Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research demonstrates how agentic AI systems are being successfully deployed within a software company to streamline critical processes.
This paper details the implementation and evaluation of agentic AI solutions for document retrieval and automated test scenario generation.
Despite advances in automation, many software engineering tasks remain labor-intensive and demand significant cognitive effort. This paper, ‘Supporting software engineering tasks with agentic AI: Demonstration on document retrieval and test scenario generation’, addresses this challenge by introducing and evaluating two agentic AI solutions within a real-world software development context. Specifically, we demonstrate an agentic system for automated test scenario generation from requirements and another for comprehensive document retrieval, encompassing search, question answering, and summarization. Could this approach to task automation with specialized, collaborative agents herald a new era of efficiency and innovation in software engineering?
Breaking the Automation Bottleneck: The Rise of Cognitive Agents
Conventional test automation frequently encounters limitations when confronted with intricate systems and evolving project requirements. These systems, often reliant on pre-defined scripts, struggle to adapt to even minor changes in application behavior or specifications, leading to brittle tests requiring constant maintenance. This rigidity becomes particularly problematic in agile development environments where rapid iteration is crucial. The sheer volume of test cases needed to achieve comprehensive coverage for complex applications further exacerbates the issue, creating a significant bottleneck in the software development lifecycle. Consequently, there’s a growing need for solutions that move beyond static scripting towards more flexible and intelligent automation capable of autonomously adjusting to change and effectively handling complex scenarios.
Agentic AI represents a fundamental shift in automated testing, moving beyond traditional, script-based approaches to systems that dynamically generate and execute test cases. This isn’t achieved through a single, monolithic AI, but rather through the coordinated efforts of multiple specialized agents – each focused on a specific task, such as requirement analysis, test case design, or defect identification. Recent deployments within a software engineering company demonstrate the practical impact of this paradigm; these systems autonomously process complex documentation, interpret evolving specifications, and create robust test suites with minimal human intervention. The result is a testing process that adapts to change far more efficiently, reducing the bottleneck traditionally experienced with complex software projects and enabling faster, more reliable releases.
Traditional automated testing often relies on pre-defined scripts, proving brittle when faced with evolving software or intricate user journeys. A newer paradigm utilizes agentic AI – systems composed of multiple specialized agents – to move beyond this limitation. These agents don’t simply execute instructions; they reason about requirements, analyze documentation, and dynamically generate test cases tailored to complex scenarios. This capability stems from the system’s ability to decompose problems, prioritize tasks, and adapt to changing conditions – mirroring human cognitive processes. The result is a testing framework capable of not only identifying bugs but also understanding the intent behind the software, leading to more robust and reliable applications.
Unlocking Knowledge: Document Intelligence for Cognitive Agents
Effective document retrieval is fundamental to agent performance, yet current systems face inherent limitations. Large Language Models (LLMs) operate within a fixed context window, restricting the amount of information they can process at any given time. This poses a challenge when dealing with lengthy documents or complex inquiries requiring broad contextual understanding. Furthermore, documentation is rarely static; frequent updates and revisions necessitate a retrieval system capable of dynamically adapting to evolving content. A robust solution must therefore prioritize not only the speed and accuracy of information access but also the ability to manage context length and accommodate changes in the source material to ensure agents consistently receive the most relevant and up-to-date information.
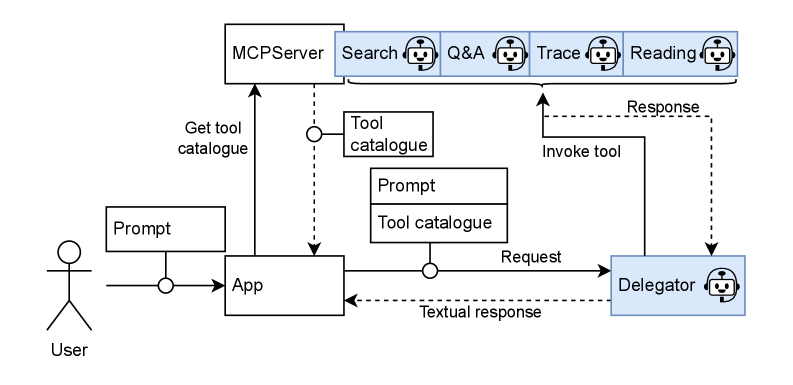
A Qdrant Database functions as a vector database, enabling semantic search and retrieval of document chunks relevant to agent queries. This integration with agents such as the Reading Agent and Trace Agent circumvents the limitations of fixed context windows in Large Language Models (LLMs) by providing access to a broader knowledge base. Instead of relying solely on information within the current context window, these agents can query Qdrant to retrieve semantically similar document segments, effectively extending the available context. The Reading Agent utilizes this expanded context for improved document comprehension, while the Trace Agent leverages it for more accurate tracing of information provenance and dependencies within the documentation.
