Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new study details the development and performance of an AI-powered chatbot designed to streamline policy information access and boost agent productivity.
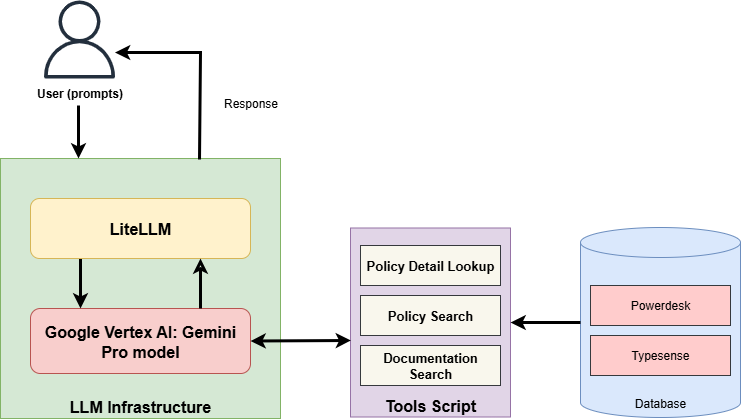
Researchers demonstrate the feasibility of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) based chatbot, Axlerod, as an effective agent-assistive tool in the insurtech landscape.
Despite growing demand for efficient workflows, independent insurance agents often face challenges accessing and interpreting complex policy information. This paper introduces Axlerod, an LLM-based chatbot designed to improve operational efficiency by serving as an agent-assistive tool. Experimental results demonstrate Axlerod’s robust capabilities in policy retrieval – achieving 93.18% accuracy and reducing search times – through the integration of natural language processing and retrieval-augmented generation. Could such agent-focused AI architectures represent a key pathway toward broader adoption of large language models within the insurtech industry?
Deconstructing the Insurance Paradigm: Agents in an Age of Intelligence
The insurance landscape is rapidly evolving, placing considerable strain on traditional agency workflows. Clients now anticipate highly personalized service and increasingly complex financial products, demanding more time and expertise from agents. This shift coincides with a surge in data availability and a growing need for sophisticated risk assessment. Consequently, agents are often overwhelmed, struggling to balance personalized attention with the administrative burdens of modern insurance-a situation that impacts both client satisfaction and operational efficiency. The traditional model, reliant on manual processes and generalized policies, is proving inadequate in meeting these new expectations, creating a critical juncture for the industry and fueling the search for innovative solutions.
The integration of artificial intelligence into insurance workflows offers a significant opportunity to enhance the capabilities of human agents, not by replacing them, but by streamlining complex tasks and providing data-driven insights. AI can automate routine processes – such as initial claim assessments and policy comparisons – freeing agents to focus on building client relationships and handling nuanced cases requiring empathy and critical thinking. However, successful implementation demands careful consideration; algorithms must be trained on representative data to avoid bias, and transparent decision-making processes are crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring regulatory compliance. Moreover, agents require training to effectively utilize AI tools and interpret their outputs, transforming data into actionable advice for clients. Ultimately, the most effective approach involves a collaborative partnership between human expertise and artificial intelligence, delivering a superior customer experience and optimizing operational efficiency.
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) represents a significant evolution in risk assessment, moving beyond traditional demographic factors to analyze real-world behavior and exposure. This innovative approach leverages the power of AI to dynamically adjust premiums based on individual usage patterns – for example, driving habits monitored through telematics, or property conditions assessed via smart home sensors. However, the success of UBI is inextricably linked to the robustness and reliability of the underlying AI systems. Accurate data processing, sophisticated machine learning algorithms, and stringent validation procedures are essential to prevent biased pricing, ensure fairness, and maintain customer trust. A flawed AI model could lead to inaccurate risk profiles, resulting in either underpricing – threatening insurer solvency – or overpricing, alienating customers and hindering adoption. Therefore, continuous monitoring, retraining, and ethical considerations are paramount for realizing the full potential of AI-driven UBI and establishing a sustainable, data-driven insurance ecosystem.
The Agent’s New Ally: Introducing the AI Assistant
The agent-assistive chatbot is designed to streamline insurance agent workflows by providing rapid responses to policy and coverage inquiries. This system functions as a direct support tool, enabling agents to address customer questions more efficiently and with increased precision. Implementation of the chatbot aims to reduce average response times and minimize errors in information delivery, ultimately enhancing both agent productivity and customer satisfaction. The system is intended to handle a high volume of inquiries, freeing up agents to focus on more complex cases and personalized customer interactions.
