Author: Denis Avetisyan
Researchers have developed an omni-multimodal assistant that proactively engages with live audio and video, marking a significant step towards truly interactive AI experiences.
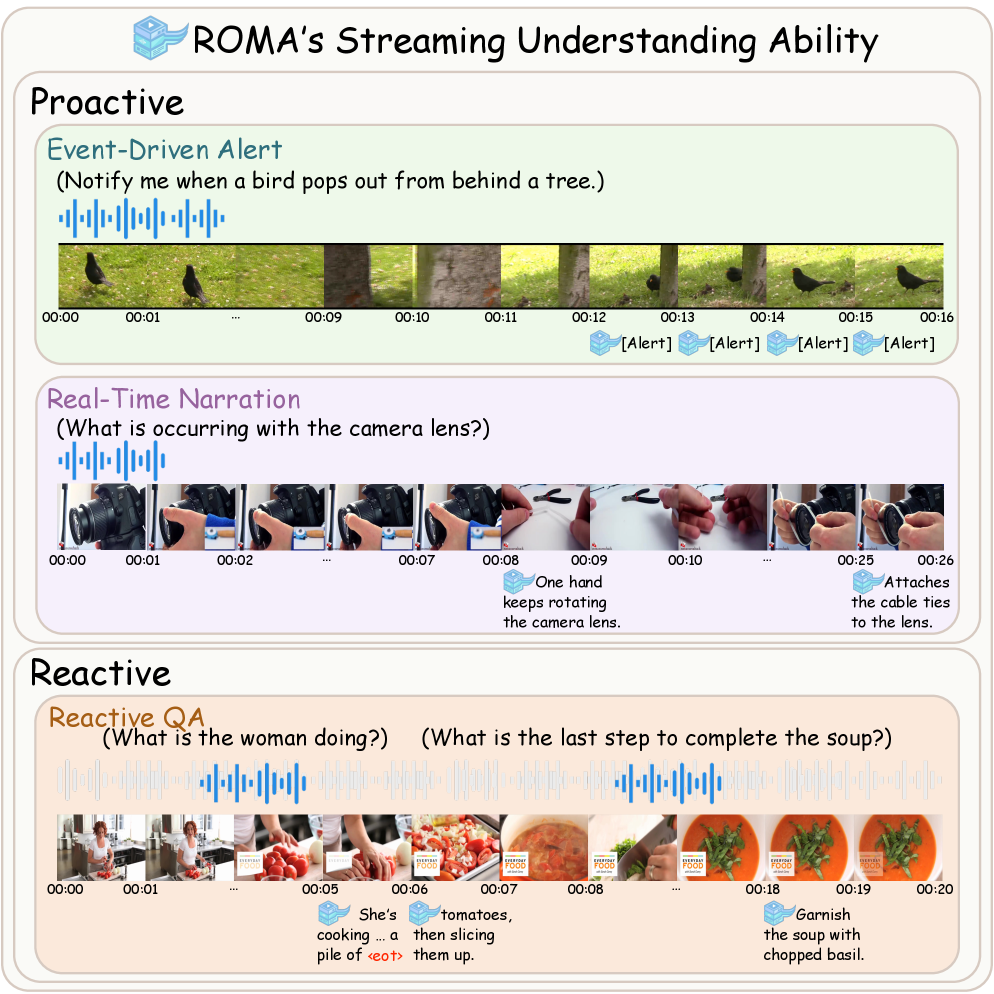
This work introduces ROMA, a system that unifies reactive question answering with proactive interaction for real-time streaming audio-video understanding through innovations in temporal alignment and model architecture.
Despite recent advances in omni-multimodal large language models, truly unified and real-time understanding of streaming audio-video data remains a significant challenge due to limitations in proactive monitoring and complete modality support. This paper introduces ROMA: Real-time Omni-Multimodal Assistant with Interactive Streaming Understanding, a novel framework designed for unified reactive and proactive interaction with continuous multimodal inputs. By introducing a lightweight ‘speak head’ for precise response initiation and a curriculum optimized for streaming data, ROMA achieves state-of-the-art performance on proactive tasks while maintaining competitive results in reactive settings. Could this approach pave the way for more intuitive and responsive AI assistants capable of seamlessly interpreting and interacting with the dynamic world around us?
