Author: Denis Avetisyan
Researchers are building artificial intelligence models that move beyond simple text generation to simulate and understand the complexities of human cognition and behavior.
This paper introduces HumanLLM, a foundation model trained on the Cognitive Genome Dataset, aiming to improve social intelligence through personalized simulation of human nature.
While large language models excel at objective tasks, they often lack the nuanced understanding of human cognition necessary for accurately simulating individual behavior. This limitation motivates the work presented in ‘HumanLLM: Towards Personalized Understanding and Simulation of Human Nature’, which introduces a foundation model designed for personalized understanding by leveraging real-world user data. Through the construction of the Cognitive Genome Dataset-a large-scale corpus of over 5.5 million user logs-and subsequent supervised fine-tuning, HumanLLM demonstrates superior performance in predicting user actions, mimicking writing styles, and generalizing to social intelligence benchmarks. Could this approach unlock more authentic and insightful simulations of human behavior across diverse applications, from social science to customer-centric business solutions?
Laying the Foundation: Understanding the Cognitive Landscape
Artificial intelligence, despite recent advancements, often struggles to accurately interpret the subtleties of human behavior, hindering its effectiveness in real-world social applications. Current models frequently operate on a surface level, failing to grasp the underlying motivations, emotional nuances, and contextual factors that drive human interactions. This limitation stems from a lack of comprehensive training data that captures the full spectrum of human expression; existing datasets often prioritize factual information over the complexities of sentiment, intent, and social dynamics. Consequently, AI systems may misinterpret cues, provide inappropriate responses, or fail to adapt to the ever-changing landscape of human communication, ultimately restricting their potential in areas like customer service, mental health support, and collaborative problem-solving.
The Cognitive Genome Dataset represents a significant step towards imbuing artificial intelligence with a more human-like understanding of the world. This expansive resource was built by systematically collecting publicly available text from a variety of online platforms-including Reddit, Twitter, Blogger, and Amazon-to capture the breadth and nuance of human expression. With a combined total exceeding 571.54 million data points from Amazon reviews and 88.1 million from Twitter, the dataset provides a large-scale repository of authentic communication. By drawing from these diverse digital spaces, researchers gain access to a rich tapestry of opinions, emotions, and thought processes, ultimately fostering the development of AI systems capable of more sophisticated social interaction and contextual awareness.
The Cognitive Genome Dataset draws upon the vast landscape of online communication, integrating contributions from multiple platforms to create a comprehensive resource for understanding human expression. Specifically, the dataset aggregates over 571.54 million data points sourced from Amazon reviews-a rich repository of opinions and detailed product feedback-alongside 88.1 million posts from Twitter, capturing concise, real-time reactions and discussions. This combined volume, representing diverse perspectives and communication styles, provides a substantial foundation for training artificial intelligence models to better interpret and respond to the nuances of human behavior in social contexts. The sheer scale of integrated data allows for more robust analysis and the identification of patterns that might be missed in smaller, more focused datasets.
The Cognitive Genome Dataset’s utility hinges on the meticulous procedures employed to guarantee data integrity. A multi-stage quality control process began with rigorous filtering to remove irrelevant or corrupted data points, followed by synthesis techniques to consolidate information from diverse sources into a standardized format. Crucially, verification protocols were implemented to cross-reference and validate entries, minimizing inconsistencies and errors. This commitment to data reliability ensures that the dataset provides a stable and trustworthy foundation for research into human cognition and behavior, allowing for meaningful analysis and robust conclusions. The resulting high-quality dataset offers researchers confidence in the accuracy and consistency of the information it contains.
HumanLLM: Modeling the Architecture of Social Intelligence
HumanLLM is a foundational large language model (LLM) specifically engineered to replicate and interpret human cognitive processes and behavioral patterns. Unlike conventional LLMs primarily focused on text generation, HumanLLM aims to model the underlying mechanisms of human thought and action. This is achieved through a novel training methodology and architectural design intended to move beyond superficial text prediction towards a functional simulation of human cognition. The model serves as a platform for researching and developing artificial intelligence systems capable of demonstrating nuanced social understanding and adaptive behavior in complex environments.
HumanLLM leverages large language model fine-tuning techniques applied to the Cognitive Genome Dataset, a curated collection of data designed to represent complex human behaviors and expressions. This training process moves beyond superficial textual analysis by exposing the model to a broad range of cognitive patterns, including emotional responses, social cues, and motivational factors. The dataset’s structure allows HumanLLM to identify and internalize intricate relationships between inputs and likely human reactions, enabling the model to predict and simulate nuanced communicative behaviors. Consequently, the model develops an ability to recognize and reproduce patterns in human expression that are often implicit or unstated in direct textual communication.
