction: The Rise of Autonomous Agents
Large language models, despite demonstrating remarkable proficiency in generating human-quality text, inherently face limitations when tasked with complex reasoning or executing multi-step actions. These models excel at identifying patterns and predicting the next word in a sequence, but this core functionality doesn’t translate directly into genuine problem-solving capabilities. While capable of simulating reasoning through extensive training data, traditional LLMs often falter when confronted with novel situations requiring sequential planning, tool use, or real-world interaction. The challenge isn’t a lack of knowledge, but rather an inability to effectively organize that knowledge into a coherent plan and persistently execute it – essentially, they struggle to move beyond being powerful text completion engines to becoming true agents capable of independent action.
Agentic AI signifies a fundamental departure from conventional language models, moving beyond the limitations of simply predicting the next word in a sequence. Instead of passive text completion, these systems are designed for autonomous action and the orchestration of complex tasks. This isn’t merely about generating human-like text; it’s about enabling AI to proactively pursue goals, break down problems into manageable steps, and utilize tools to achieve desired outcomes. The shift represents a move toward artificial intelligence that doesn’t just respond to prompts, but independently plans, executes, and adapts – effectively functioning as an intelligent agent capable of navigating and interacting with the world to accomplish defined objectives.
The limitations of large language models extend beyond textual generation; true intelligence often demands interaction with the world. Consequently, a pivotal advancement in artificial intelligence involves equipping these models with access to tools and the capacity to engage with external systems. This isn’t simply about providing information; it’s about granting agency. Researchers are developing frameworks where LLMs can utilize APIs to perform actions – booking flights, analyzing data from spreadsheets, or controlling physical robots – effectively transforming them from passive respondents into active problem-solvers. The ability to dynamically leverage specialized tools allows the LLM to overcome inherent knowledge gaps and tackle tasks far exceeding its pre-trained capabilities, marking a significant step towards genuinely intelligent and autonomous systems.
The effective deployment of agentic AI hinges on a design philosophy centered around modularity and specialized capabilities. Rather than monolithic models attempting to handle all tasks, successful systems decompose complex problems into smaller, manageable components. Each module is then meticulously trained to excel at a specific function – be it web searching, data analysis, or code execution – and these specialized tools are orchestrated by the language model. This approach mirrors the efficiency of biological systems, where specialized organs collaborate to achieve complex goals, and offers several advantages, including improved reliability, easier debugging, and the capacity to readily incorporate new functionalities without retraining the entire system. Ultimately, this division of labor allows agentic AI to transcend the limitations of general-purpose language models and tackle increasingly sophisticated real-world challenges.

Orchestrating Intelligence: A Modular Workflow
Agentic AI workflows decompose complex tasks into discrete units of work handled by individual agents, each designed with a singular, well-defined responsibility. This modular approach contrasts with monolithic AI systems and promotes increased flexibility and maintainability. By assigning specific functions – such as data retrieval, analysis, or report generation – to dedicated agents, the overall workflow benefits from improved error isolation and parallel processing capabilities. The design principle of single responsibility ensures that each agent’s function is narrowly focused, reducing complexity and facilitating independent development, testing, and scaling of individual components within the larger system.
Tool calls are a core component of agentic AI workflows, allowing agents to overcome the limitations of Large Language Models (LLMs) which are typically restricted to text-based input and output. These calls function as standardized requests to external APIs or functions, enabling agents to perform actions such as retrieving data from databases, interacting with websites, executing code, or utilizing specialized services. By defining a set of available tools and their parameters, the agent can dynamically select and invoke the appropriate tool based on the current task and context, effectively extending its operational scope beyond purely linguistic processing. The responses from these tool calls are then fed back into the LLM, enabling it to reason over the results and continue the workflow, or to formulate further actions.
Containerization with Docker packages each agent and its dependencies into a standardized unit, ensuring consistent execution across different environments and eliminating “works on my machine” issues. This portability is crucial for scalability, as Docker containers can be easily deployed and replicated. Kubernetes then automates the deployment, scaling, and management of these containerized agents. It handles tasks such as load balancing, service discovery, and self-healing, ensuring the workflow remains stable under varying loads and automatically recovers from failures. Kubernetes’ orchestration capabilities allow for dynamic scaling of individual agents based on demand, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing downtime, ultimately enabling a highly resilient and scalable agentic AI system.
Externalized prompts represent a method of managing Large Language Model (LLM) instructions as discrete data files, separate from the application codebase. This decoupling offers several advantages: prompt revisions do not require code redeployment, facilitating rapid iteration and A/B testing; version control systems can track prompt changes, ensuring reproducibility and auditability; and prompts can be dynamically loaded and modified without altering the core application logic. This practice is crucial for maintaining consistent AI behavior and simplifies collaboration between developers and prompt engineers, as instructions become a shareable and manageable asset.

