Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new PostgreSQL extension, MorphingDB, brings AI inference directly into your database for streamlined model management and faster insights.

MorphingDB is an AI-native DBMS utilizing a task-centric paradigm, transfer learning, and optimized vectorization for efficient model serving and in-database analytics.
Despite growing demand for deep learning inference within databases, existing AI-native systems often burden developers with manual model management or incur high computational costs. To address these limitations, we introduce MorphingDB: A Task-Centric AI-Native DBMS for Model Management and Inference, a PostgreSQL extension that automates model storage, selection, and inference using a task-centric paradigm and transfer learning. MorphingDB achieves significant gains in throughput and resource efficiency across diverse tasks by optimizing inference via techniques like vectorization and cost-aware batch processing. Could this approach represent a new standard for seamless integration of AI and database capabilities?
Beyond Conventional Limits: AI-Native Databases
Conventional database systems, architected for transactional workloads and structured data, encounter significant obstacles when applied to the demands of deep learning inference. These systems typically rely on row-and-column storage formats and SQL-based query processing, proving inefficient for the tensor-based operations and complex mathematical computations inherent in neural networks. The impedance mismatch between these traditional approaches and the requirements of AI leads to substantial performance bottlenecks, particularly when handling large datasets or serving real-time applications. Data must often be extracted, transformed, and loaded (ETL) into specialized AI frameworks, introducing latency and resource overhead. Furthermore, existing systems struggle with the irregular and dynamic data access patterns common in deep learning, hindering the ability to effectively leverage hardware acceleration and parallel processing capabilities. This inefficiency necessitates the development of database systems specifically designed to natively support the unique characteristics of AI workloads.
The demand for instantaneous insights from artificial intelligence is driving a fundamental change in how data is managed and processed. Traditional database systems, designed for structured queries and transactional consistency, are increasingly ill-equipped to handle the complex, iterative computations inherent in deep learning inference. Applications ranging from real-time fraud detection and personalized recommendations to autonomous vehicles and adaptive robotics require sub-second response times, a feat often impossible with conventional architectures. This has spurred the development of AI-native database management systems (DBMS), engineered from the ground up to natively support machine learning workflows, allowing for seamless integration of data storage, model training, and inference – ultimately enabling a new generation of responsive and intelligent applications.