The training process for HumanLLM moves beyond traditional language modeling tasks focused solely on predicting subsequent text. By utilizing the Cognitive Genome Dataset, the model learns to associate linguistic patterns with underlying cognitive states and social contexts. This enables HumanLLM to infer the motivations, intentions, and emotional states driving human communication, and to model the complex interplay of social dynamics present in various interactions. Consequently, the model doesn’t simply reproduce language; it develops a representational understanding of why certain language is used in given situations, facilitating more nuanced and contextually appropriate responses.
The HumanLLM architecture incorporates a multi-layered approach to simulate cognitive processes relevant to social intelligence. Specifically, it utilizes a combination of transformer networks and attention mechanisms to model not only linguistic input but also inferred emotional states and behavioral intentions. This is achieved through the integration of the Cognitive Genome Dataset during fine-tuning, allowing the model to learn complex relationships between expressed language, underlying motivations, and predicted social responses. The architecture prioritizes the representation of nuanced contextual information, enabling a more sophisticated understanding of social dynamics than traditional language models and extending the capabilities of AI in areas requiring social awareness and interaction.
Measuring Social Acumen: The MotiveBench and TomBench Assessments
MotiveBench is a benchmark dataset designed to evaluate a language model’s capacity for reasoning about the underlying motivations and intentions of human actors in diverse situations. The benchmark presents scenarios requiring the model to infer the reasons behind observed actions, considering factors such as goals, beliefs, and desires. Evaluation metrics focus on the accuracy of these inferred motivations, assessing whether the model can correctly identify the driving forces behind human behavior as presented in the scenarios. HumanLLM was subjected to MotiveBench testing to quantitatively measure its performance in this specific area of social intelligence, providing a comparative basis against other language models.
TomBench is a benchmark designed to assess a language model’s comprehension of human social dynamics, focusing on the interpretation of communicative intent and behavior. The benchmark presents scenarios requiring an understanding of subtle social cues, such as implied meaning, politeness, and the ability to infer unstated beliefs or goals from dialogue and actions. Evaluation metrics within TomBench quantify the model’s accuracy in predicting appropriate responses, identifying deceptive statements, and recognizing the emotional states of individuals within given social contexts. Its construction emphasizes scenarios that require reasoning beyond literal interpretations of language, testing the model’s capacity for pragmatic and affective understanding of human interaction.
Quantitative evaluation using MotiveBench and TomBench demonstrates a performance advantage for the HumanLLMQwen3 model compared to GPT-4o. HumanLLMQwen3 achieved an average score of 0.7427 on MotiveBench, a benchmark designed to assess reasoning about human motivations, and a score of 0.6589 on TomBench, which evaluates understanding of social reasoning and communication. These scores represent the model’s overall performance across the respective benchmark datasets and indicate a higher level of accuracy in interpreting and predicting human behavior compared to GPT-4o on these specific tests.
Evaluation using MotiveBench and TomBench indicates HumanLLM, specifically the HumanLLMQwen3 version, demonstrates a statistically significant improvement in understanding human social intelligence compared to GPT-4o. HumanLLM achieved an average score of 0.7427 on MotiveBench and 0.6589 on TomBench, exceeding the performance of GPT-4o on both benchmarks. These scores suggest a greater capacity to accurately interpret human motivations, intentions, and nuanced social cues, providing empirical support for the claim of a more profound grasp of social intelligence.
Expanding the Horizon: Real-World Applications and Future Directions
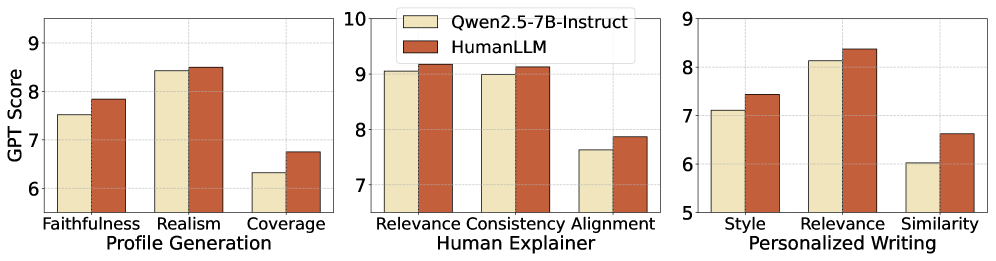
HumanLLM demonstrates a notable capacity for constructing comprehensive and believable user profiles, moving beyond simple demographic data to encompass nuanced behavioral patterns and preferences. This profile generation isn’t merely about identifying traits; the model synthesizes information to create a holistic representation of an individual, anticipating potential needs and responses with surprising accuracy. Such detailed profiles unlock the potential for truly personalized AI experiences, allowing applications to adapt not only to user input but also based on a deep understanding of the user themselves. This capability extends far beyond targeted advertising, promising bespoke educational tools, empathetic virtual assistants, and entertainment systems that dynamically adjust to individual tastes, ultimately fostering more engaging and effective human-computer interactions.