The agent-assistive chatbot utilizes Google Gemini 2.5 Pro, a Large Language Model (LLM), to process and interpret complex natural language queries related to insurance policies and coverage. Gemini 2.5 Pro’s architecture enables the chatbot to understand nuanced phrasing, identify key information within user requests, and formulate relevant responses. This LLM was selected for its demonstrated capabilities in contextual understanding and generation of human-quality text, allowing for a more effective and efficient interaction with insurance agents seeking information. The model’s parameters are optimized for the specific domain of insurance, improving its ability to accurately address agent inquiries.
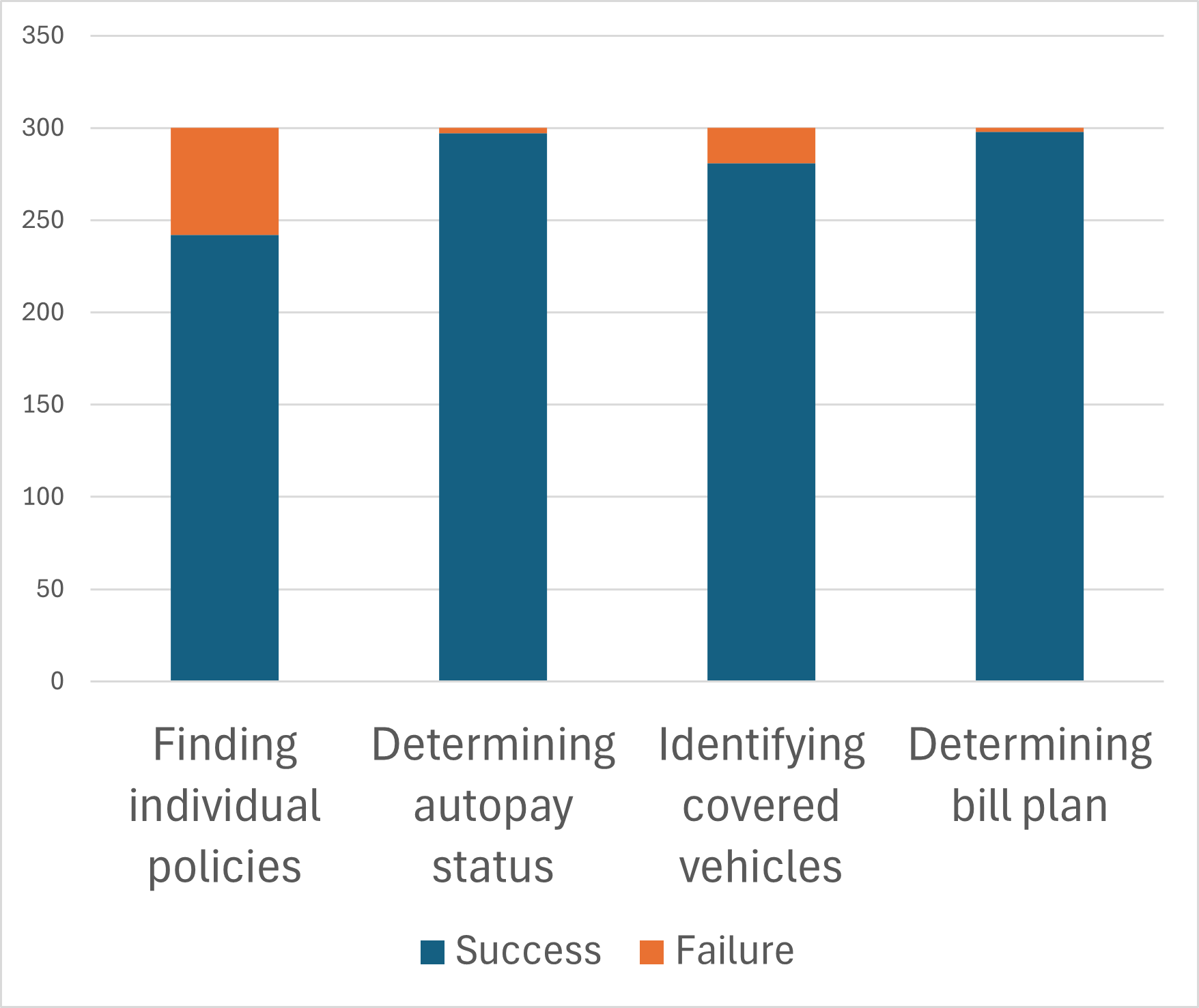
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a core component of the chatbot’s functionality, enabling it to synthesize responses based on a curated and current knowledge base of policy documentation and related data. This process involves first retrieving relevant information from the knowledge base based on the user’s query, and then using that retrieved content to inform the Large Language Model’s response generation. Testing has demonstrated an overall accuracy of 93.18% in retrieving pertinent policy-related information, ensuring responses are factually consistent and grounded in reliable sources, rather than relying solely on the LLM’s pre-trained parameters.
