Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research demonstrates that equipping AI agents with curated skills dramatically boosts performance across diverse tasks, offering a significant leap beyond simple prompt engineering.
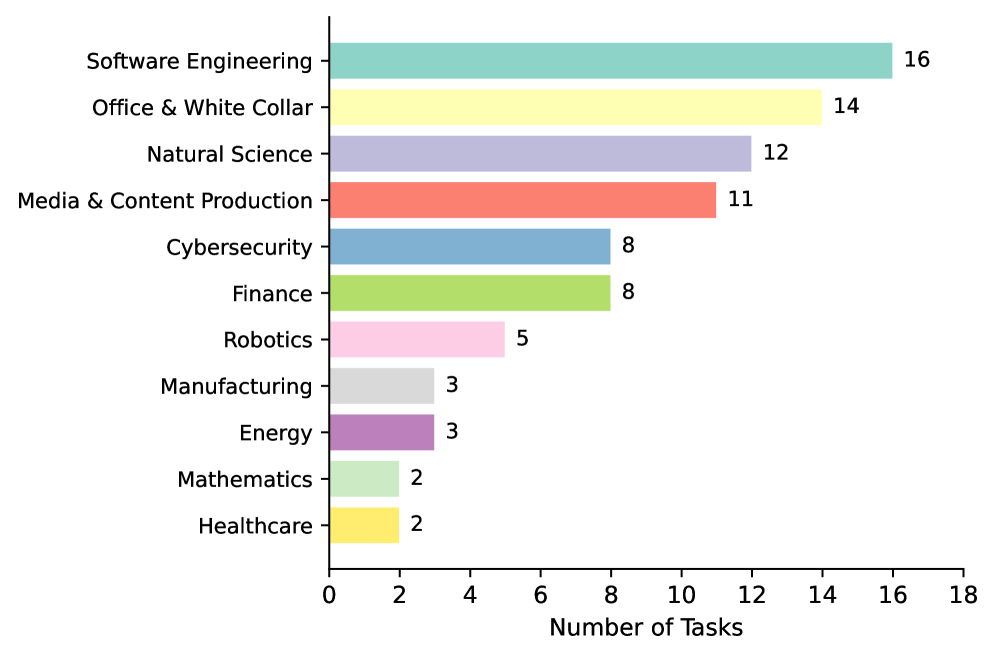
SkillsBench, a new benchmark, reveals that pre-defined agent skills consistently outperform self-generated skills in real-world task completion.
Despite the increasing use of ‘Agent Skills’ to augment large language model agents, a standardized evaluation of their efficacy has remained elusive. To address this gap, we introduce SkillsBench: Benchmarking How Well Agent Skills Work Across Diverse Tasks, a comprehensive benchmark evaluating curated and self-generated skills across 86 tasks and 11 domains. Our results demonstrate that curated skills significantly improve average pass rates by [latex]16.2[/latex] percentage points, though performance varies substantially, while self-generation offers no discernible benefit. This raises a critical question: can we reliably engineer procedural knowledge to consistently enhance agent capabilities, and what constitutes the optimal structure for these skills?
The Inevitable Plateau of Intelligence
While Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased remarkable abilities in generating text and responding to prompts, their performance often diminishes when confronted with tasks demanding extended reasoning or multiple sequential steps. These models, though proficient at pattern recognition and information retrieval, frequently struggle with maintaining context and consistently applying logic across a prolonged series of operations. This limitation stems from their inherent design – optimized for predicting the next token in a sequence rather than for deliberate, goal-oriented problem-solving. Consequently, LLM-based agents, even with sophisticated prompting, can falter in scenarios requiring careful planning, error correction, and the integration of information gathered over time, highlighting a crucial need for architectures that enhance sustained cognitive processes.
Successful execution of intricate tasks by intelligent agents isn’t solely dependent on the power of large language models, but critically relies on providing them with both specialized knowledge and clear instructions. Access to relevant, domain-specific information allows an agent to move beyond generalized responses and address the nuances of a particular challenge, while robust procedural guidance establishes a framework for tackling multi-step problems. Without this combination, even sophisticated models can falter, demonstrating the necessity of equipping agents with the right information and a well-defined process to follow. This suggests that future advancements will likely focus on methods for seamlessly integrating external knowledge sources and formalized workflows into agent architectures, rather than simply scaling model size.