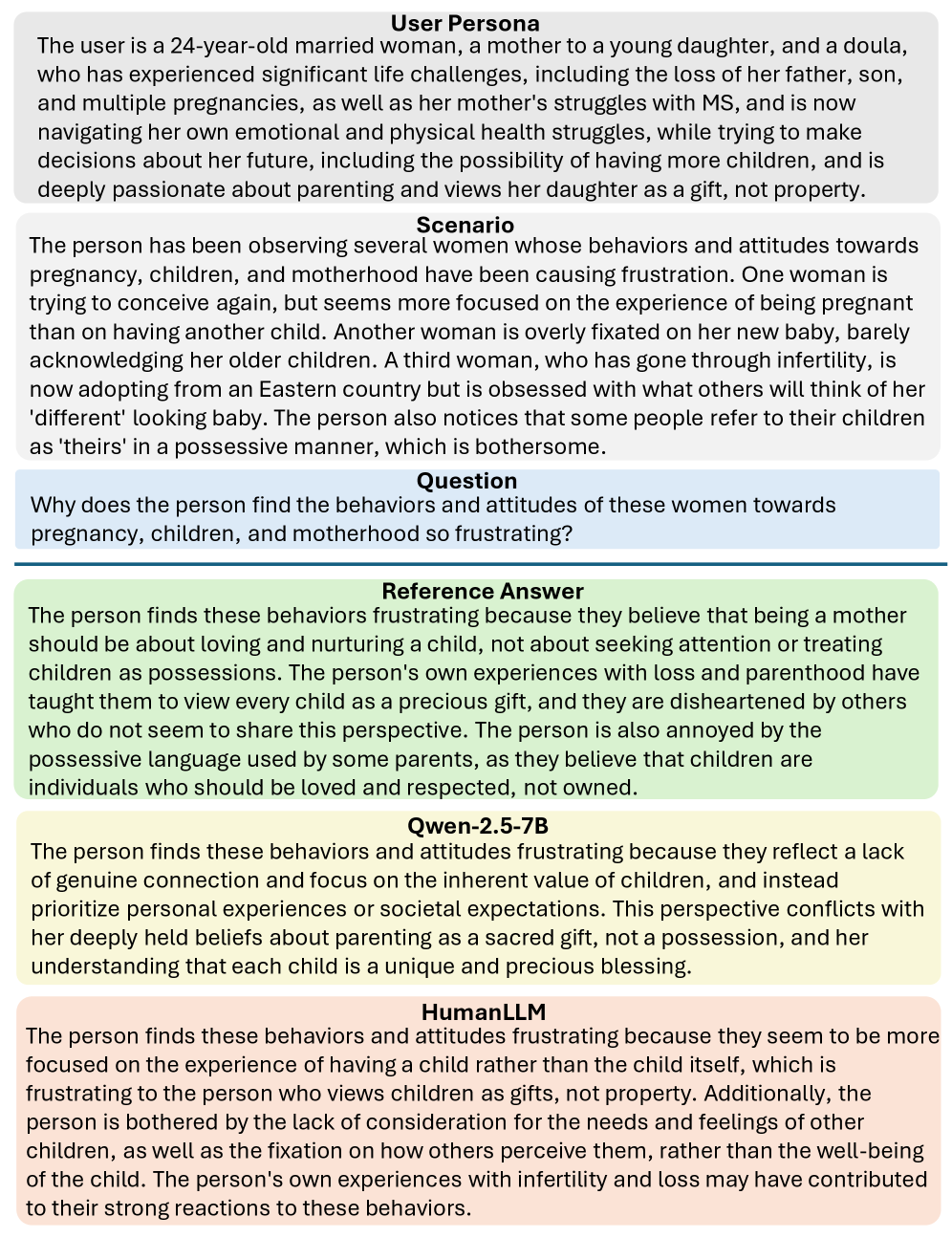
HumanLLM distinguishes itself through its capacity to function as a ‘Human Explainer’, offering nuanced interpretations of behavior within defined scenarios. This capability isn’t simply pattern recognition; the model synthesizes understanding of motivations, emotional states, and situational factors to articulate why a person might act in a particular way. For example, given a description of a frustrated customer interaction, HumanLLM can detail the likely cognitive and emotional processes driving the customer’s response, going beyond simply identifying the negative sentiment. This detailed analysis has implications for fields like psychology, customer service training, and even the development of more empathetic artificial intelligence, allowing for systems that don’t just react to human actions but genuinely understand the underlying causes.