Dissecting the Machine: Technical Architecture and Key Components
The system’s Web API is built using FastAPI, a modern, fast (high-performance), web framework for building APIs in Python. This API serves as the primary interface through which the chatbot frontend communicates with the backend services. Specifically, the API receives user queries from the chatbot interface, routes them to the appropriate backend components for processing – including the LiteLLM proxy and the Policy Database – and then returns the processed responses back to the interface for display. FastAPI’s asynchronous capabilities are leveraged to handle concurrent requests efficiently, ensuring responsiveness even under high load. The API is designed to be stateless, promoting scalability and ease of deployment.
LiteLLM functions as an intermediary between the application and the Google Gemini 2.5 Pro large language model (LLM), abstracting the complexities of direct API interaction. This proxy layer streamlines API requests by handling request formatting, rate limiting, and error handling, reducing the development overhead associated with integrating the LLM. Crucially, LiteLLM manages authentication with the Google Gemini 2.5 Pro API, securely storing and transmitting API keys and tokens, thereby preventing direct exposure of credentials within the application code and simplifying key rotation procedures. This approach enhances security and facilitates easier management of the connection to the LLM.
The system’s knowledge base for policy-related questions is a dedicated Policy Database. This database stores and manages policy information and is paired with Typesense, a fast, open-source information search and analytics engine. Typesense functions as the indexing layer, enabling rapid and precise searches within the policy data. This indexing is critical for delivering timely and accurate responses to user inquiries, as it minimizes search latency and maximizes relevance of returned policy information.
Smoltalk is a microframework designed to facilitate agentic interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides the necessary infrastructure for LLMs to act as agents, enabling them to perform actions and utilize tools beyond simple text generation. This framework prioritizes a lightweight architecture, minimizing dependencies and maximizing performance. Specifically, Smoltalk handles the orchestration of tool calls, manages state during multi-step interactions, and simplifies the process of integrating LLMs with external APIs and services, allowing for complex, automated workflows.
Reshaping the Landscape: Impact and the Future of AI-Powered Insurance
The integration of an AI-powered chatbot is demonstrably streamlining insurance workflows through automation and readily available information. By handling routine tasks – such as addressing frequently asked questions and initiating standard requests – the chatbot significantly reduces the manual effort previously required of human agents. Studies reveal a quantifiable efficiency gain, with each task completed 2.42 seconds faster compared to traditional methods. This seemingly small reduction accumulates into substantial time savings over larger operational scales, allowing personnel to concentrate on more complex issues demanding critical thinking and personalized attention, ultimately boosting overall productivity and potentially improving customer satisfaction.
The integration of artificial intelligence into insurance workflows is redefining the role of the agent, shifting focus from repetitive tasks to nuanced client interactions. By automating routine inquiries and administrative duties, this agent-assistive AI frees up valuable time, allowing insurance professionals to concentrate on complex cases demanding critical thinking and personalized solutions. This newfound capacity facilitates deeper engagement with customers, enabling agents to build stronger, more trusting relationships based on a thorough understanding of individual needs and a proactive approach to service. Ultimately, the technology isn’t intended to replace the agent, but to augment their abilities, fostering a more human-centered experience within a rapidly evolving industry.
Recent advancements in AI-powered insurance demonstrate a remarkable capacity for automation with exceptionally high precision. The system consistently achieves 99.3% accuracy in correctly identifying customer bill plans, a critical function for efficient billing and account management. Furthermore, the technology exhibits 99.0% accuracy when enrolling policies in AutoPay, streamlining the payment process and reducing administrative overhead. This level of performance signifies a substantial improvement over manual processes, minimizing errors and freeing up human agents to concentrate on more nuanced customer interactions and complex case resolutions. The consistent reliability in these key tasks positions AI not simply as a cost-saving measure, but as a tool to enhance the overall quality and accuracy of insurance services.