Evaluating the true impact of equipping Large Language Model-based agents with specialized skills has proven challenging, as standardized benchmarks have been largely absent. Recent work introducing SkillsBench directly addresses this gap by offering a rigorous evaluation framework. Through curated ‘Skills’ – modular, reusable functions designed to enhance agent capabilities – the study demonstrates a significant average performance improvement of +16.2 percentage points across a diverse set of tasks. This finding highlights the potential of augmenting LLMs with focused expertise, moving beyond general language proficiency towards more reliable and capable agents capable of tackling complex, real-world problems, and provides a clear methodology for assessing the value of these augmentations.
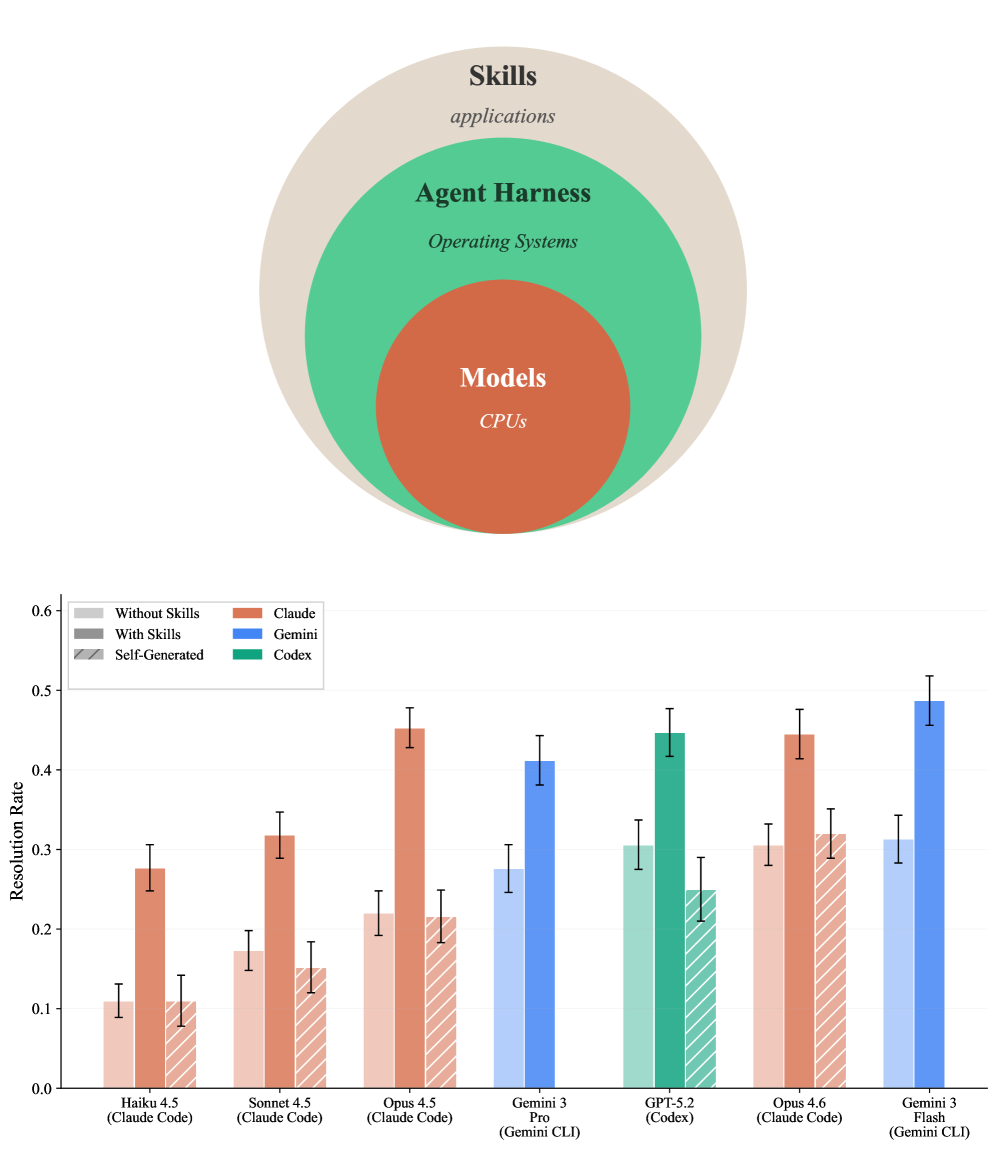
Deconstructing the Agent: A Modular Approach to Intelligence
SkillsBench is a newly developed benchmark intended to rigorously assess the performance of discrete Agent Skills when utilized as independent, evaluable components. Unlike traditional end-to-end agent evaluation, SkillsBench focuses on isolating and measuring the efficacy of individual skills – such as tool use, planning, or memory – allowing for granular analysis of agent capabilities. This approach treats skills as first-class artifacts, meaning they are explicitly defined, versioned, and subject to dedicated testing procedures. The framework facilitates a modular evaluation process, enabling developers to identify skill-specific bottlenecks and optimize individual components without requiring complete retraining of the entire agent system, ultimately promoting more targeted and efficient agent development.