Current AI-native database management systems, including platforms like EvaDB, MADlib, and GaussML, often struggle to meet the demands of increasingly complex artificial intelligence applications due to inherent limitations in scalability and workflow design. These systems frequently exhibit performance bottlenecks when handling large datasets or intricate, multi-step AI tasks, as their architectures aren’t optimized for the dynamic computational graphs characteristic of modern machine learning. MorphingDB aims to bridge these performance gaps by introducing a novel, adaptable architecture that dynamically reshapes data layouts and query execution plans to align with the specific requirements of each AI workload, promising improved efficiency and responsiveness for real-time AI deployments. This adaptive approach allows the system to overcome the rigid constraints of traditional and existing AI-native databases, effectively optimizing resource allocation and minimizing latency for complex AI inference.

MorphingDB: A Task-Centric Foundation
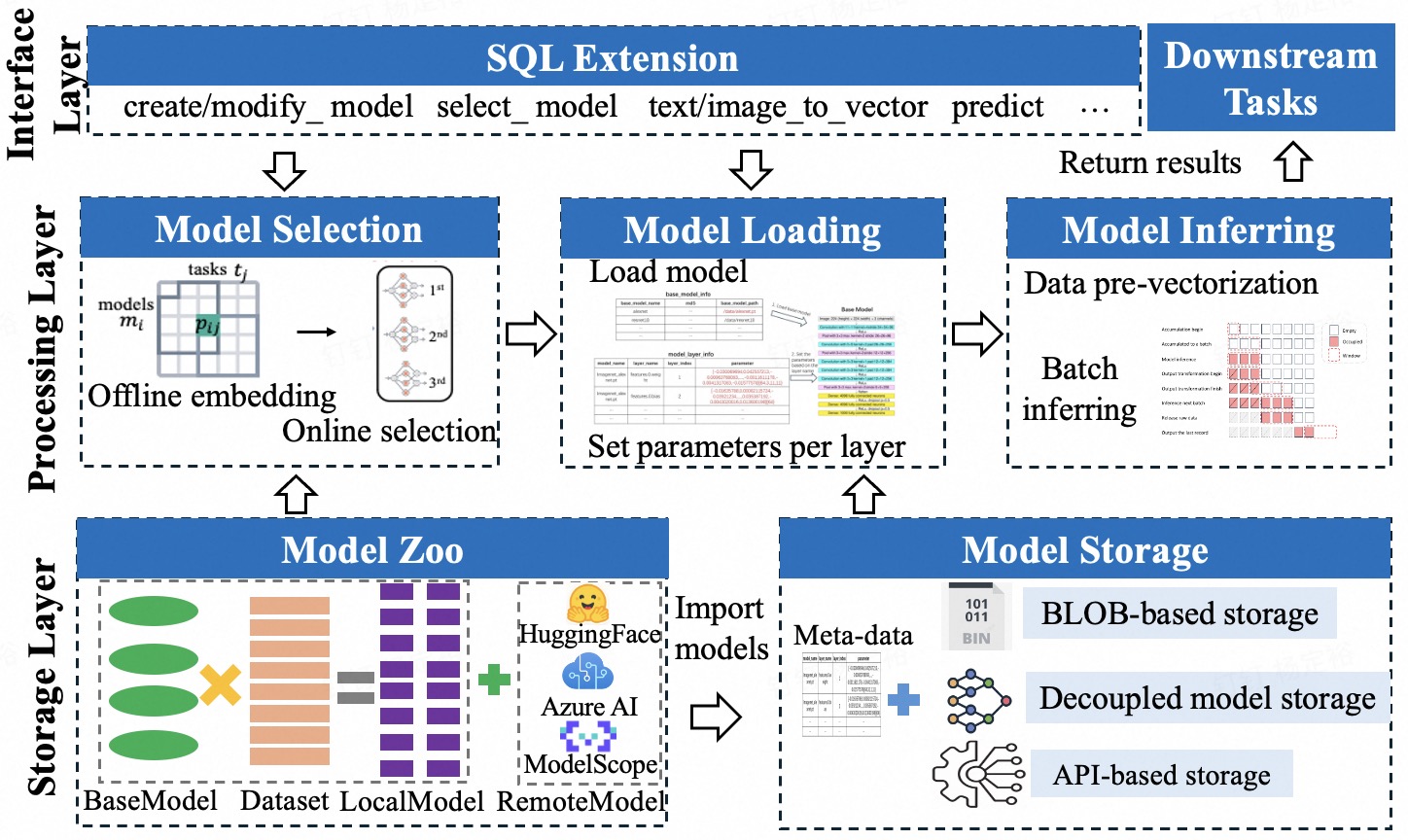
MorphingDB builds upon the established PostgreSQL database system to integrate artificial intelligence capabilities. This approach avoids the complexities of creating a database management system (DBMS) from scratch and instead leverages PostgreSQL’s existing strengths in data storage, transaction processing, and scalability. By extending PostgreSQL, MorphingDB inherits features such as ACID compliance, support for complex queries using SQL, and a mature ecosystem of tools and extensions. The extension architecture allows for the incorporation of AI models and algorithms without fundamentally altering the core DBMS functionality, ensuring compatibility and maintainability. This foundation provides a robust and reliable base for AI-driven database operations, minimizing development risk and maximizing performance.
MorphingDB’s task-centric paradigm represents a shift from traditional database management systems that emphasize procedural execution. Instead of specifying the exact steps for data manipulation, users define the desired outcome or task. This is achieved through a declarative interface where the user describes what data transformation is needed – for example, “identify fraudulent transactions” – without detailing the specific algorithms or query plans. The system then autonomously determines the optimal execution strategy, leveraging AI models and optimization techniques to fulfill the defined task. This abstraction simplifies database interaction, reduces the need for specialized database expertise, and allows MorphingDB to dynamically adapt to changing data characteristics and task requirements.
MorphingDB employs a two-phase process for model selection centered around a transferability subspace. The Offline Embedding Phase analyzes a diverse set of models and datasets to establish this subspace, effectively capturing inherent relationships between data characteristics and optimal model configurations. Subsequently, the Online Projection Phase rapidly identifies the most suitable model for a given task by projecting the task’s data into this pre-computed subspace and determining the closest matching model. This approach circumvents the need for training models from scratch for each new task, resulting in substantial reductions in model selection time – benchmark results demonstrate speedups exceeding several orders of magnitude compared to traditional training methods.