From RSS to Podcast: A Demonstration of Autonomous Content Creation
The Podcast Generation Workflow utilizes an agentic AI system to fully automate podcast creation, beginning with the sourcing of information from news feeds. This workflow bypasses manual content curation and scriptwriting by employing a series of specialized agents. These agents autonomously handle tasks including RSS feed searching, topic filtering, web scraping, and the generation of initial script drafts utilizing multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) – specifically Llama, OpenAI, and Gemini – in a parallelized fashion. A dedicated reasoning agent then consolidates these disparate drafts, ensuring factual consistency and narrative coherence, before a final agent adapts the consolidated text into a format suitable for audio or video production. This end-to-end automation demonstrates the capacity of agentic AI to manage complex, multi-step processes with minimal human intervention.
The initial phase of podcast content acquisition relies on an RSS Feed Search Agent which systematically queries defined RSS feeds for articles relevant to pre-determined subject matter. This agent doesn’t simply collect all articles; it operates in conjunction with a Topic Filtering Agent. The Topic Filtering Agent employs keyword analysis and potentially semantic understanding to evaluate each article’s content, ensuring it aligns with the overall podcast theme and established topical boundaries. This dual-agent system prevents irrelevant or off-topic material from progressing further into the podcast generation workflow, maintaining content focus and quality. The filtering criteria are configurable, allowing for adjustments to content breadth and specificity.
Following RSS feed analysis and topic filtering, a Web Scrape Agent retrieves content from identified URLs. This extracted data is then distributed to multiple Podcast Script Generation Agents, each powered by a different Large Language Model (LLM). The system utilizes a consortium of LLMs, specifically Llama, OpenAI, and Gemini models, to generate diverse script drafts. This parallel processing approach allows for comparative analysis of content interpretations and leverages the unique strengths of each LLM in script formulation, increasing the quality and breadth of the generated podcast material before consolidation by the Reasoning Agent.
The Reasoning Agent functions as a critical consolidation step within the podcast generation workflow, receiving multiple draft scripts generated by various Large Language Models (LLMs). This agent doesn’t simply concatenate the drafts; it actively analyzes them for redundancies, inconsistencies, and factual inaccuracies. Utilizing a defined set of rules and potentially external knowledge sources, it resolves conflicting information and ensures a logically coherent narrative. The output of the Reasoning Agent is a single, unified script, formatted and validated for accuracy, before being delivered to the subsequent Audio/Video Script Generation Agents for final refinement and media adaptation.

Final Polish and Publication: Completing the Automated Loop
The system dynamically crafts compelling multimedia through the integration of advanced generative technologies. Specifically, Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesizes natural-sounding audio from textual data, while Text-to-Video (Veo-3) translates written prompts into visually rich video content. This synergistic approach bypasses traditional content creation bottlenecks, enabling the rapid production of engaging media assets. The resulting audio and video aren’t merely illustrative; they are designed to capture attention and enhance information retention, offering a more immersive and accessible experience for the intended audience. The combination allows for the creation of content formats previously requiring significant resources and expertise, now achievable through automated processes.
The system’s automated workflow reaches its conclusion with a dedicated PR Agent, which intelligently compiles the synthesized audio and video components into a cohesive package. This agent doesn’t simply gather files; it meticulously structures them and publishes the complete output as a pull request on GitHub. Crucially, this process includes the generation of valid JSON prompts specifically designed for Google’s Veo-3 text-to-video platform, ensuring seamless integration and immediate usability of the created content. This automated submission not only streamlines content delivery but also establishes a verifiable record of the entire generative process, from initial text input to finalized media asset.
The fully automated content pipeline delivers substantial benefits beyond simply saving time and resources. By removing human intervention from core production stages, the system guarantees a consistently high standard across all generated materials, eliminating variability introduced by individual interpretation or skill. More importantly, this automation unlocks true scalability; content creation is no longer limited by available personnel or time constraints, allowing for a rapid increase in output to meet growing demands or adapt to dynamic information flows. This capacity to consistently produce and disseminate information at scale represents a fundamental shift in content creation possibilities, enabling responsive communication and widespread knowledge distribution.
Automated content creation systems are poised to redefine information dissemination by enabling hyper-personalization at scale. Rather than relying on broad, generalized messaging, these systems can dynamically tailor content to individual preferences and needs, fostering deeper engagement and understanding. This capability extends beyond simple customization; the speed of automated generation allows for a rapid response to emerging trends and breaking news, ensuring information remains current and relevant in an ever-changing world. The ability to quickly adapt and deliver bespoke content unlocks new possibilities for education, marketing, and public service, effectively transforming how information is consumed and utilized across diverse landscapes.