SkillsBench utilizes containerization, specifically Docker, to encapsulate each task’s execution environment, ensuring consistent results regardless of the host system. This isolation addresses concerns about dependency conflicts and environment variability that can impact reproducibility in agent evaluation. Deterministic verification is achieved through the use of predefined input-output pairs for each task; agent responses are rigorously compared against these expected outputs using exact matching, eliminating ambiguity in performance assessment. This combination of containerization and deterministic verification provides a robust and reliable system for evaluating agent skills, minimizing the influence of external factors and maximizing the validity of comparative results.
SkillsBench incorporates robust context management to mitigate the limitations of token constraints inherent in large language model (LLM) interactions. The benchmark’s evaluation protocol specifically addresses the need to retain relevant input history while staying within model token limits, a critical factor for maintaining performance across multi-turn tasks. Through testing 7 distinct agent-model configurations across a diverse set of 84 tasks, SkillsBench quantitatively demonstrates how effective context management, facilitated by skill augmentation, impacts agent performance and reliability. These evaluations establish a measurable correlation between the implemented context management strategies and the agent’s ability to successfully complete tasks requiring memory of prior interactions.
![SkillsBench combines skills from diverse sources-open-source repositories, the Claude Code ecosystem, and corporate partners-to create a benchmark of 84 rigorously vetted tasks, demonstrating a [latex] +12.66\% [/latex] average performance improvement when utilizing curated skills across three commercial agent harnesses and seven agent-model configurations.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.12670v1/x2.png)
Measuring the Increment: Quantifying Skill Efficacy
SkillsBench employs Normalized Gain as its primary metric for evaluating skill efficacy, addressing the necessity for a baseline-adjusted performance measurement. Normalized Gain calculates the improvement in performance relative to the agent’s initial capabilities on a given task, providing a standardized value independent of task difficulty or absolute performance level. This metric is calculated as the difference between post-skill and pre-skill performance, divided by the maximum possible improvement from the baseline. Utilizing Normalized Gain allows for a direct comparison of skill effectiveness across diverse tasks and agent states, facilitating objective assessment of skill acquisition and refinement, and ensuring that observed gains are genuinely attributable to the implemented skills rather than inherent improvements over time or task repetition.
The SkillsBench framework accommodates two distinct skill origins: Curated Skills, which are pre-defined by human experts, and Self-Generated Skills, which are dynamically created by the agent during operation. Analysis of self-generated skills reveals an average change in task pass rate of -1.3 percentage points, indicating a slight performance decrease when compared to baseline or curated skill application. This suggests that while agents can autonomously develop skills, refinement and optimization are often necessary to achieve performance parity with expertly designed solutions.
Performance improvements resulting from the implementation of Skills are directly correlated with task complexity; more challenging tasks exhibit the most significant gains. Analysis demonstrates that tasks requiring higher cognitive load, such as mario-coin-counting, sales-pivot-analysis, flood-risk-analysis, and sec-financial-report, benefited substantially from skillful augmentation. Specifically, these tasks showed normalized gain improvements of up to +85.7 percentage points, indicating a considerable increase in successful task completion rates attributable to the deployed Skills framework.