Optimized Inference: A Pipeline for Efficiency
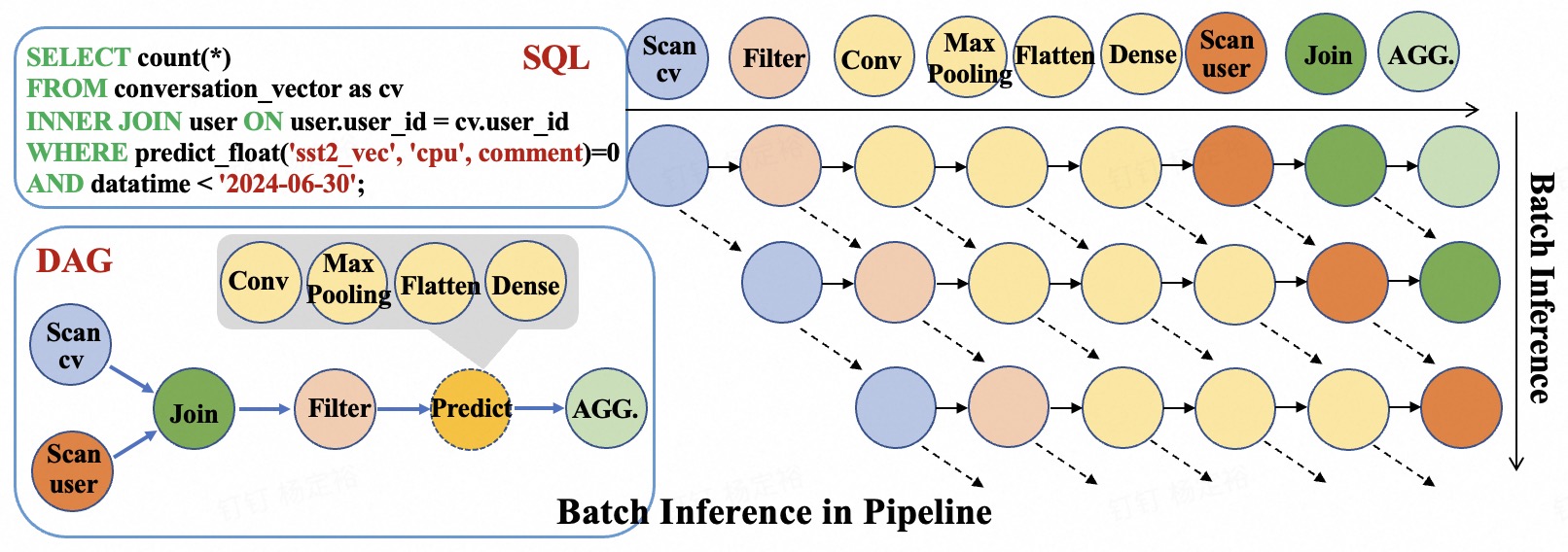
MorphingDB utilizes a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)-based pipeline for scheduling and executing inference tasks. This approach enables parallelization of operations by representing dependencies between tasks as edges in the graph; tasks without dependencies can be executed concurrently. The DAG structure facilitates optimization of the execution order, minimizing overall latency and maximizing throughput. By dynamically scheduling tasks based on data availability and resource constraints, the system avoids unnecessary delays and efficiently utilizes available computational resources. This pipeline-based execution is particularly effective for complex inference workloads involving multiple sequential or parallel operations, resulting in significant performance gains compared to linear execution models.
The Mvec Representation within MorphingDB is a tensor format specifically engineered for performance gains in multi-dimensional tensor operations. Unlike traditional tensor storage methods, Mvec prioritizes contiguous memory allocation and optimized data layouts to reduce memory access overhead. This format facilitates efficient vectorization and parallel processing, particularly beneficial for deep learning workloads involving large tensors. By minimizing data movement and maximizing computational throughput, Mvec directly contributes to MorphingDB’s ability to handle complex inference tasks with reduced latency and improved resource utilization. The representation supports common tensor operations such as matrix multiplication and convolution with optimized kernels designed for the Mvec data structure.
MorphingDB utilizes Batch Inference to improve performance by processing multiple queries in parallel. This technique aggregates incoming requests and executes them as a single batch, leveraging the inherent parallelism of modern hardware, particularly GPUs. Benchmarking demonstrates that Batch Inference within MorphingDB achieves a 4x increase in throughput when handling series-based tasks compared to systems that process queries individually. This improvement stems from reduced overhead associated with kernel launches and data transfer, as well as increased hardware utilization.