Toward Responsible Automation: A Call for Ethical AI Design
The escalating capabilities of agentic AI necessitate a fundamental commitment to responsible AI principles. As these systems gain autonomy and complexity, their potential impact – both positive and negative – expands dramatically. Prioritizing ethical considerations isn’t merely about preventing harm; it’s about fostering trust and ensuring equitable outcomes. This requires diligent attention to data integrity, actively mitigating biases embedded within training datasets, and designing algorithms that are demonstrably fair. Furthermore, the development of explainable AI – systems capable of articulating the reasoning behind their actions – is crucial for accountability and transparency. Ultimately, a proactive focus on responsible AI isn’t a constraint on innovation, but rather a catalyst for building genuinely beneficial and sustainable agentic technologies.
A core tenet of deploying agentic AI systems responsibly lies in proactively mitigating inherent risks to fairness, accountability, and security. Datasets used to train these agents often reflect existing societal biases, which can be inadvertently amplified in algorithmic outputs, leading to discriminatory outcomes. Simultaneously, the complex, often opaque, nature of advanced AI models demands increased transparency in their decision-making processes; understanding why an agent arrived at a particular conclusion is crucial for building trust and identifying potential errors. Crucially, safeguarding user privacy is paramount; agentic AI systems frequently operate on sensitive personal data, necessitating robust data protection measures and adherence to ethical guidelines to prevent misuse or unauthorized access. Addressing these interconnected challenges-bias, opacity, and privacy-is not merely a technical hurdle, but a foundational requirement for realizing the benefits of agentic AI while upholding societal values.
A critical frontier in the development of agentic AI lies in establishing dependable oversight of autonomous systems. Current research is increasingly focused on creating mechanisms that go beyond simple on/off switches, exploring dynamic monitoring systems capable of assessing an agent’s internal reasoning and predicting potential unintended consequences. This includes the development of ‘guardrails’ – configurable boundaries defining acceptable behavior – and robust anomaly detection algorithms designed to flag deviations from established norms. Furthermore, investigations are underway to create interpretable AI models, allowing developers and potentially even end-users to understand why an agent made a particular decision, facilitating course correction and building trust. The ultimate goal is not to stifle innovation, but to ensure that as these agents gain complexity and independence, there remains a verifiable and adaptable system of control, promoting safety and responsible deployment.
The successful integration of agentic AI into daily life hinges not simply on technological advancement, but on a concurrent commitment to ethical foresight. Proactive attention to potential biases within training data and algorithmic design is crucial, as these can perpetuate and amplify existing societal inequalities. Simultaneously, building systems that offer transparency – allowing users to understand why an agent made a particular decision – fosters trust and accountability. Furthermore, robust privacy safeguards are essential to protect sensitive user information as these autonomous systems collect and process data. By prioritizing these considerations from the outset, the transformative benefits of agentic AI – increased efficiency, novel problem-solving capabilities, and personalized experiences – can be realized while simultaneously minimizing the potential for harm and ensuring equitable access for all.

The pursuit of reliable agentic AI, as detailed in this guide, demands a precision mirroring mathematical rigor. The framework advocates for deterministic execution, ensuring repeatability and predictability-essential qualities for any system intended for production deployment. This echoes Blaise Pascal’s sentiment: “The eloquence of the tongue is not the measure of truth.” Just as a beautifully phrased argument lacks validity without logical foundation, a seemingly functional agentic workflow is insufficient without demonstrable, consistent behavior. The focus on modular design and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) serves to establish this foundational integrity, reducing the ‘chaos of data’ through disciplined construction.
What’s Next?
The presented framework, while a step toward taming the inherent stochasticity of large language models, does not, of course, solve the problem of artificial intelligence. Deterministic execution, even within a modular agentic system, merely pushes the locus of uncertainty into the initial conditions and the very definition of ‘correctness.’ The case study, focused on news-to-podcast generation, serves as a useful, contained demonstration, but its limitations are clear. Scaling such a system to truly complex, open-ended tasks will inevitably reveal new failure modes – and with those, the urgent need for formal verification techniques. Proving the safety and reliability of these workflows will require more than simply passing tests; it demands mathematical guarantees.
Future work must address the thorny issue of context propagation. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) offers a pragmatic solution, but a deeper theoretical understanding of information loss and distortion within multi-agent interactions is essential. Can a mathematically rigorous framework be developed to bound the error introduced at each stage of an agentic workflow? Furthermore, the current emphasis on responsible AI remains largely descriptive. True progress demands provable fairness, accountability, and transparency – qualities that are conspicuously absent in most contemporary LLM deployments.
The field now faces a crucial juncture. It can continue down the path of empirical tinkering, celebrating incremental improvements in performance metrics, or it can embrace the rigor of formal methods. The former may yield short-term gains, but the latter is the only path toward building truly trustworthy and dependable artificial intelligence. The elegance of a provable solution, after all, always outweighs the illusion of functionality.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.08769.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Clash Royale Best Boss Bandit Champion decks
- Mobile Legends January 2026 Leaks: Upcoming new skins, heroes, events and more
- Vampire’s Fall 2 redeem codes and how to use them (June 2025)
- Clash Royale Furnace Evolution best decks guide
- Best Hero Card Decks in Clash Royale
- Mobile Legends: Bang Bang (MLBB) Sora Guide: Best Build, Emblem and Gameplay Tips
- Best Arena 9 Decks in Clast Royale
- Clash Royale Witch Evolution best decks guide
- Dawn Watch: Survival gift codes and how to use them (October 2025)
- Brawl Stars December 2025 Brawl Talk: Two New Brawlers, Buffie, Vault, New Skins, Game Modes, and more
2025-12-11 01:05