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) – including GPT-4 and Mistral – with specialized agents enhances document processing precision. The Delegator Agent orchestrates complex queries, breaking down tasks and assigning them to appropriate components. Simultaneously, the Search Agent leverages LLM capabilities to perform semantic searches within document stores, identifying relevant information beyond simple keyword matching. This combined approach allows agents to access and utilize information with greater accuracy, overcoming limitations inherent in traditional search methods and enabling more nuanced responses to complex inquiries. The LLMs provide the reasoning and understanding necessary to interpret search results and formulate effective responses, while the agents manage the retrieval and processing workflow.
From Specification to Execution: Agent-Driven Test Creation
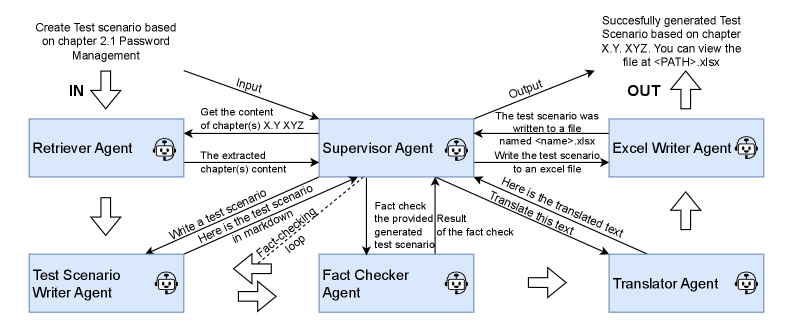
The automated creation of test scenarios relies on a multi-agent system that directly processes the Functional Specification Document. The Test Scenario Writer Agent is responsible for formulating test cases, while the Retriever Agent functions to extract relevant information from the specification document to inform scenario development. This agent-based approach enables intelligent interpretation of requirements, moving beyond simple keyword matching to understand the intended functionality as defined in the source documentation. The interplay between these agents allows for a dynamic and context-aware generation of test scenarios, reducing the need for manual creation and improving test coverage.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is employed to enhance the accuracy and relevance of generated test scenarios by directly utilizing information from the original Functional Specification Document. This technique involves first retrieving relevant passages from the document based on the current task or query, and then providing those passages as context to large language models, specifically GPT-3.5 and GPT-4. By grounding the scenario generation process in the source documentation, RAG minimizes the risk of hallucination or the introduction of inaccurate information, ensuring that the generated tests remain faithful to the specified requirements and functional behavior.
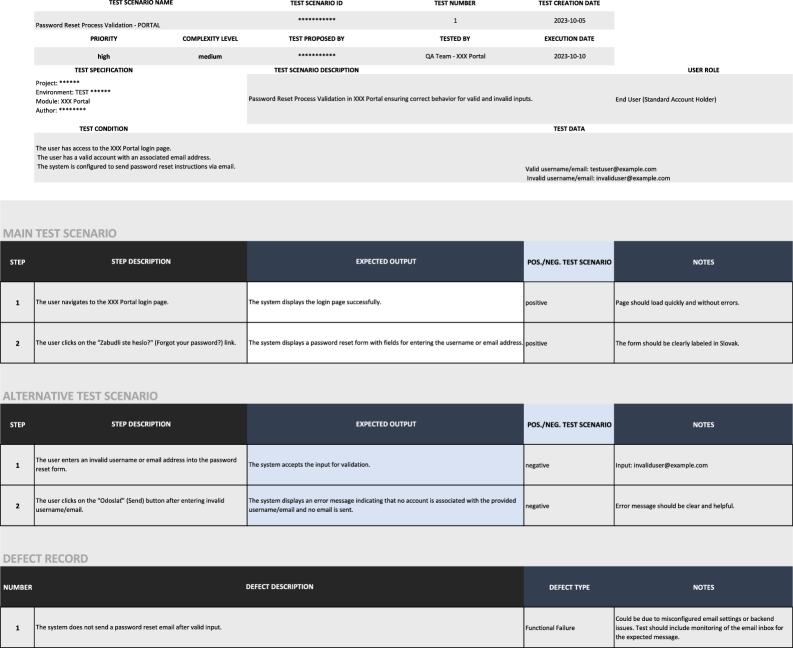
The Fact Checker Agent performs critical validation of generated test scenarios against the originating Functional Specification Document. This agent verifies the accuracy of each scenario element and confirms its direct alignment with specified requirements. Supporting this process, the Translator Agent adapts specifications and scenarios to different languages as needed, while the Excel Writer Agent facilitates the conversion of scenario data into tabular formats for reporting and analysis. This multi-agent system ensures that all generated test scenarios are factually correct and consistently represented, regardless of the source document’s format or the target output medium.