The economic implications of this AI-powered chatbot extend beyond mere efficiency gains; at a cost of just $0.0075 per answer provided, the system dramatically reduces operational expenses for insurance providers. This remarkably low cost-per-interaction stems from the chatbot’s ability to handle a high volume of inquiries simultaneously, eliminating the need for extensive human resources dedicated to routine customer service. Such cost savings allow insurers to reinvest in innovation, offer more competitive pricing, or expand services without significantly impacting profitability. The economic model suggests a scalability that could fundamentally reshape customer interaction within the industry, making personalized and readily available support accessible at an unprecedentedly low cost.
The effective integration of artificial intelligence into insurance hinges not merely on technological capability, but on a steadfast commitment to ethical principles. Responsible AI implementation demands transparency in algorithmic processes, allowing for scrutiny of how decisions are reached and mitigating potential biases. Accountability mechanisms are crucial, establishing clear lines of responsibility when AI systems err or produce unintended consequences. Furthermore, fairness must be actively engineered into these systems, ensuring equitable outcomes across diverse customer demographics and avoiding discriminatory practices. Without careful consideration of these ethical dimensions, the benefits of AI in insurance risk being overshadowed by concerns regarding trust, equity, and societal impact, ultimately hindering widespread adoption and eroding public confidence.
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) is actively shaping the responsible integration of artificial intelligence within the insurance sector. Recognizing the transformative potential – and inherent risks – of AI, the NAIC is focused on establishing a robust framework of principles and standards to govern its application. This involves developing guidelines for data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and fairness to prevent biased outcomes in areas like risk assessment and claims processing. By fostering collaboration between state regulators, industry stakeholders, and AI experts, the NAIC aims to create a consistent national approach that encourages innovation while safeguarding consumer interests and maintaining the stability of the insurance market. This proactive stance positions the NAIC as a critical force in ensuring that AI’s benefits are realized equitably and ethically across the insurance landscape.
The development of Axlerod, as detailed in this paper, exemplifies a core principle of systems analysis: to truly understand a construct, one must relentlessly probe its boundaries. The chatbot isn’t merely a tool for retrieving policy information; it’s a stress test for the existing knowledge base and retrieval processes. As Claude Shannon observed, “Communication is the process of conveying meaning using symbols.” Axlerod forces a translation of complex insurance policies into accessible language, revealing ambiguities and gaps in the original ‘symbols’-the policy documents themselves. This iterative process of questioning and refinement, inherent in the LLM’s function, is akin to reverse-engineering reality, uncovering the inherent limitations and potential for improvement within the system.
Beyond Assistance: Deconstructing the Insurance Workflow
The demonstrated functionality of Axlerod, while promising, merely scratches the surface of what a language model integrated into the insurance ecosystem can achieve. Current iterations address information retrieval; the truly interesting challenge lies in automating the interpretive leaps agents routinely make. The system currently offers answers; future work must focus on enabling it to formulate questions – to proactively identify gaps in policy coverage or potential client needs before the agent even considers them. This isn’t about replacing expertise, but about externalizing the tedious aspects of it, allowing human agents to concentrate on genuinely novel situations.
A critical limitation remains the reliance on existing, structured data. Insurance, however, thrives on nuance – on the unwritten understandings between agent and client, and the grey areas within policy language. Future development should explore methods for Axlerod to ingest and learn from unstructured data – call transcripts, email correspondence, even agent notes – effectively reverse-engineering the tacit knowledge that currently defines exceptional service. Only then will the system move beyond being a sophisticated search engine and approach genuine cognitive augmentation.
The ultimate test won’t be whether Axlerod can answer questions about insurance, but whether it can find the questions that haven’t been asked yet – uncovering hidden risks and opportunities obscured by the very structure of the industry itself. The goal, fundamentally, isn’t automation for efficiency’s sake, but a controlled demolition of existing workflows, allowing for the construction of something demonstrably more robust – and, perhaps, more elegantly simple.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.09715.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Clash Royale Best Boss Bandit Champion decks
- Vampire’s Fall 2 redeem codes and how to use them (June 2025)
- World Eternal Online promo codes and how to use them (September 2025)
- Best Arena 9 Decks in Clast Royale
- Mobile Legends January 2026 Leaks: Upcoming new skins, heroes, events and more
- Country star who vanished from the spotlight 25 years ago resurfaces with viral Jessie James Decker duet
- How to find the Roaming Oak Tree in Heartopia
- Solo Leveling Season 3 release date and details: “It may continue or it may not. Personally, I really hope that it does.”
- M7 Pass Event Guide: All you need to know
- Kingdoms of Desire turns the Three Kingdoms era into an idle RPG power fantasy, now globally available
2026-01-17 23:49