The Illusion of Real-Time: Why Today’s AI Still Can’t Keep Up
Conventional Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable proficiency when confronted with defined, static datasets, excelling at tasks like text completion or translation given a fixed input. However, their architecture often falters when applied to the complexities of real-time data streams – think live video feeds, sensor networks, or continuous conversations. These models typically process information in discrete batches, creating a bottleneck when dealing with the unending flow of streaming data. This limitation significantly restricts their practical application in dynamic environments requiring immediate responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles navigating unpredictable conditions or sophisticated financial trading systems reacting to market fluctuations. The inability to efficiently process and interpret continuous inputs hinders the development of truly interactive and adaptive AI systems capable of functioning effectively in the real world.
The development of truly intelligent artificial systems necessitates a move beyond simply responding to immediate stimuli; a core obstacle lies in the efficient integration and sustained interpretation of multimodal data streams. Current AI frequently struggles to synthesize information arriving from diverse sources – such as video, audio, and text – and, crucially, to retain a coherent understanding of that information over time. This limitation prevents the creation of systems capable of anticipating needs or detecting subtle shifts in complex environments. Instead of merely reacting to questions, the next generation of AI requires the ability to proactively summarize ongoing events, identify emerging patterns, and maintain contextual awareness across extended periods, mirroring the human capacity for continuous comprehension and anticipatory reasoning.
The prevailing paradigm in artificial intelligence development currently emphasizes responding to specific queries – a reactive approach that limits the potential for genuinely interactive systems. While significant progress has been made in question answering, this often overshadows the crucial need for AI to proactively synthesize information and identify unfolding events. Instead of simply reacting to requests, a truly engaging AI requires the capacity for anticipatory summarization, distilling meaning from continuous data streams, and recognizing patterns that signal important developments. This shift from reactive response to proactive understanding is fundamental; it’s the difference between an AI that feels like a tool and one that feels like a collaborative partner, capable of offering insights before being asked and adapting to dynamic real-world scenarios.
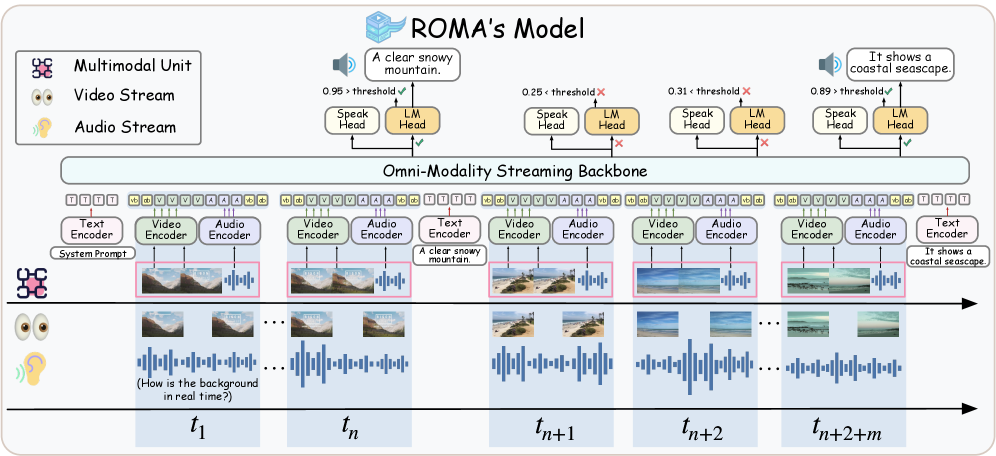
ROMA: A Band-Aid on the Latency Problem
ROMA is a novel system architecture designed for real-time processing of continuous data streams. Unlike traditional models focused on discrete inputs, ROMA simultaneously supports both reactive question answering – responding to user queries about the ongoing stream – and proactive narration, providing contextual descriptions of the stream’s content as it unfolds. This dual capability is achieved through a unified framework that handles incoming audio and video data as a continuous sequence, enabling the model to maintain context and provide relevant responses or narrations without requiring complete data ingestion. The architecture prioritizes low-latency processing to facilitate natural, interactive experiences with streaming content.