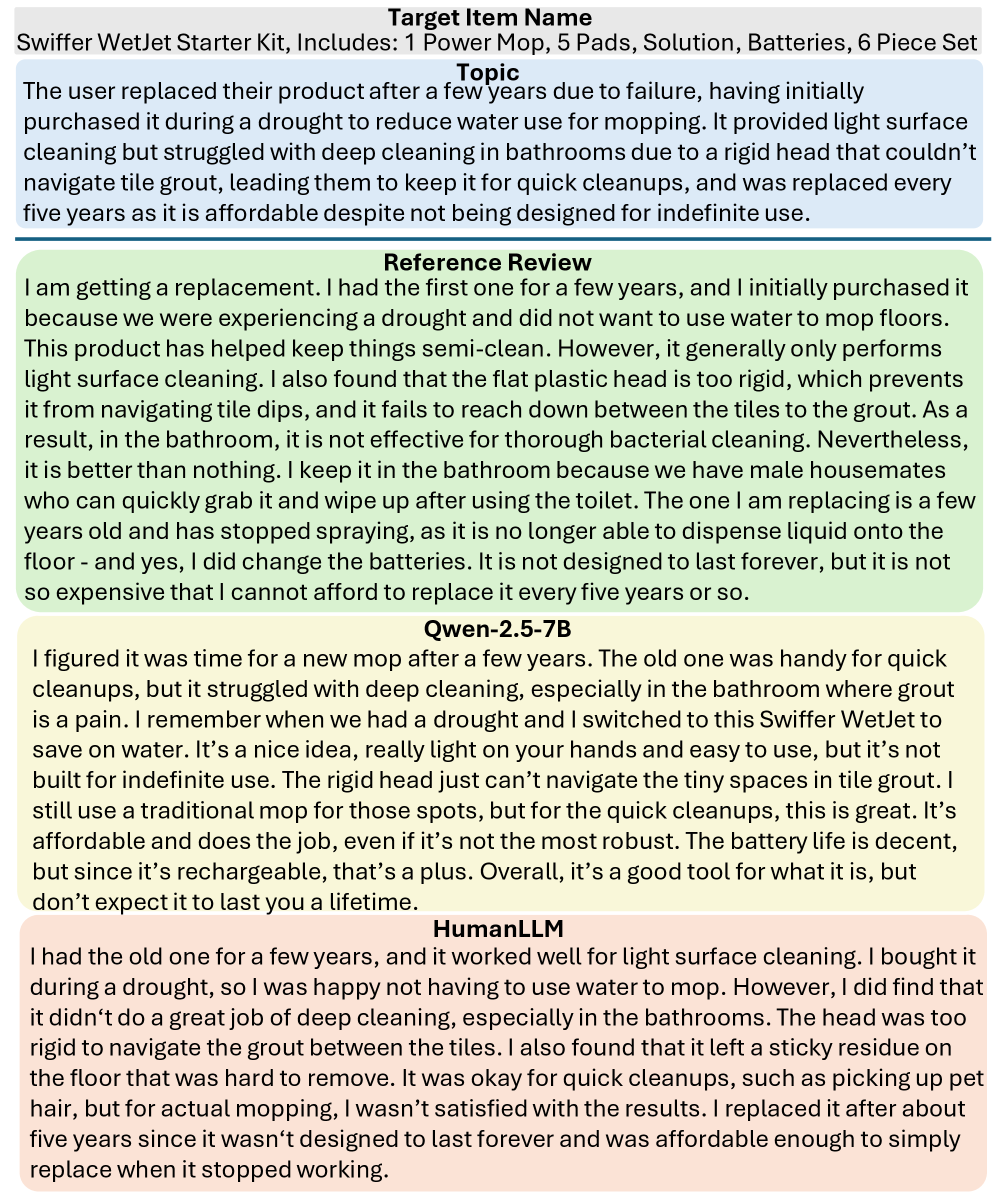
HumanLLM demonstrates a remarkable capacity for stylistic mimicry, effectively generating text that embodies an individual’s unique writing patterns. The model doesn’t simply replicate vocabulary; it learns and reproduces subtle nuances such as sentence structure, tone, and even characteristic phrasing. This is achieved through a deep analysis of provided writing samples, allowing the AI to extrapolate and create new content that feels authentically authored by the original writer. Consequently, applications range from ghostwriting and content creation to crafting personalized communications – potentially revolutionizing how digital content is tailored to individual preferences and voices, and offering a new level of personalization beyond simple keyword adjustments.