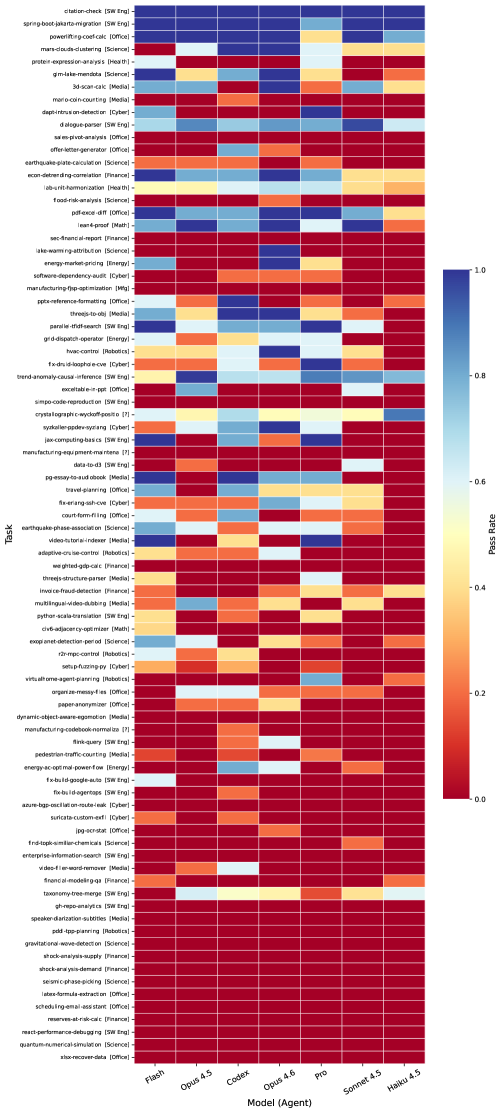
The Ecosystem of Intelligence: Diverse Harnesses and Diminishing Returns
The SkillsBench framework is actively leveraging a diverse collection of agent harnesses – including powerful language models like Claude Code, the versatile Codex CLI, and Google’s Gemini CLI – to rigorously deploy and evaluate Agent Skills. This multi-harness approach isn’t simply about choice; it’s a crucial element in ensuring the robustness and generalizability of skill augmentation. By testing skills across these varied platforms, researchers can identify which capabilities consistently enhance agent performance, regardless of the underlying execution environment. The utilization of these established harnesses streamlines the evaluation process and allows for standardized benchmarking, fostering a more reliable comparison of different skill implementations and ultimately accelerating the development of truly capable skill-augmented agents.
The Harbor Framework addresses a critical need for reliable agent evaluation by providing a consistent and isolated execution environment. This system leverages containerization technology, ensuring that agent tasks are run under standardized conditions, irrespective of the underlying hardware or software configurations. By encapsulating all dependencies within a container, Harbor minimizes variations that could skew results and impede reproducibility – a common challenge in complex agent-based systems. This approach allows researchers and developers to confidently compare agent performance across different setups and iterations, fostering a more robust and verifiable development process. The framework’s emphasis on consistency facilitates not only rigorous testing but also streamlined deployment, enabling the reliable translation of research findings into practical applications.
The development of skill-augmented agents is increasingly driven by a collaborative spirit, evidenced by a growing ecosystem of tools and frameworks designed to rigorously evaluate and deploy these systems. Recent studies utilizing this infrastructure reveal a key principle for optimization: while integrating skills demonstrably enhances agent performance, the benefits plateau after incorporating two to three skills. Beyond this threshold, diminishing returns are observed, suggesting that simply adding more skills does not necessarily translate to continued improvement. This finding underscores the importance of strategic skill selection and careful evaluation, moving the field towards a more nuanced understanding of how to best augment agent capabilities and maximize their potential.