ROMA’s performance is significantly enhanced by a two-stage fine-tuning process. Initially, the model undergoes pre-training on a large corpus of general data to establish a foundational understanding of language and multimodal inputs. Subsequently, a specialized fine-tuning stage focuses on streaming data formats and minimizing response latency. This second stage utilizes datasets specifically designed to simulate real-time interaction, emphasizing the ability to generate coherent responses with low delay. The process optimizes the model for both the accurate interpretation of continuous data streams and the timely delivery of relevant outputs, resulting in a system capable of near real-time performance in multimodal assistant applications.
The Speak Head module within the ROMA architecture addresses the challenge of latency in real-time multimodal assistants by separating the generation of content from the determination of when to deliver a response. Traditionally, these processes are tightly coupled, forcing the model to complete content generation before any output can be initiated. Speak Head introduces a dedicated mechanism for controlling response timing, allowing the system to begin speaking or displaying information incrementally as it becomes available, even before the complete response is formulated. This decoupling facilitates a more natural and responsive interaction by minimizing perceived delays and enabling the assistant to react to streaming data with lower latency, improving the user experience.
ROMA utilizes Time-aligned Multimodal RoPE (TMRoPE) as a core component for processing audio-video streams. TMRoPE is an encoding technique designed to efficiently represent and align temporal information within multimodal data. This alignment is achieved by incorporating positional encodings that are sensitive to the timing of audio and video frames, enabling the model to understand the relationships between events across both modalities. Critically, TMRoPE supports incremental processing, meaning the model can process data as it arrives in a stream without requiring the entire sequence to be available beforehand, which is essential for real-time applications and reduces computational latency.
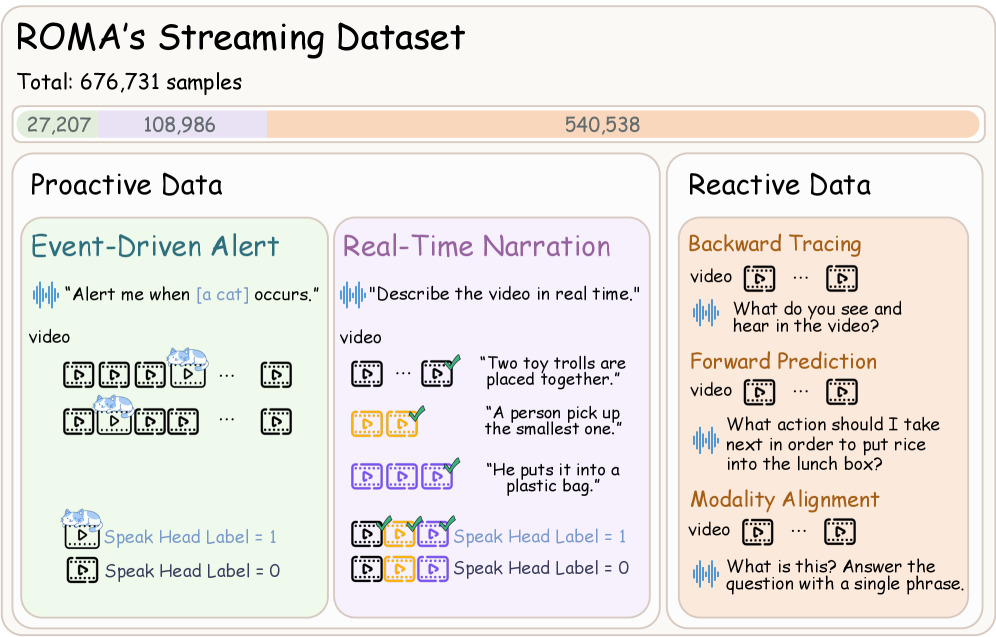
Benchmarking: Proving What We Already Know
The Streaming Dataset was designed to provide a comprehensive and rigorous evaluation of video understanding models in real-time scenarios. It incorporates three core task types: proactive narration, which requires generating descriptions of ongoing events; reactive question answering, assessing the model’s ability to respond to queries about the video content; and event detection, focusing on identifying specific occurrences within the video stream. This multi-faceted approach ensures a holistic assessment of a model’s capabilities beyond static video analysis, simulating the demands of live video processing applications. The dataset’s composition allows for evaluation of both descriptive and analytical skills in a dynamic context, providing a robust platform for benchmarking and comparative analysis.