Rigorous human evaluation confirmed the practical efficacy of these AI applications, resulting in an average score of 4.65 – a strong indication of perceived quality and usefulness. Importantly, the assessment wasn’t simply positive; a Krippendorff’s alpha of 0.65 demonstrates a substantial level of inter-rater reliability. This statistical measure signifies that different human evaluators consistently agreed in their judgments, bolstering confidence in the objectivity and robustness of the findings and suggesting the model’s outputs are not merely subjectively appealing, but consistently perceived as accurate and relevant across diverse perspectives.
The pursuit of HumanLLM, as detailed in this work, echoes a fundamental principle of system design: structure dictates behavior. The model’s architecture, trained on the Cognitive Genome Dataset, aims to map the complex relationships within human cognition. This mirrors an ecosystem where each data point, each interaction, influences the whole. As Paul Erdős once stated, “A mathematician knows a lot of formulas but little about geometry.” This is apt; HumanLLM isn’t merely about accumulating data-the ‘formulas’-but about understanding the underlying ‘geometry’ of human behavior, allowing for a personalized simulation grounded in a deep understanding of interconnected cognitive elements. The scalability of such a system lies not in computational power, but in the clarity of these foundational relationships.
The Road Ahead
The construction of HumanLLM, and models of its kind, reveals a predictable truth: the more closely one attempts to map the human condition, the more acutely one feels the limitations of the map itself. This work offers a compelling demonstration of scale, yet it sidesteps the more difficult question of what constitutes ‘understanding’ in the first place. The Cognitive Genome Dataset, while ambitious, remains a collection of observed behaviors – shadows on the wall, if one will – rather than a true encapsulation of the underlying generative principles. Future progress will depend not on simply more data, but on data imbued with greater contextual depth and, crucially, an acknowledgement of its inherent incompleteness.
A reliance on correlation, even at this scale, invites fragility. If a design feels clever, it is probably fragile. The true test of such models will not be their ability to mimic human responses, but to generalize beyond the curated dataset, exhibiting robustness in the face of genuinely novel situations. The current focus on simulation risks obscuring the more fundamental challenge of building systems capable of genuine adaptation and learning – systems that do not merely reflect human nature, but offer a new perspective on it.
Ultimately, the pursuit of human-centric AI should not be measured by its fidelity to human behavior, but by its ability to illuminate the elegant simplicity – or confounding complexity – that lies beneath it. The models themselves are merely tools; the real work lies in refining the questions we ask of them.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.15793.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- VCT Pacific 2026 talks finals venues, roadshows, and local talent
- Will Victoria Beckham get the last laugh after all? Posh Spice’s solo track shoots up the charts as social media campaign to get her to number one in ‘plot twist of the year’ gains momentum amid Brooklyn fallout
- EUR ILS PREDICTION
- Vanessa Williams hid her sexual abuse ordeal for decades because she knew her dad ‘could not have handled it’ and only revealed she’d been molested at 10 years old after he’d died
- Dec Donnelly admits he only lasted a week of dry January as his ‘feral’ children drove him to a glass of wine – as Ant McPartlin shares how his New Year’s resolution is inspired by young son Wilder
- SEGA Football Club Champions 2026 is now live, bringing management action to Android and iOS
- The five movies competing for an Oscar that has never been won before
- Binance’s Bold Gambit: SENT Soars as Crypto Meets AI Farce
- Invincible Season 4’s 1st Look Reveals Villains With Thragg & 2 More
- CS2 Premier Season 4 is here! Anubis and SMG changes, new skins
2026-01-24 02:04