Beyond Automation: The Dawn of Cognitive Intelligence
The synergy between LangChain and LangGraph represents a significant advancement in the orchestration of intelligent agents, moving beyond simple task execution to enable genuinely complex workflows. LangChain provides the foundational building blocks – the chains of thought and connections to language models – while LangGraph introduces a graph-like structure that allows for dynamic and adaptive agent behavior. This combination facilitates the creation of agents capable of not only responding to prompts but also of planning, executing multi-step reasoning, and even self-correcting based on feedback. The resulting framework empowers developers to design systems where agents can collaborate, decompose problems into manageable sub-tasks, and navigate intricate information landscapes with a degree of autonomy previously unattainable, paving the way for more robust and versatile AI applications.
The architecture underpinning automated test generation extends far beyond its initial application, offering substantial benefits to document-intensive workflows. Utilizing large language models and intelligent agents, systems can now autonomously extract critical knowledge from extensive documentation, identifying key insights and relationships previously requiring significant manual effort. This capability proves particularly valuable in areas like compliance verification, where agents can meticulously analyze documents against regulatory standards, flagging potential issues with a level of thoroughness and speed unattainable through traditional methods. Consequently, this approach promises to revolutionize processes demanding comprehensive document analysis, from legal discovery and contract review to detailed risk assessment and policy enforcement, ultimately increasing efficiency and reducing the potential for human error.
Advancements in Large Language Models, such as LLaMA, coupled with sophisticated information retrieval techniques, are poised to substantially enhance the performance of automated intelligence systems. Recent deployments within a software engineering company showcase this potential, with two agentic AI solutions successfully navigating complex tasks demanding both accuracy and efficiency. These systems don’t simply process information; they actively retrieve, analyze, and synthesize knowledge, demonstrating an increasing capacity to address increasingly intricate requirements. This suggests a trajectory where LLM-powered agents will not only automate existing workflows but also unlock solutions to problems previously considered beyond the scope of artificial intelligence, continually pushing the boundaries of what’s computationally achievable.
The pursuit of automated solutions, as demonstrated by the agentic AI for document retrieval and test scenario generation, inherently involves a willingness to dismantle established workflows to rebuild them more efficiently. This resonates with Donald Knuth’s observation: “Premature optimization is the root of all evil.” The paper doesn’t merely apply AI; it actively probes the limits of existing software engineering processes, identifying bottlenecks and rebuilding them with agentic systems. The creation of these agents isn’t about flawless execution from the start, but rather iterative refinement through controlled “breaking” of the conventional, ultimately enhancing automation and realizing gains in efficiency. This embodies a philosophy of understanding through deconstruction, a hallmark of both effective hacking and robust engineering.
What’s Next?
The presented work doesn’t simply automate tasks; it externalizes assumptions. These agentic systems, successful as demonstrations, highlight the fragility of implicit knowledge within software engineering. If a language model can generate a test scenario, one must ask: what previously unarticulated criteria drove its creation? Was it efficiency, coverage, or simply pattern matching on existing tests? The seeming ‘intelligence’ may merely be a refined echo of existing, potentially flawed, practices.
Future work isn’t about achieving perfect automation, but about rigorously interrogating the models’ reasoning. The retrieval system, for instance, doesn’t just find documents; it embodies a specific information hierarchy. What biases are encoded within its search parameters? What knowledge is systematically excluded? The next step isn’t to expand the scope of these agents, but to build tools that dissect how they arrive at solutions, exposing the underlying logic – or lack thereof.
One considers the possibility that these ‘bugs’ – the unexpected outputs, the illogical connections – aren’t failures, but signals. They point to gaps in understanding, to unacknowledged dependencies within the software development lifecycle. Perhaps the true value of agentic AI isn’t in replacing engineers, but in forcing a continuous re-evaluation of the fundamental principles guiding their work.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.04726.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Robots That React: Teaching Machines to Hear and Act
- Mobile Legends: Bang Bang (MLBB) February 2026 Hilda’s “Guardian Battalion” Starlight Pass Details
- UFL soft launch first impression: The competition eFootball and FC Mobile needed
- Here’s the First Glimpse at the KPop Demon Hunters Toys from Mattel and Hasbro
- eFootball 2026 Epic Italian League Guardians (Thuram, Pirlo, Ferri) pack review
- Katie Price’s husband Lee Andrews explains why he filters his pictures after images of what he really looks like baffled fans – as his ex continues to mock his matching proposals
- Arknights: Endfield Weapons Tier List
- Davina McCall showcases her gorgeous figure in a green leather jumpsuit as she puts on a love-up display with husband Michael Douglas at star-studded London Chamber Orchestra bash
- Olivia Wilde teases new romance with Ellie Goulding’s ex-husband Caspar Jopling at Sundance Film Festival
- 1st Poster Revealed Noah Centineo’s John Rambo Prequel Movie
2026-02-05 08:50