ROMA achieved state-of-the-art performance on the YouCook2 dataset for real-time narration, attaining a F1 Score of 35.21. This result represents the highest score currently reported on this benchmark, indicating ROMA’s advanced capabilities in proactively describing ongoing activities within video content. The YouCook2 dataset specifically assesses a model’s ability to generate narrations that accurately reflect the actions and events as they unfold, requiring both temporal understanding and descriptive accuracy. This performance underscores ROMA’s effectiveness in streaming video analysis tasks where immediate and precise narration is critical.
Evaluation of ROMA on QVHighlights demonstrates strong performance in video understanding tasks. Specifically, the model achieved a mean Average Precision (mAP) of 53.7 on the static temporal grounding benchmark. Furthermore, ROMA attained a Recall at 0.5 (R@0.5) score of 44.3 on the Charades-STA dataset, indicating its ability to accurately identify and localize actions within video sequences. These metrics quantify the model’s proficiency in associating actions with specific temporal segments within the video data.
ROMA’s capacity for Event-Driven Alert tasks indicates its suitability for applications demanding immediate reactions to changing circumstances. This functionality allows the model to detect and flag specific events within a video stream, enabling real-time notifications or automated responses. The system is designed to process incoming video data and identify pre-defined events with minimal latency, which is critical for scenarios like security monitoring, anomaly detection, or interactive assistance where timely awareness of dynamic occurrences is paramount. Performance metrics in this area focus on both detection accuracy and response time, highlighting the model’s potential for deployment in time-sensitive, real-world applications.
Real-time narration quality was assessed using GPT-4o to evaluate ROMA’s generated summaries for coherence, alignment with visual content, and conciseness. This evaluation, conducted on both the YouCook2 and OVO-Bench datasets, resulted in an F1 score of 14.54, representing the highest performance achieved on these benchmarks to date. The results demonstrate ROMA’s capacity to produce accurate and succinct descriptions of dynamic events as they unfold, confirming its effectiveness in applications requiring continuous and relevant commentary.

The Illusion of Progress: Where Do We Go From Here?
To effectively handle increasingly complex real-time data streams, continued refinement of the Retrieval-augmented Open Memory Architecture (ROMA) is paramount. Current research focuses on optimizing core components like the KV-Cache, employing techniques such as intelligent scheduling and data compression. These advancements aren’t merely about speed; they address the escalating memory demands inherent in processing prolonged, multifaceted streams. By minimizing the storage footprint and maximizing retrieval efficiency of the KV-Cache, ROMA can maintain responsiveness even with extensive contextual information. This focus on efficient resource management isn’t simply a technical necessity, but a key enabler for deploying proactive intelligence in resource-constrained environments and scaling to applications involving numerous concurrent data streams, ultimately broadening the scope of real-time AI possibilities.
The true potential of real-time intelligence systems like ROMA lies in their ability to synthesize information beyond simple text or speech. Integrating diverse multimodal inputs – encompassing sensor data such as temperature, pressure, and motion, alongside environmental streams like weather patterns or traffic flow – allows for a far richer and more nuanced understanding of the surrounding world. This expanded awareness moves beyond reactive responses to enable genuinely proactive intelligence, where systems anticipate needs and opportunities based on a holistic assessment of conditions. For example, a ROMA-powered system could correlate rising humidity with predicted pollen levels and preemptively adjust building ventilation, or combine traffic data with calendar appointments to suggest optimal departure times. By effectively merging these varied data streams, the system can move beyond processing information to generating insightful, context-aware actions that are truly predictive and adaptive.
Refinements to the Speak Head module represent a crucial pathway towards more compelling and natural human-computer interactions. Current research indicates that tailoring response timing – the pauses and pacing of generated speech – to individual user preferences dramatically improves perceived responsiveness and reduces cognitive load. Beyond timing, variations in stylistic elements, such as formality, emotional tone, and even subtle linguistic choices, promise to create a uniquely personalized experience. This adaptation isn’t merely cosmetic; studies suggest that aligning the AI’s communication style with a user’s own preferences fosters trust, enhances engagement, and ultimately increases the effectiveness of the interaction. Future iterations of Speak Head will likely incorporate machine learning algorithms capable of dynamically adjusting these parameters based on ongoing analysis of user behavior and feedback, moving beyond a one-size-fits-all approach to truly personalized conversational AI.