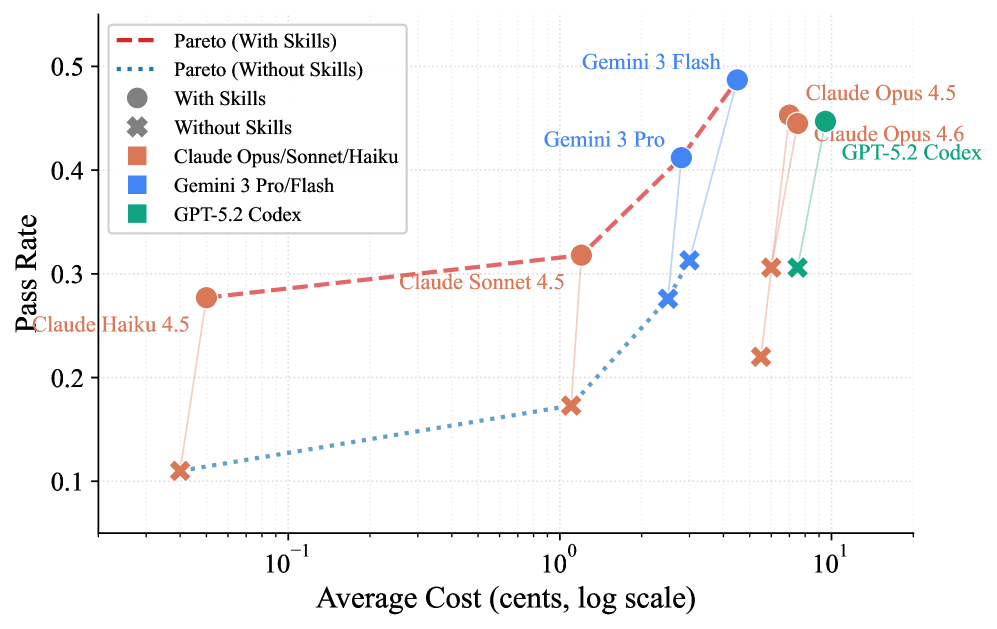
The pursuit of robust agent capabilities, as demonstrated by SkillsBench, isn’t about imposing rigid structures, but cultivating an environment where pre-defined competencies can flourish. This echoes a fundamental truth: systems aren’t built, they’re grown. The benchmark’s findings-that curated skills dramatically outperform self-generated ones-suggests a similar principle applies to artificial intelligence. It’s not enough to simply task an agent with learning a skill; the efficacy lies in providing a foundation of procedural knowledge, a carefully cultivated skillset upon which true resilience begins where certainty ends. As Linus Torvalds observed, ‘Talk is cheap. Show me the code.’ SkillsBench doesn’t just discuss improved agent performance; it demonstrates it, offering concrete evidence of what works and, crucially, what doesn’t.
What Lies Ahead?
SkillsBench reveals a familiar pattern: curation outperforms generation. The system does not discover competence; it accumulates it. This is less a breakthrough and more a restatement of ecological principles. A forest doesn’t invent trees; it inherits them. The benchmark itself is not the destination, but a carefully illuminated patch within a vast, unmapped wilderness of potential failure modes. Each curated skill represents a known constraint, a prediction of where the system will falter when presented with the unexpected.
The true challenge isn’t building agents that perform well today, but understanding how to build systems that gracefully degrade tomorrow. The observed limitations of self-generated skills suggest a fundamental mismatch between the procedural knowledge agents currently claim to possess and the tacit knowledge required for genuine adaptation. A useful line of inquiry lies not in perfecting skill generation, but in developing methods to reliably audit an agent’s internal model – to expose the gaps between assertion and ability before they manifest as critical errors.
Ultimately, SkillsBench is a cartography of present ignorance. It maps what works now, but says little about the inevitable drifts and distortions that will occur as the system evolves. The benchmark will age, its tasks will become trivial, and new failure modes will emerge. The work, therefore, is not to solve the problem of agent skill, but to design systems capable of continuously re-evaluating, and re-curating, themselves.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.12670.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Star Wars Fans Should Have “Total Faith” In Tradition-Breaking 2027 Movie, Says Star
- Jessie Buckley unveils new blonde bombshell look for latest shoot with W Magazine as she reveals Hamnet role has made her ‘braver’
- Country star Thomas Rhett welcomes FIFTH child with wife Lauren and reveals newborn’s VERY unique name
- eFootball 2026 is bringing the v5.3.1 update: What to expect and what’s coming
- Decoding Life’s Patterns: How AI Learns Protein Sequences
- Mobile Legends: Bang Bang 2026 Legend Skins: Complete list and how to get them
- Denis Villeneuve’s Dune Trilogy Is Skipping Children of Dune
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Peppa Pig will cheer on Daddy Pig at the London Marathon as he raises money for the National Deaf Children’s Society after son George’s hearing loss
- Are Halstead & Upton Back Together After The 2026 One Chicago Corssover? Jay & Hailey’s Future Explained
2026-02-17 07:04