Expanding Cognitive Horizons: Supported Tasks
MorphingDB distinguishes itself through its inherent capacity to handle a diverse spectrum of cognitive tasks, moving beyond simple data management. The system is engineered to natively process complex inputs for Image Recognition, allowing it to identify and categorize visual content; Object Recognition, enabling the pinpointing of specific items within images; and Sentiment Classification, which determines the emotional tone of text. Furthermore, MorphingDB readily performs Face Detection, isolating and analyzing faces in images or videos, and Entity Resolution, accurately identifying and linking real-world entities mentioned in text. This broad support for computationally intensive cognitive tasks positions MorphingDB as a versatile platform for applications ranging from automated image analysis to sophisticated natural language processing.
MorphingDB streamlines the implementation of artificial intelligence by integrating LibTorch, a powerful and versatile inference engine from the PyTorch ecosystem. This strategic choice not only ensures seamless compatibility with a widely adopted machine learning framework, simplifying the transition for developers already familiar with PyTorch, but also markedly eases model deployment. By leveraging LibTorch, MorphingDB circumvents the complexities often associated with deploying models developed in diverse environments, fostering a more fluid and efficient workflow. The system effectively bridges the gap between model training and real-world application, allowing for rapid prototyping and scalable deployment of AI-powered solutions within a database context.
MorphingDB demonstrably accelerates artificial intelligence applications through substantial gains in inference performance, achieving up to a 70% improvement over current AI-native Database Management Systems. This heightened speed is attained without compromising analytical precision; the system maintains accuracy levels comparable to those achieved by leading AutoML frameworks. A key innovation driving this efficiency is MorphingDB’s decoupled storage approach, which dramatically reduces model loading times – a common bottleneck in AI deployments. By separating storage from computation, the system facilitates quicker access to models, enabling faster response times and more efficient processing of complex queries, ultimately streamlining the integration of AI into data-driven applications.

The design of MorphingDB embodies a principle of focused functionality. The system prioritizes the efficient execution of AI tasks within the database, eschewing extraneous features. This approach aligns with Kernighan’s assertion that “Complexity is our enemy. Simplicity is our only hope.” By integrating AI inference directly into PostgreSQL and adopting a task-centric paradigm, MorphingDB achieves a streamlined architecture. The emphasis on transfer learning and optimizations like vectorization further demonstrates a commitment to minimizing overhead and maximizing performance, a direct reflection of the value placed on clarity and essential functionality over elaborate designs.
What’s Next?
The pursuit of an ‘AI-native’ database invariably invites further complication. MorphingDB rightly identifies a need to bring computation closer to the data, but the elegance of that proposition rests on ruthless simplification. Future iterations must resist the temptation to become general-purpose AI platforms within a database shell. The true test isn’t how many models it can host, but how few are necessary to address prevalent tasks. A system burdened by optionality is a system defeated by choice.
Transfer learning, as implemented, provides a valuable bridge. However, the reliance on pre-trained models still implies a debt to external dependencies and the associated risks of drift. A more robust architecture would internalize the capacity for continual, task-specific refinement – a database that learns from its workload, not merely adapts to it. This demands a deeper consideration of what constitutes ‘knowledge’ within a relational context and how that knowledge can be represented and evolved without sacrificing the core principles of data integrity.
Ultimately, the performance gains achieved through vectorization and batching are merely tactical advantages. The strategic imperative lies in questioning the fundamental assumption that all data benefits from ‘AI-powered’ analysis. A truly intelligent system would discern what requires computation and what does not, applying its resources with a precision born of understanding, not a compulsion to process.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.21160.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Clash Royale Best Boss Bandit Champion decks
- Clash Royale Furnace Evolution best decks guide
- Chuck Mangione, Grammy-winning jazz superstar and composer, dies at 84
- December 18 Will Be A Devastating Day For Stephen Amell Arrow Fans
- Clash Royale Witch Evolution best decks guide
- Now That The Bear Season 4 Is Out, I’m Flashing Back To Sitcom Icons David Alan Grier And Wendi McLendon-Covey Debating Whether It’s Really A Comedy
- All Soulframe Founder tiers and rewards
- Deneme Bonusu Veren Siteler – En Gvenilir Bahis Siteleri 2025.4338
- Riot Games announces End of Year Charity Voting campaign
- BLEACH: Soul Resonance Character Tier List
2025-11-29 21:20