The architectural foundations of Real-time Omnimodal Multitask Agent – namely its emphasis on anticipating information needs, processing diverse data streams concurrently, and separating cognitive processing from temporal constraints – represent a broadly applicable blueprint for intelligent systems. These principles transcend the specific application of conversational AI and hold significant promise for advancements in fields like robotics, where agents must react to dynamic environments and integrate visual, tactile, and auditory information in real-time. Similarly, autonomous systems, from self-driving vehicles to drone navigation, could benefit from ROMA’s decoupled timing, allowing for robust performance even with variable sensor input and computational delays. By prioritizing proactive understanding over reactive responses, and by efficiently handling multiple modalities, this approach offers a pathway toward more adaptable, resilient, and truly intelligent machines capable of operating effectively in complex, real-world scenarios.
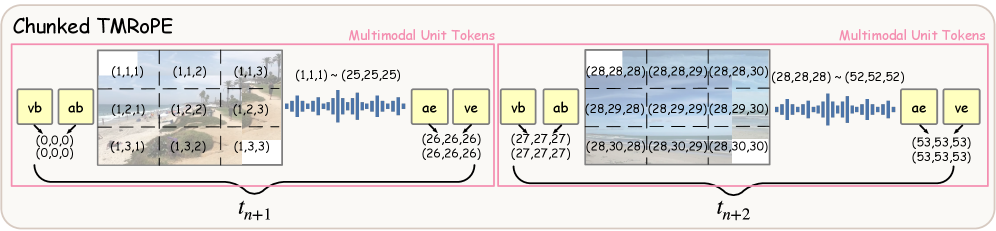
The pursuit of a truly ‘real-time’ omni-multimodal assistant, as demonstrated by ROMA, inevitably courts future technical debt. This framework, with its innovations in temporal alignment and chunked Time-aligned Multimodal RoPE, attempts to bridge the gap between reactive and proactive interaction. However, it’s a temporary victory. As David Marr observed, “A system must do enough to support the appearance of intelligent behavior.” ROMA achieves that appearance now, but production environments will undoubtedly reveal edge cases and necessitate further refinement. The elegance of the architecture is almost beside the point; the system’s stability, and the reproducibility of its responses, will ultimately define its worth, not its initial benchmark scores.
Beyond the Stream
The pursuit of a truly ‘omniscient’ assistant, as ROMA attempts, invariably reveals the limitations of current alignment strategies. Achieving state-of-the-art results on standardized benchmarks offers a fleeting comfort; production environments will undoubtedly expose corner cases where temporally aligned multimodal reasoning collapses under the weight of unpredictable input. The elegance of chunked Time-aligned Multimodal RoPE will be tested not by carefully curated datasets, but by overlapping speech, background noise, and the sheer chaos of unscripted interaction.
Future work will likely focus on robustness, specifically on graceful degradation rather than brittle perfection. The proactive/reactive dichotomy, while useful for framing the problem, feels inherently incomplete. Real intelligence isn’t simply answering questions or anticipating needs; it’s knowing when to do neither. The field will need to grapple with the problem of ‘helpful silence’ – a system’s ability to recognize its own uncertainty and refrain from confidently offering incorrect information.
One suspects that the true measure of success won’t be accuracy, but resilience. A system that can survive Monday morning, despite being bombarded with edge cases, is a far more valuable achievement than one that excels in a lab. Tests are, after all, a form of faith, not certainty. The next iteration won’t be about building a smarter assistant; it will be about building one that’s simply… less likely to break.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.10323.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Clash Royale Best Boss Bandit Champion decks
- Vampire’s Fall 2 redeem codes and how to use them (June 2025)
- World Eternal Online promo codes and how to use them (September 2025)
- Best Arena 9 Decks in Clast Royale
- Mobile Legends January 2026 Leaks: Upcoming new skins, heroes, events and more
- Country star who vanished from the spotlight 25 years ago resurfaces with viral Jessie James Decker duet
- How to find the Roaming Oak Tree in Heartopia
- M7 Pass Event Guide: All you need to know
- Solo Leveling Season 3 release date and details: “It may continue or it may not. Personally, I really hope that it does.”
- Kingdoms of Desire turns the Three Kingdoms era into an idle RPG power fantasy, now globally available
2026-01-18 13:11